Dermatology
Wounds and Scratches - it doesn't hurt at all
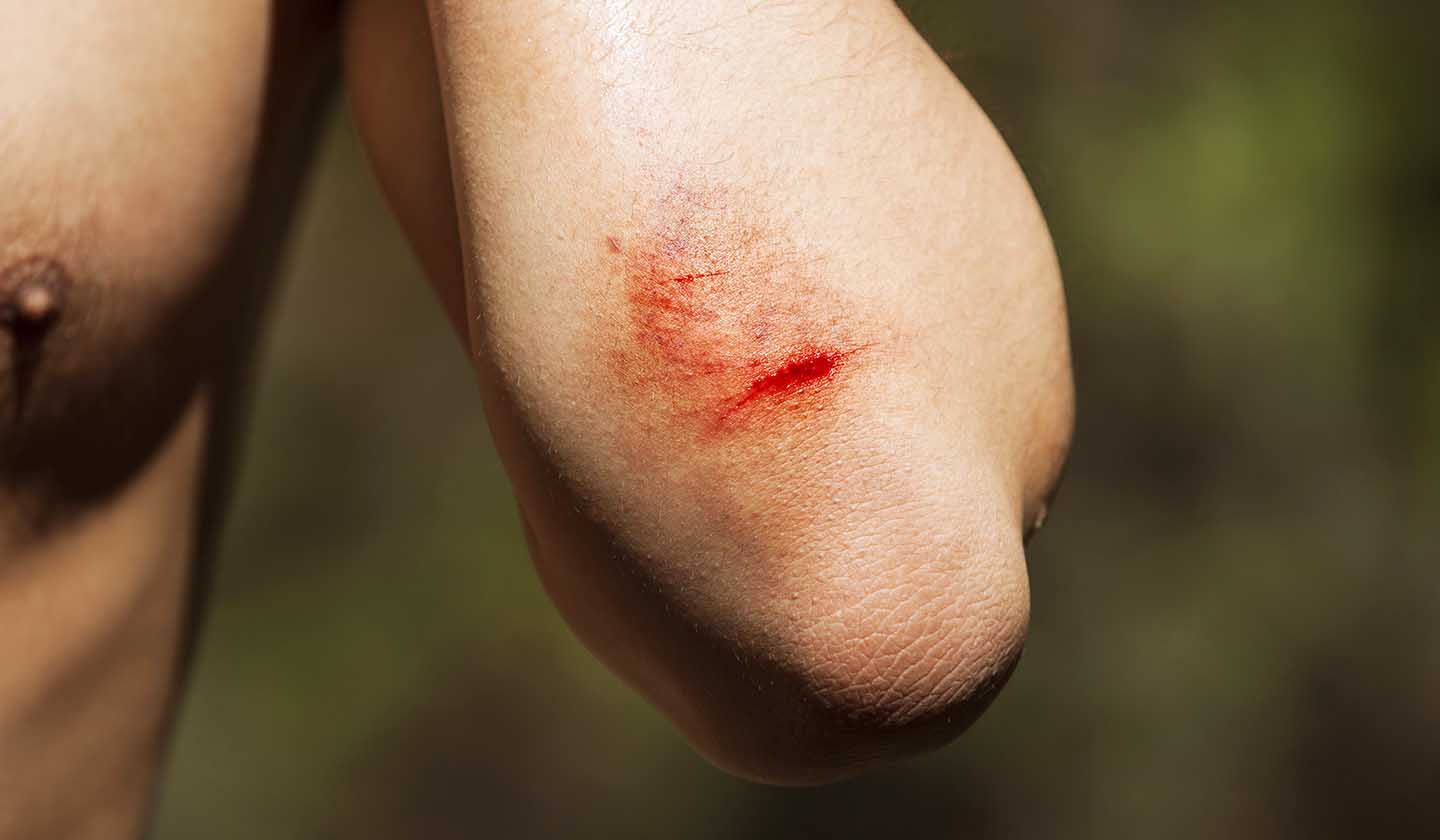
Wounds and scratches are minor injuries that happen when a sharp object creates a mark on the skin. Superficial wounds reach only the most superficial layers of the skin (epidermis and superficial or intermediate dermis), while deep wounds reach other levels (deep dermis, adipose tissue, fasciae, tendons, muscles, bones, cartilage, ligaments).
