Prevention and treatment
First in aid
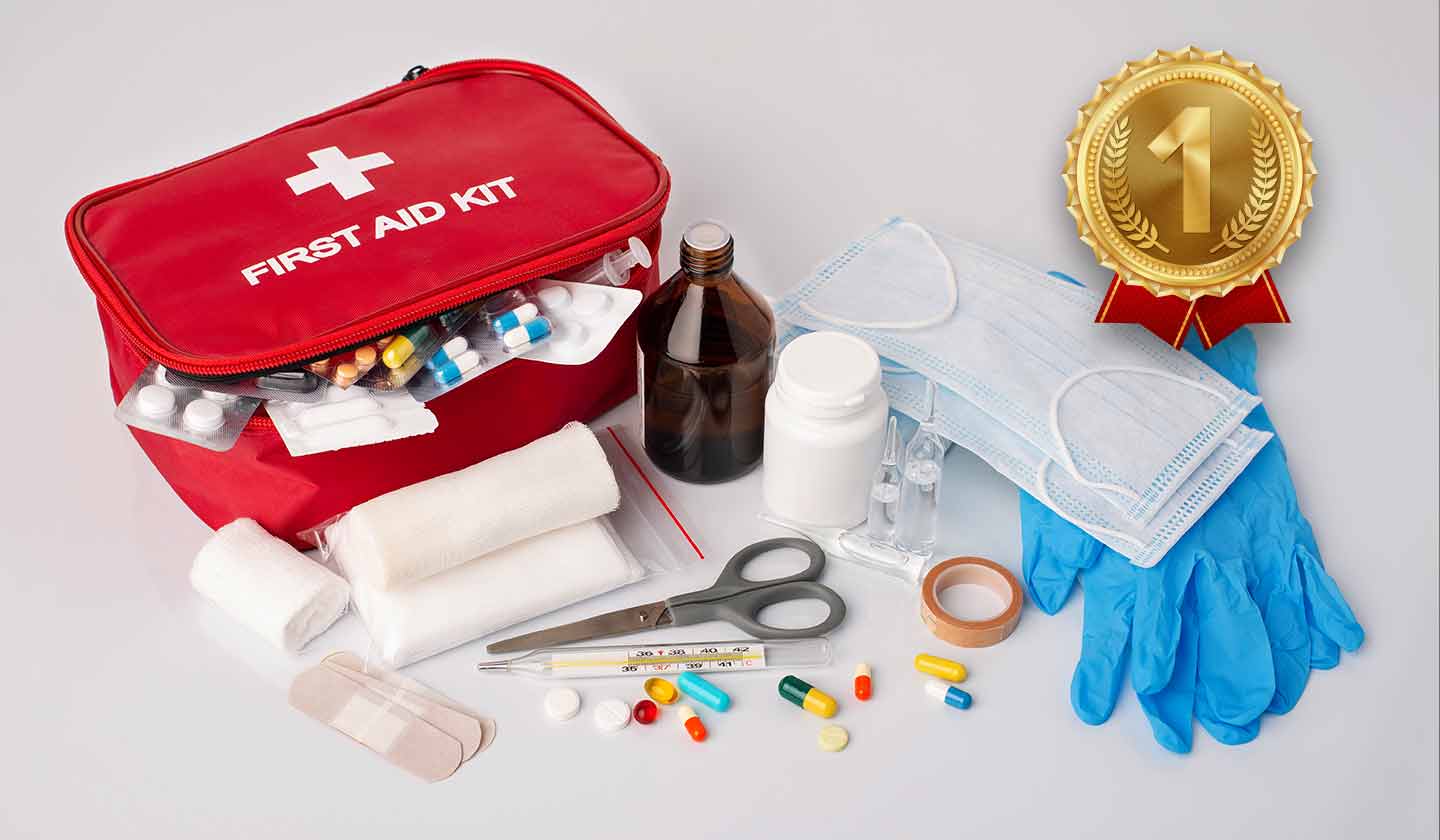
Having a first aid kit close by is essential when accidents occur, because they can happen even when all precautions are taken to avoid them.
Whether at work, on vacation, in the car or at home, small mishaps can happen, and the health centre or hospital may not be accessible.
Therefore, it is important to have a first aid kit ready and easily accessible to provide the necessary assistance.

First aid kit
In your first aid kit you should absolutely have:
- Sterile compresses of different sizes;
- Plasters of various sizes;
- Elastic crepe bandage;
- Adhesive tape;
- Rolled bandage;
- 70% ethyl alcohol (v / v);
- 10 volume hydrogen peroxide;
- Unidose saline (to clean wounds);
- Antiseptic solution (based on chlorhexidine, for example, which exists in the pharmaceutical form of cream and cutaneous solution);
- Blunt-ended scissors;
- Tweezers;
- Syringe for washing;
- Thermometer (preferably digital);
- Disposable gloves;
- Small plastic bags (to store used materials and put them in the trash);
- Liquid or gel antiseptic solution for hand washing.
Complementary products of the first aid kit
- Painkillers (such as paracetamol);
- Disinfectant ointment;
- Healing ointment;
- Ointment for burns;
- Ointment for bruises;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (for example ibuprofen).
