Dermatology
Rosacea - Control redness of the skin
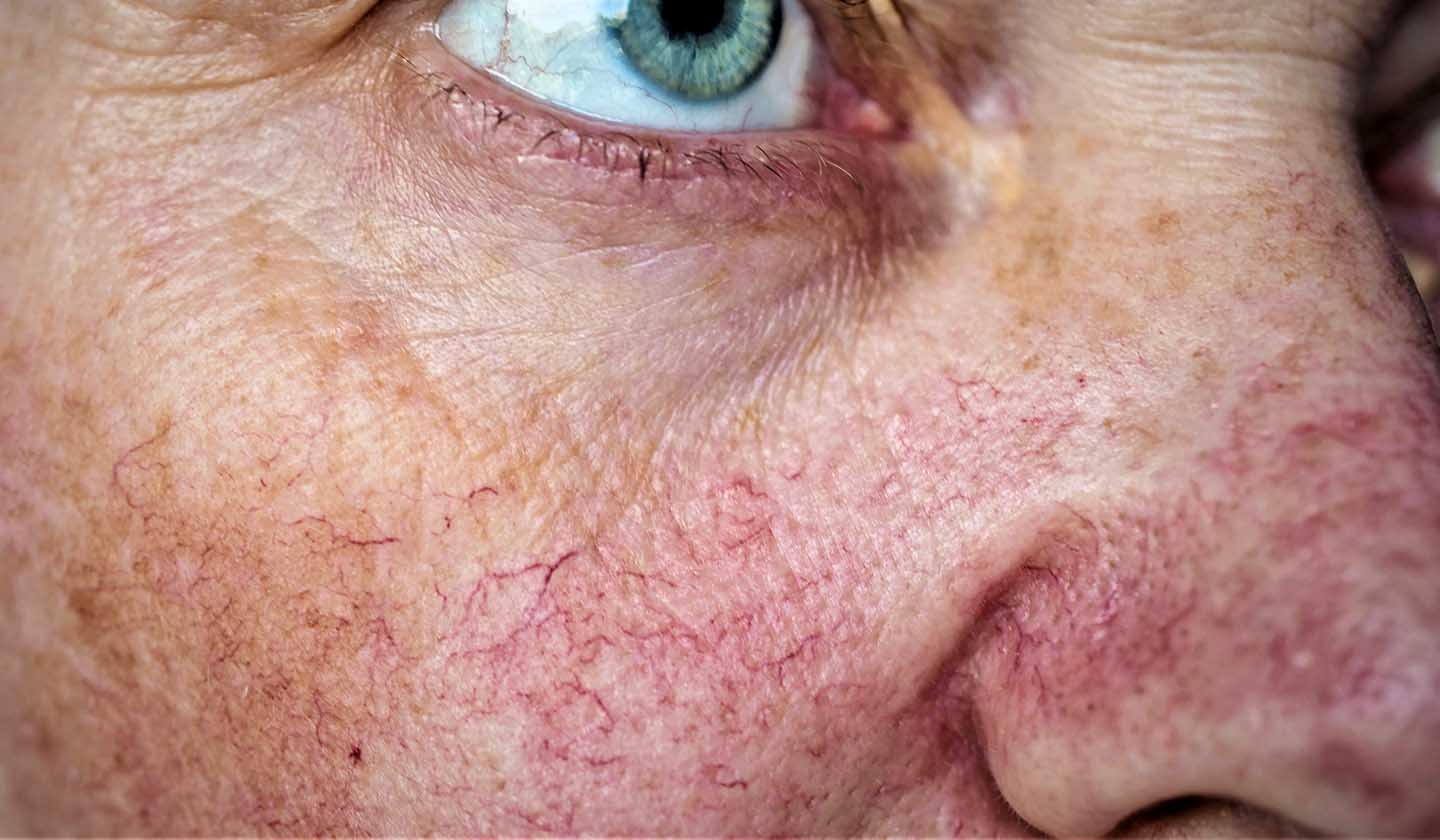
Rosacea (or coupe rosé) is a quite common inflammatory and chronic skin disease, being more frequent in women from 30 years old, with light and thin skin, eyes, and light hair.
As a disease that affects blood vessels and sebaceous glands, it usually appears in the central area of the face (such as cheeks, forehead, chin, and nose), with redness and strokes being the most frequent manifestations. It is characterized by a dysfunctional skin barrier, which translates into dehydration and skin sensitivity.
