Dermatology
Identify the degree of burn and treat immediately
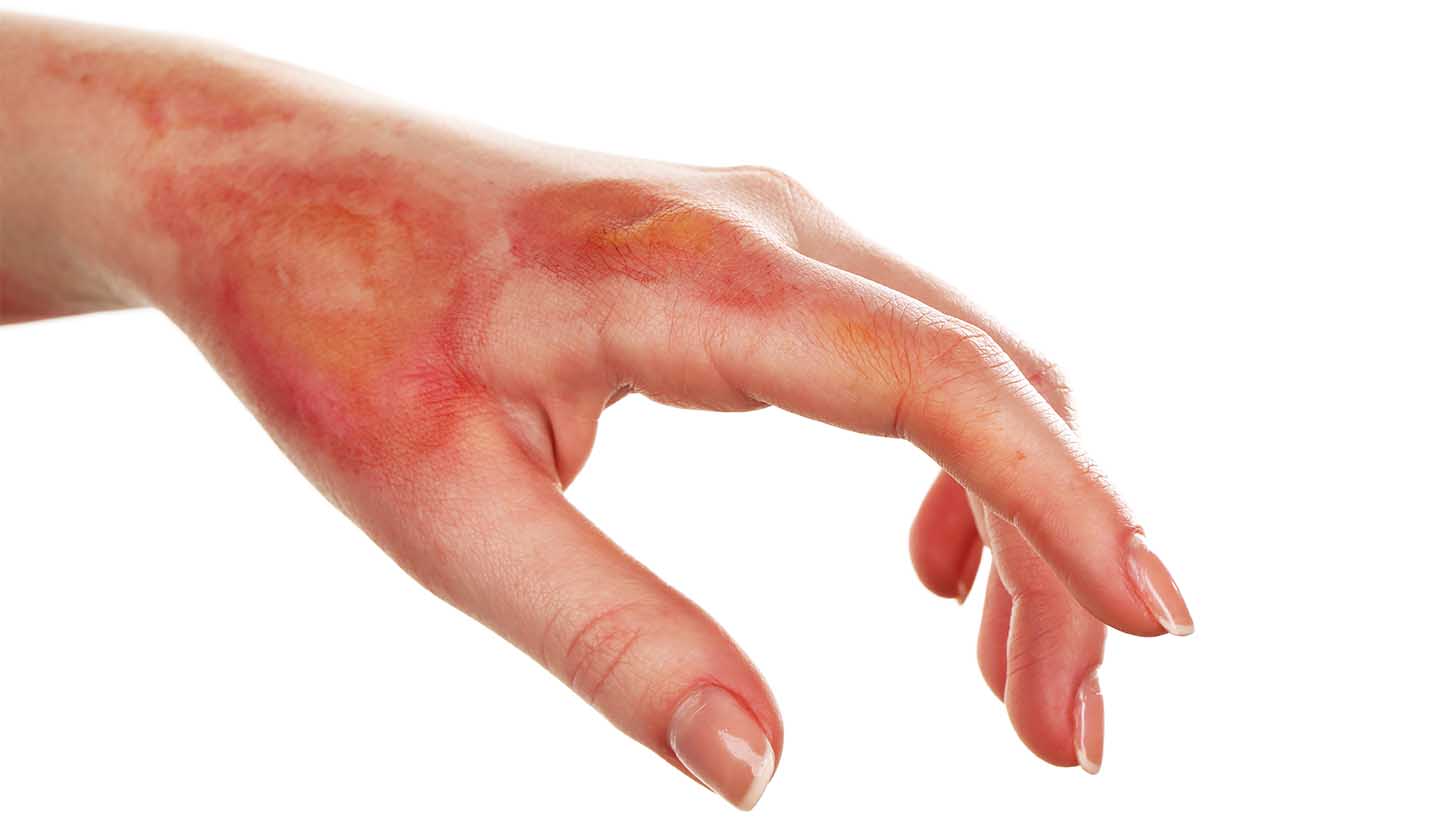
Burns are injuries caused by direct contact with a heat source, chemicals, or electricity, and may cause pain, blistering or loosening of the skin.
The classification of burns is made depending on how deeply and severely they penetrate the skin's surface. A burn is considered all the more serious as the area it affects.