Care to be taken with the first aid kit?
To provide help safely, it is necessary to guarantee certain requirements, such as:
- Store in a cool, dry place;
- The location of the first aid kit must be known to everybody so that it can be available and ready to use;
- Periodically review the contents of your first aid bag and confirm the expiration dates.
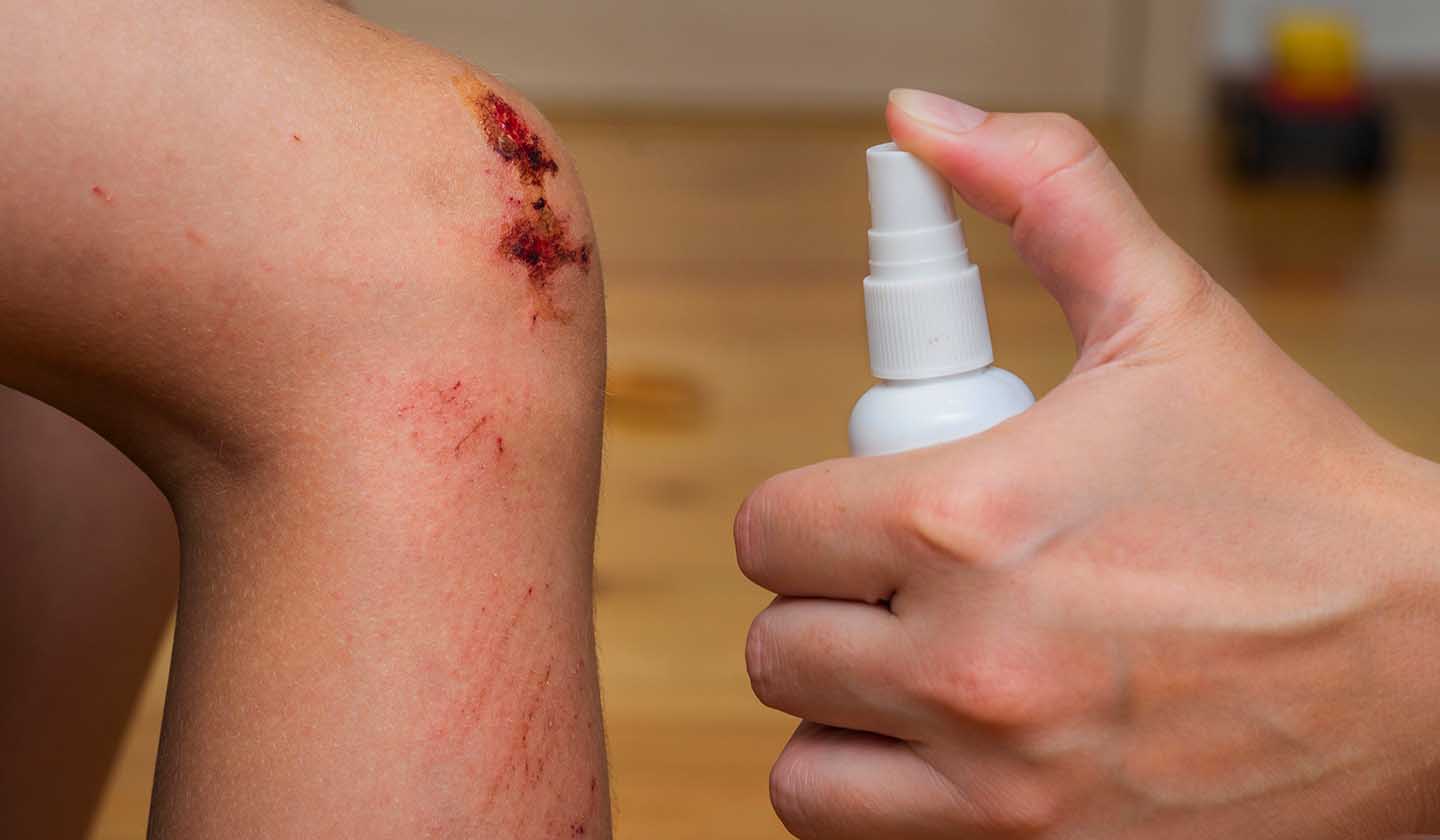
How to treat a wound?