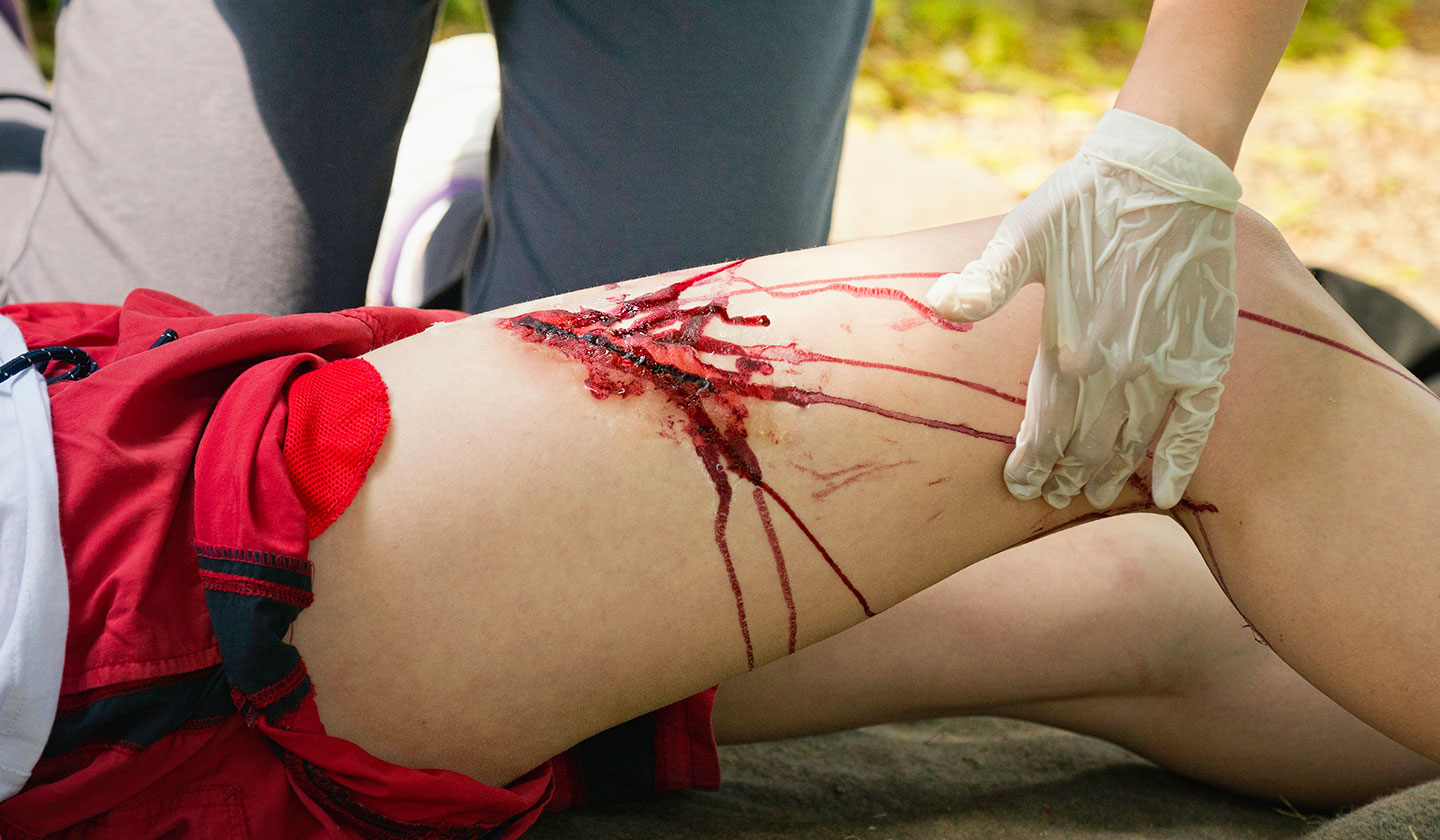

What are the symptoms?
Simple wounds are superficial and free of signs of infection/contamination/colonisation by microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, fungi), tending to spontaneous healing. Deeper wounds usually cause bleeding (which can be more or less intense depending on the affected area), as well as pain, with a greater likelihood of infection, particularly if the extension of the affected area is larger.
What is the cause?
The causative agent of the wound or scratch (sharp object, stones, or earth, etc.) will determine the form of the wound, its healing time and adopted method in terms of healing and treatment.
How to prevent it?
To prevent a wound or scratch from scarring, you must take good care of it. Avoid blowing into the wound or scratch, as it can cause bacteria to develop.