Not being considered a serious pathology, it can generate great discomfort and cause a negative impact on the quality of life of patients, even leading to problems of self-esteem, since their skin undergoes changes that are visible.
If you think you may have rosacea, know that there are certain cares and treatments that help to alleviate the manifestations of this disease. Ask any questions with your doctor or pharmacist.
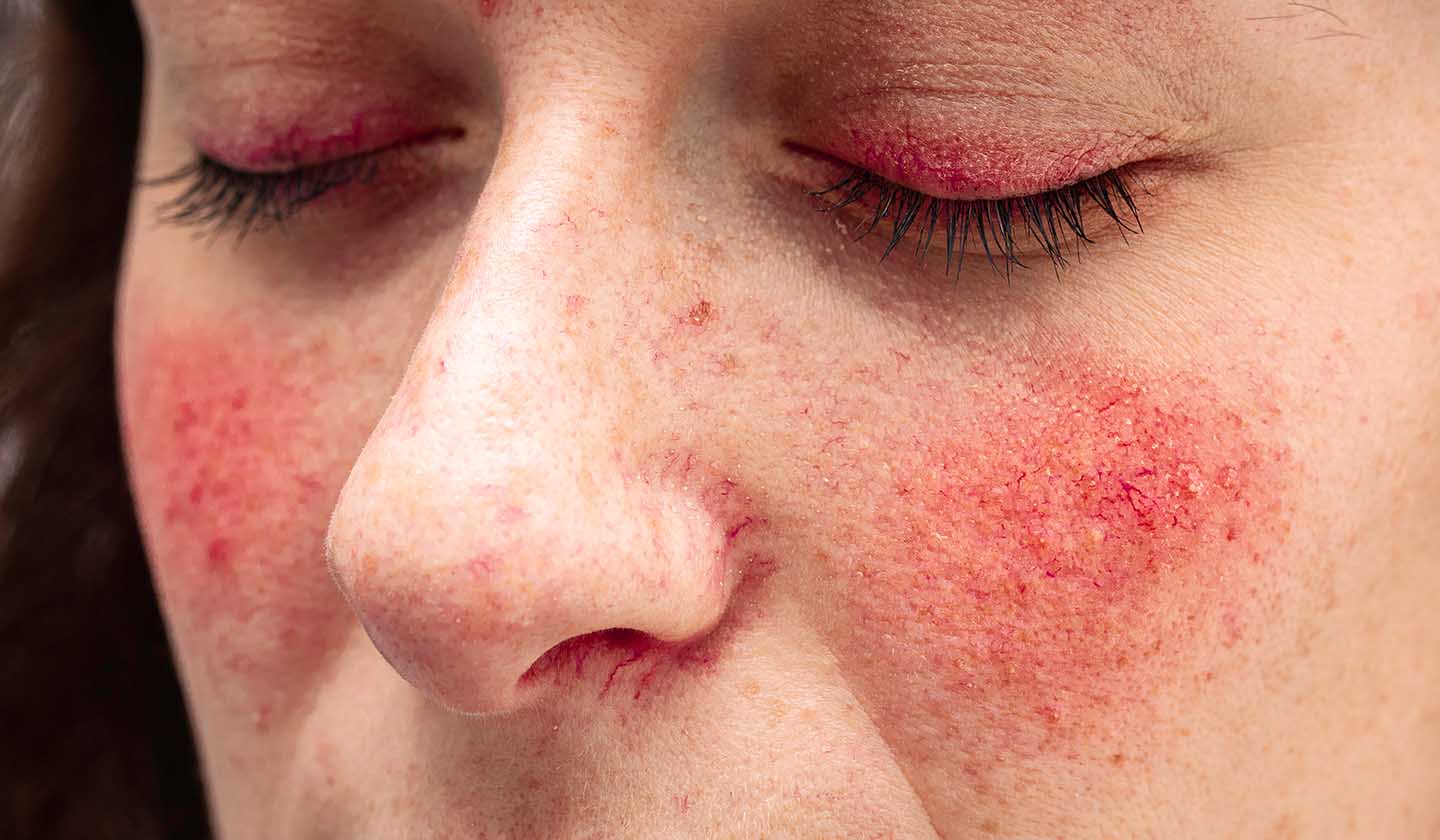
Manifestations of rosacea
They mainly appear on the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin, but may occur less frequently in other exposed areas such as ears, scalp, neck or upper back.
- Erythema (redness), persistent or transient;
- Papules, pustules, inflammatory nodules;
- Telangiectasias (strokes);
- Feeling of burning or stinging;
- Itching;
- Dehydration of the skin;
- Itching, redness, and dry eyes (rosacea can affect the eyes).