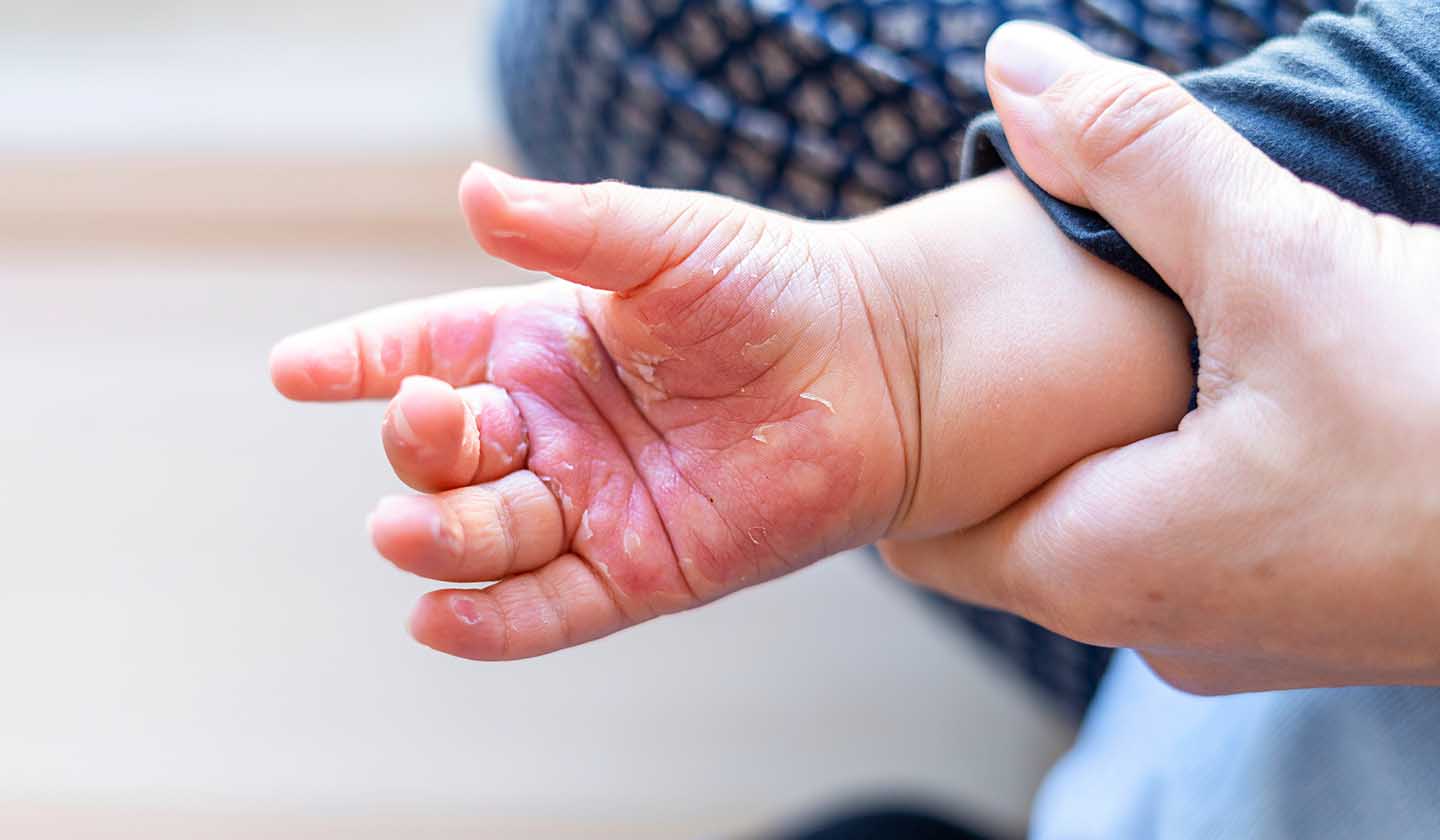
Burn degrees:
First-degree - mild to severe redness. The skin becomes white when pressing down the affected area.
Second-degree - severe redness with intense heat. If the burn is less than 7 cm around, it can be treated as a minor burn.
Third-degree - it can cause skin destruction and the burn may vary in colour.
In case of severe burns, such as second- and third-degree burns, medical advice and care by a health care professional should be sought. First degree burns can be treated at home considering some advices. These burns should be treated as fast as possible so that they do not get infected and become more serious.
How to treat a first-degree burn?
-
Cool down the burn immediately with cold water for 10 to 20 minutes. Never put ice on the burn.
-
If a blister is formed, do not pop it.
-
Apply a cream or an ointment to the burn. This cream or ointment will moisturize and help regenerate damaged skin. You can also apply an antibiotic ointment to prevent an infection.
-
There are appropriate patches for burns that protect them against dirt and bacteria, and also keep the wound safe from external aggressions, like skin picking and pressure.