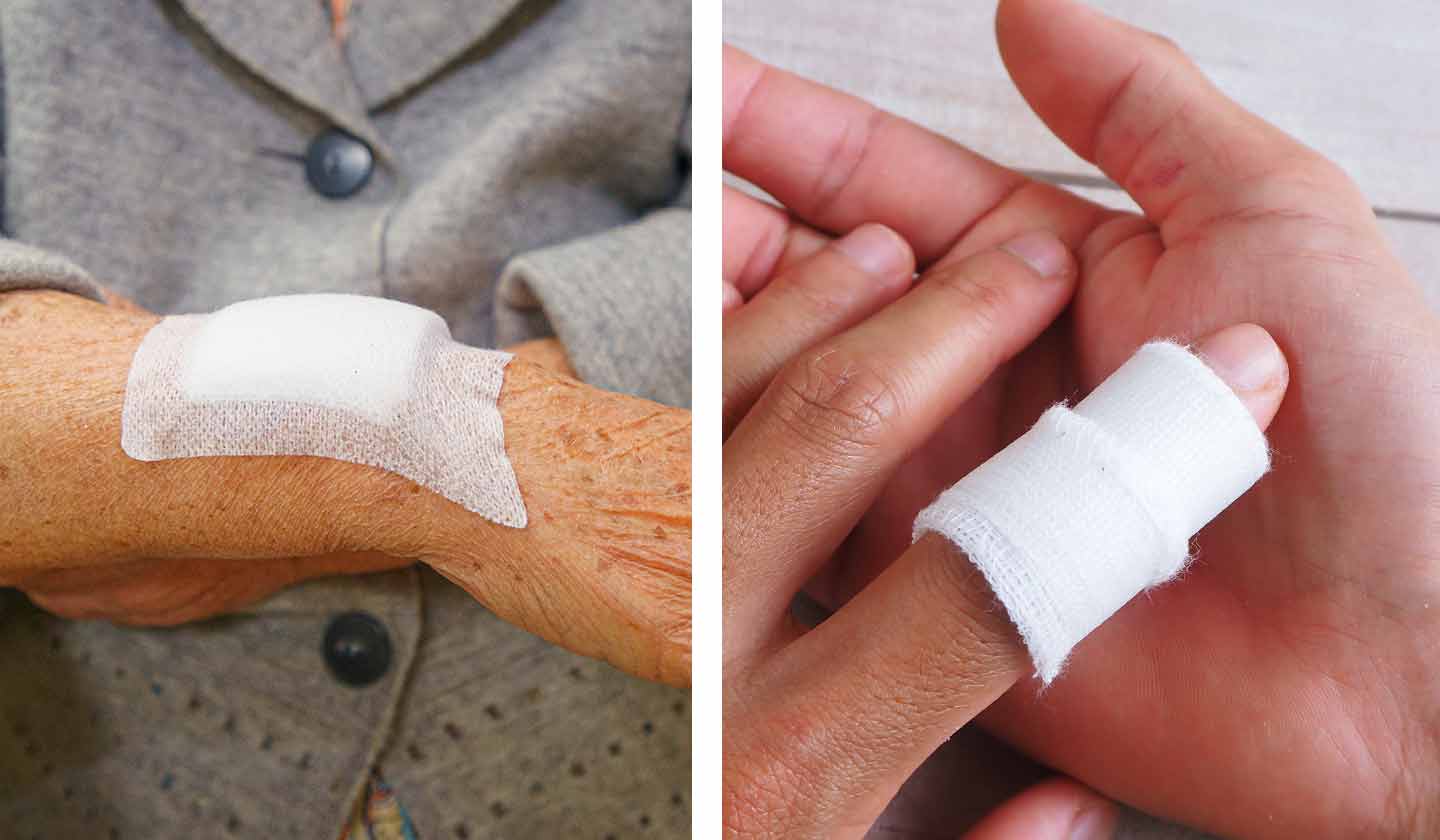
How to treat it?
Avoid bleeding by pressing on the wound with a clean, soft cloth. After checking that the wound is not serious, wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water. Then wash the wound well, without pressing too much, with mild soap and warm running water (preferably). Make sure the wound is clean and free of particles that could cause infection and scarring. Apply an antiseptic product and dry the skin around the wound. Depending on the size of the lesion, cover the area with a sterile dressing or gauze. Do not use cotton wool as the fibres can get into the wound or stick to it. Observe the wound daily and try to keep it clean and dry, changing the dressing frequently for this purpose.