A wound, even a small one, is an open door for the entry of harmful microorganisms, so it requires treatment quickly:
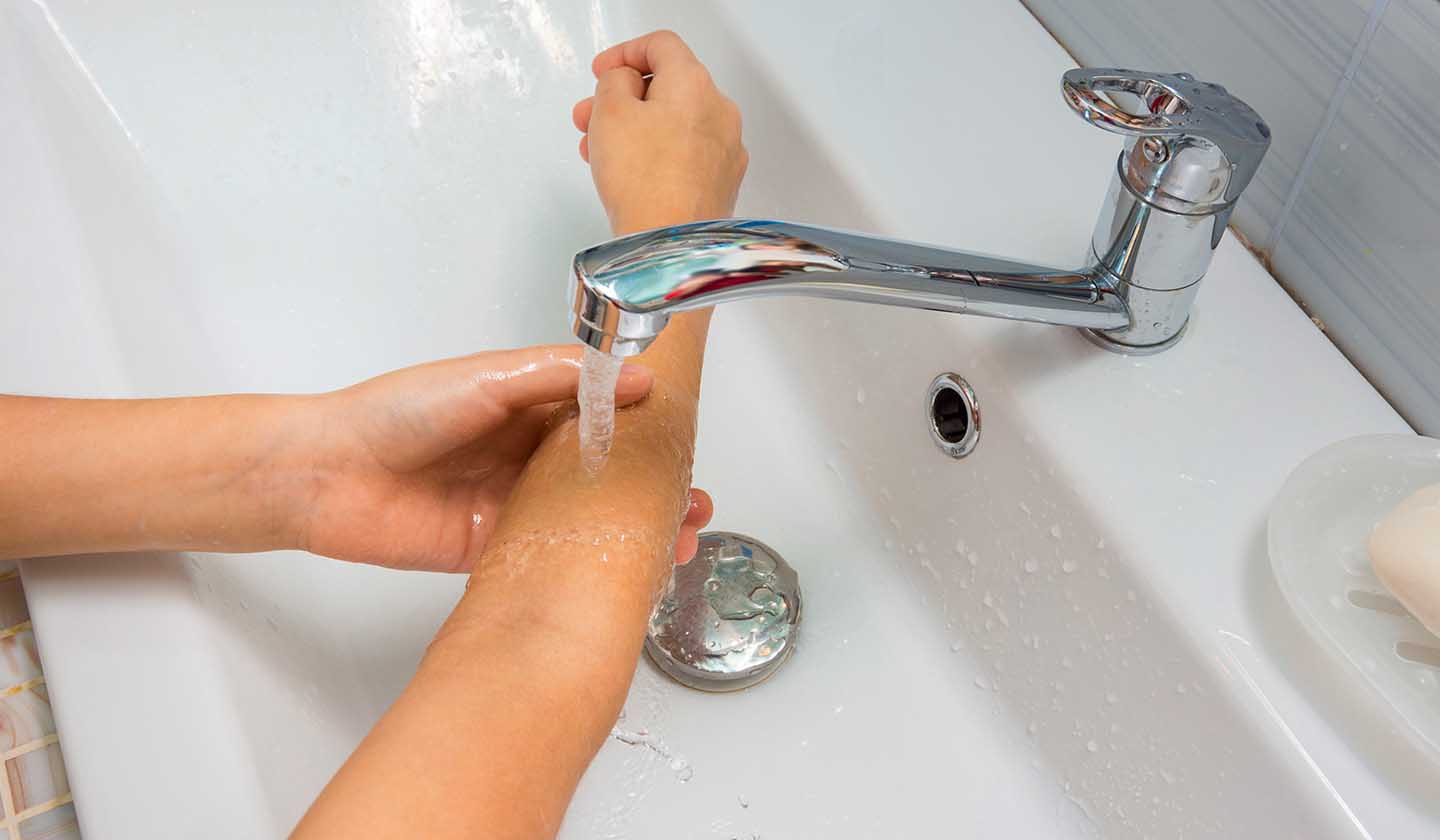
- Wash your hands. Before starting to treat a wound, it is important to wash your hands to prevent the development of infection;
- Control the bleeding: with a clean towel, apply light pressure to the area until the bleeding stops (medicines such as aspirin and warfarin affect the blood flow, which in these situations may take longer to stop);
- Clean the wound with unidose saline or warm water, wash the wound to remove dirt, in order to reduce the risk of infection;
- Dry the wound: using a compress, gently clean the skin around the wound;
- Treat the wound: if a little skin is raised, but stuck, put it back on the wound using a cotton swab;
- Disinfect the wound: apply an antiseptic after washing the wound to prevent infection;
- Cover the wound: using a bandage or a sterile compress and adhesive tape, cover the wound. Try to avoid adhesive tape on fragile skin, as it can cause some other trauma.
When to go to the doctor?
- Signs of infection;
- Difficulty in stopping bleeding;
- Glass residues in the wound;
- Deep long cut;
- Difficulty healing;
- Wound caused by animal bite;
- Person with diabetes.

How to act in case of a burn?
A burn is an injury that can occur as a result of contact with extreme cold or heat, chemicals, or electricity. Usually, at home, burns are small without major complications.
However, learn how to act:
- Assess the situation and ensure that you have security conditions to treat the burn;
- Remove the agent that has caused the burn or, alternatively, the victim;
- Cool down and wash the burn area abundantly with tepid water (if you are in the presence of a chemical that reacts with water, do not do it) until substantial pain relief;
- Cover the burnt areas with compresses moistened with saline or water;
- Control body temperature;
- Do not remove clothing if it is attached to the victim's body;
- Do not use ice, toothpaste, butter, olive oil or other products to cool or moisturise the burn (as it can aggravate injuries).
When to go to the doctor?
- Signs of infection
- Intense pain
- Blisters
- Fever
Sources
iSaúde
Farmácia Distribuição Magazine
Também lhe poderá interessar
Prevention and treatment
Got everything you need for the summer?
Prevention and treatment