You should seek advice from your pharmacist even in case of a first-degree burn, so that he/she can better evaluate the severity of your lesion.
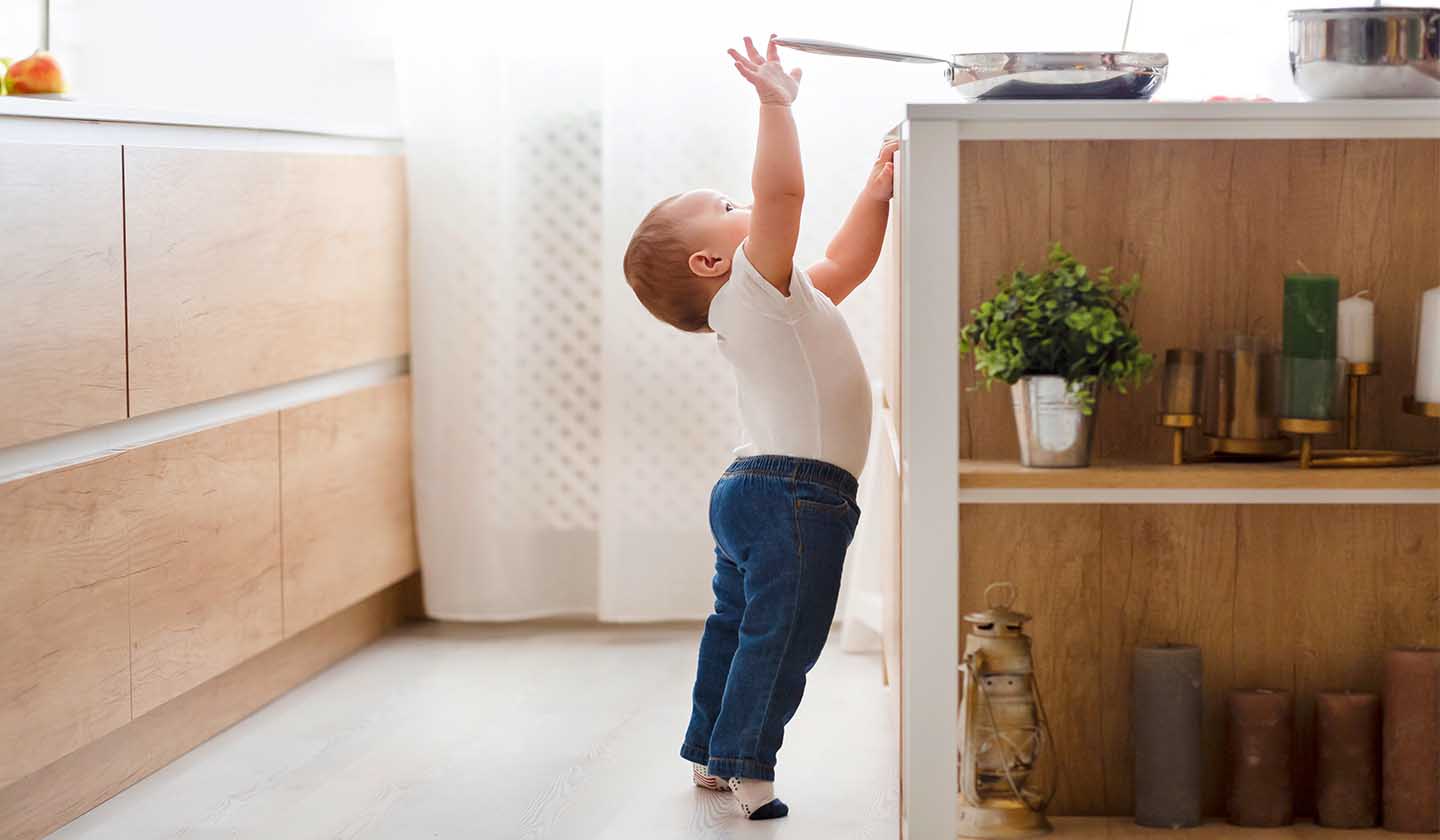

Always seek medical advice from a health professional in the following cases:
-
Extensive burn
-
Burn with blister or burn not completely clean
-
Burns in children or pregnant women
-
Burns in sensitive areas, such as the face or genitals
-
Burns in diabetic patients
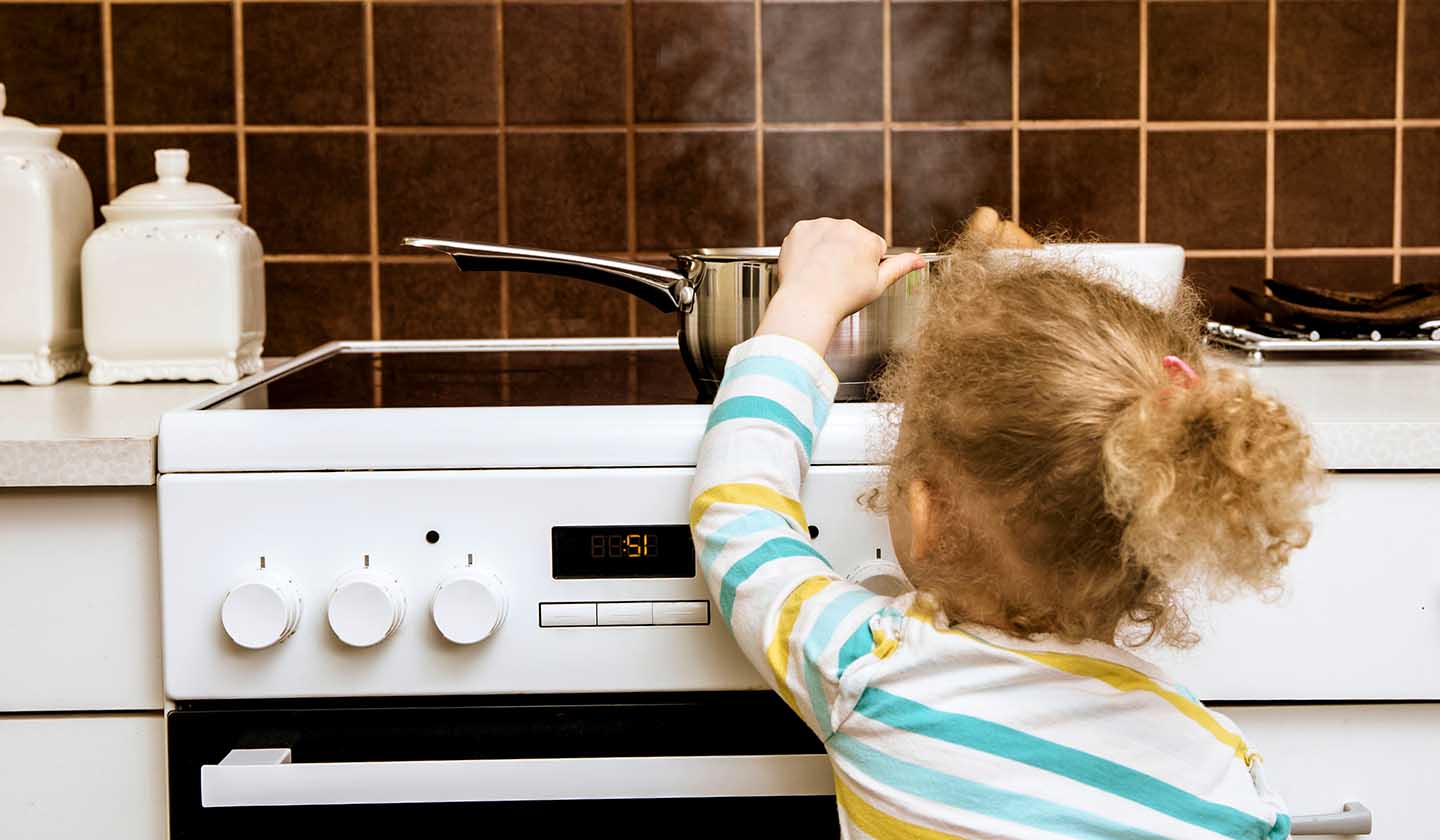

Advices to avoid accidents
-
In case you are at work, follow all the safety norms.
-
When using hot-water bottles, check for leaks and make sure they are properly closed.
-
When pouring hot water into a container, always put it on top of a counter and do not hold it with your free hand.
-
Avoid pouring boiling water into glass containers because they may break.
-
Use proper protective equipment to take hot containers out from the oven or stove.
In case there are children involved, further precautions should be taken:
- Always pay attention to what the children is doing.
- Make sure that pot and frying pan handles are oriented towards the inside of the oven.
- All corrosive or flammable products shall be kept in closed closets and out of reach of children.
- Never leave matches nor lighters in places that can be reached by children.
- Cover electrical outlets.
- Teach the child about the dangers of working ovens and burning fireplace.
Sources
iSaúde
Farmácia Distribuição Magazine
Também lhe poderá interessar
Infections