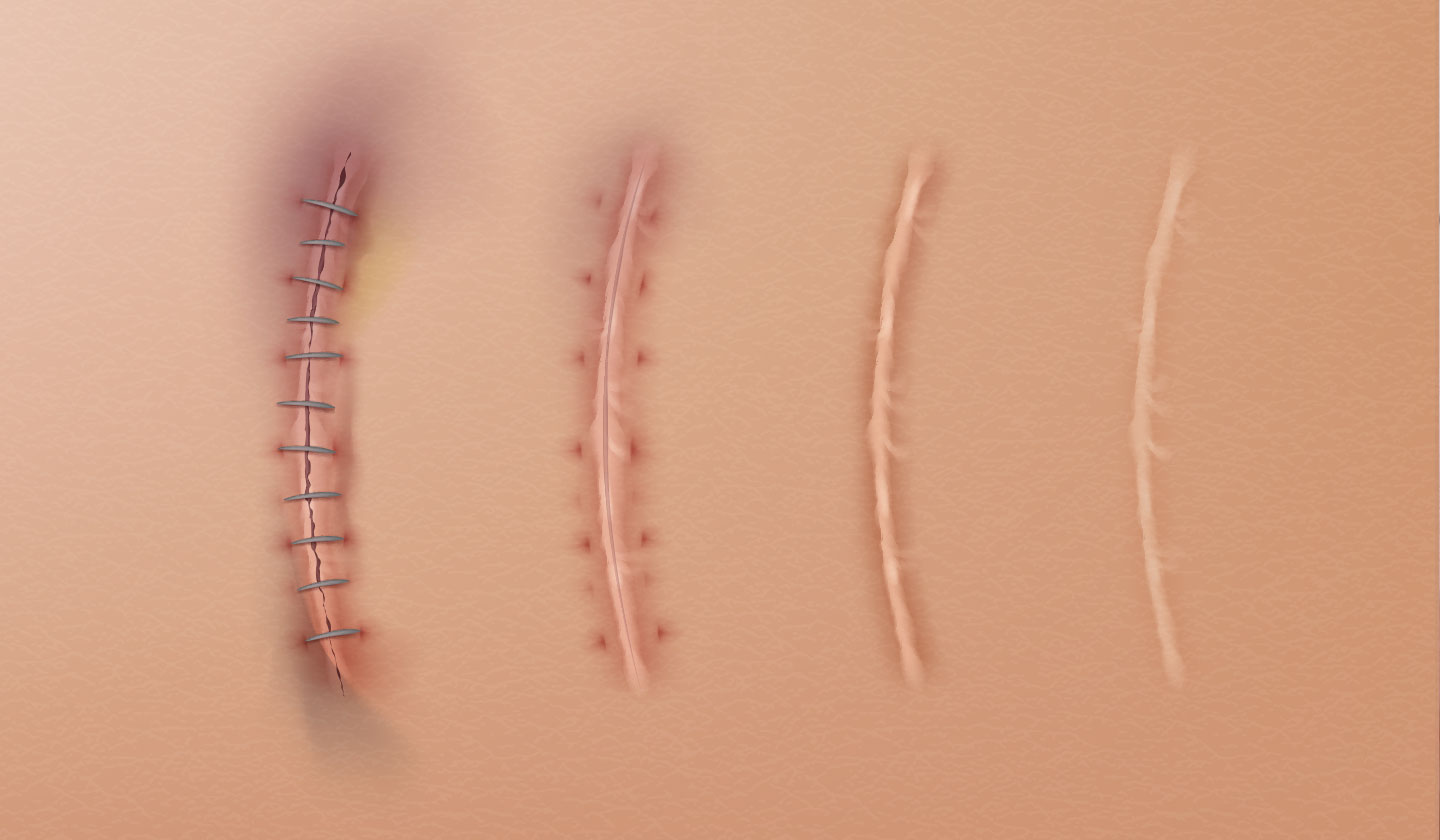

How to know if the wound is well healed?
The pain begins to decrease, the size of the lesion becomes smaller and the healing process is perceived by the appearance of granulation tissue, which is the harder and redder skin that forms in the area. Note that during “healing”, the wound goes through
three processes: the inflammatory process - which is when pain, heat and redness symptoms occur. At this stage, the defence cells migrate to the wound area, which will clean and prevent wound contamination. Then, there is the granulation stage - in which the formation of the base tissue for healing takes place and, after that, the maturation process, which will reconstitute the skin.
And what are the symptoms of an infected wound?
Increased pain, heat, and redness around the wound. Although these are similar to the healing process symptoms, if they are excessive, they can be a sign of infection. Also, the presence of pus in the wound and fever are not normal.

António Hipólito de Aguiar
(Pharmacist; University Professor)
Também lhe poderá interessar
Parasites
Literally, don't get scabies to scratch
Prevention and treatment