The disease often evolves due to outbreaks that can have variable duration, with spontaneous worsening of the lesions or exposure to triggering factors.
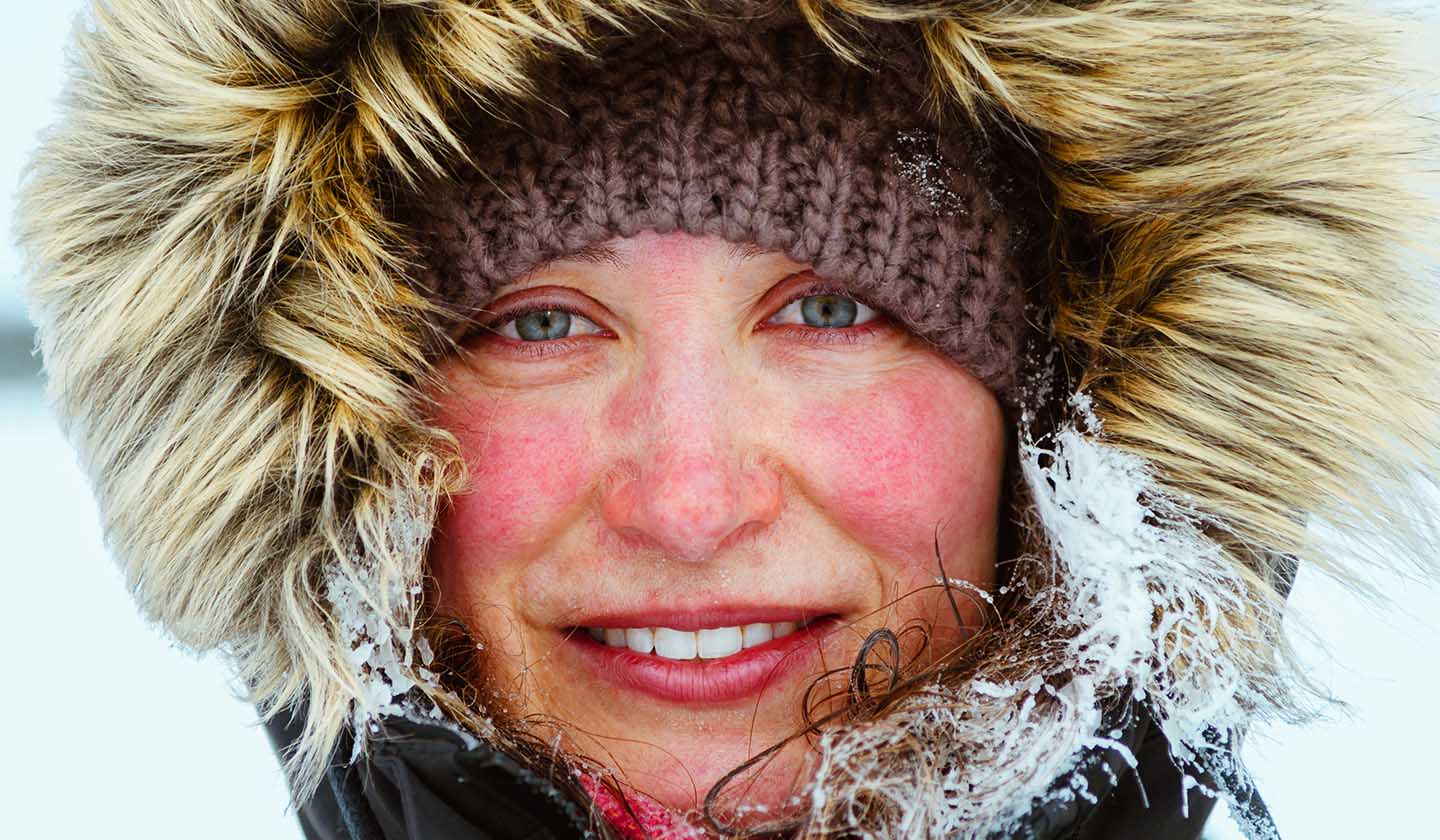

Triggering factors of rosacea
- Hot and cold temperatures
- Sun exposure
- Wind
- Hot beverages
- Alcohol
- Tobacco
- Physical exercise
- Spicy food, spices, caffeine
- Menopause
- Stress and anxiety
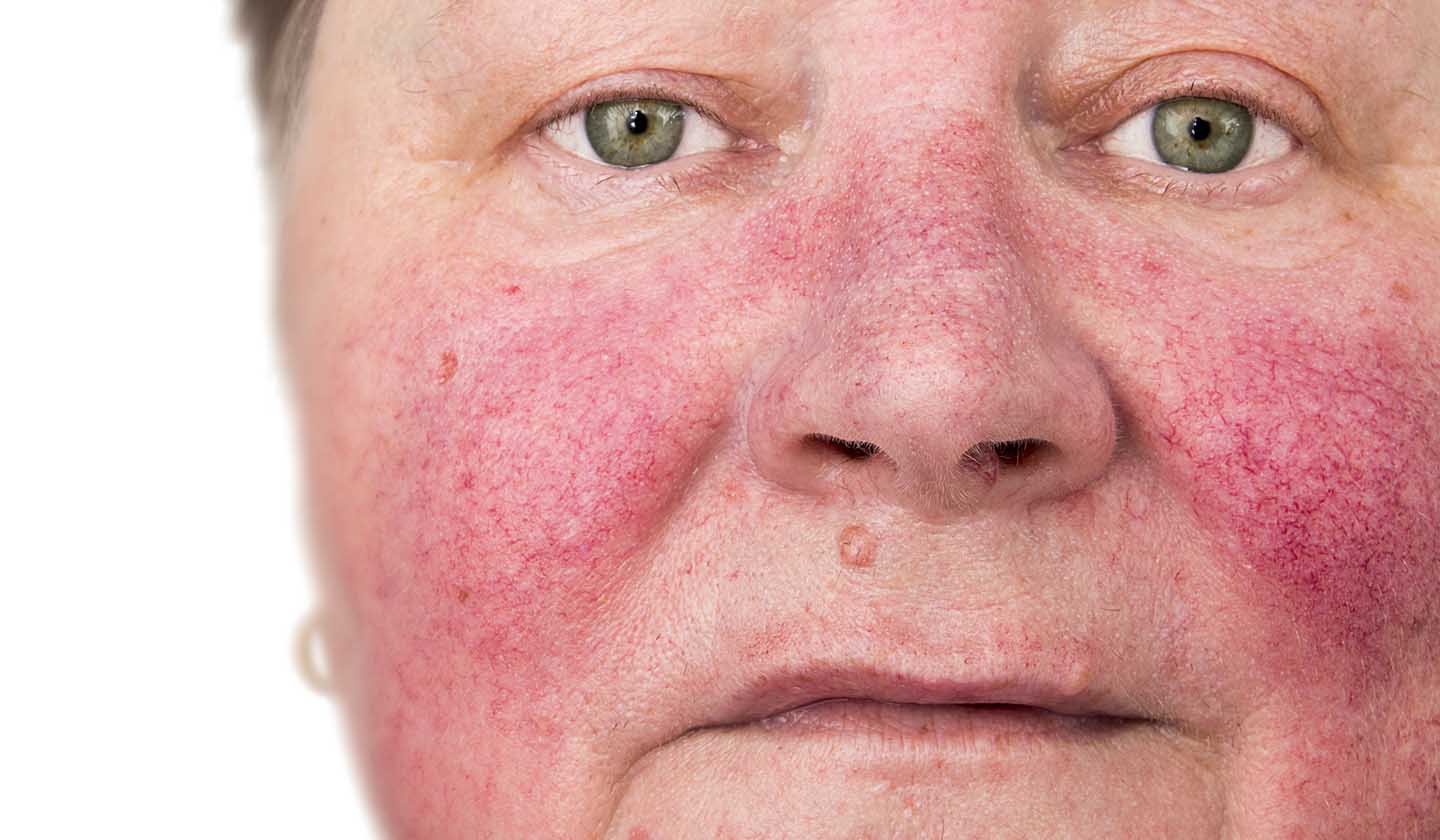
Types of Rosacea
Subtype I (erythematous-telangiectatic rosacea) - characterized by persistent redness, dilation of small blood vessels on the face, reactive skin, stinging, burning and dryness;
Subtype II (papule-pustular rosacea) - in addition to what is described for subtype I, there are also papules and pustules;
Subtype III (fimatous rosacea) - rarer, the skin appears thickened and very inflamed with irregular nodules that cause changes in the face (especially the nose);
Subtype IV (ocular rosacea) - it can occur simultaneously or not with the skin manifestations and is characterized by swelling, itching and redness of the eyes.
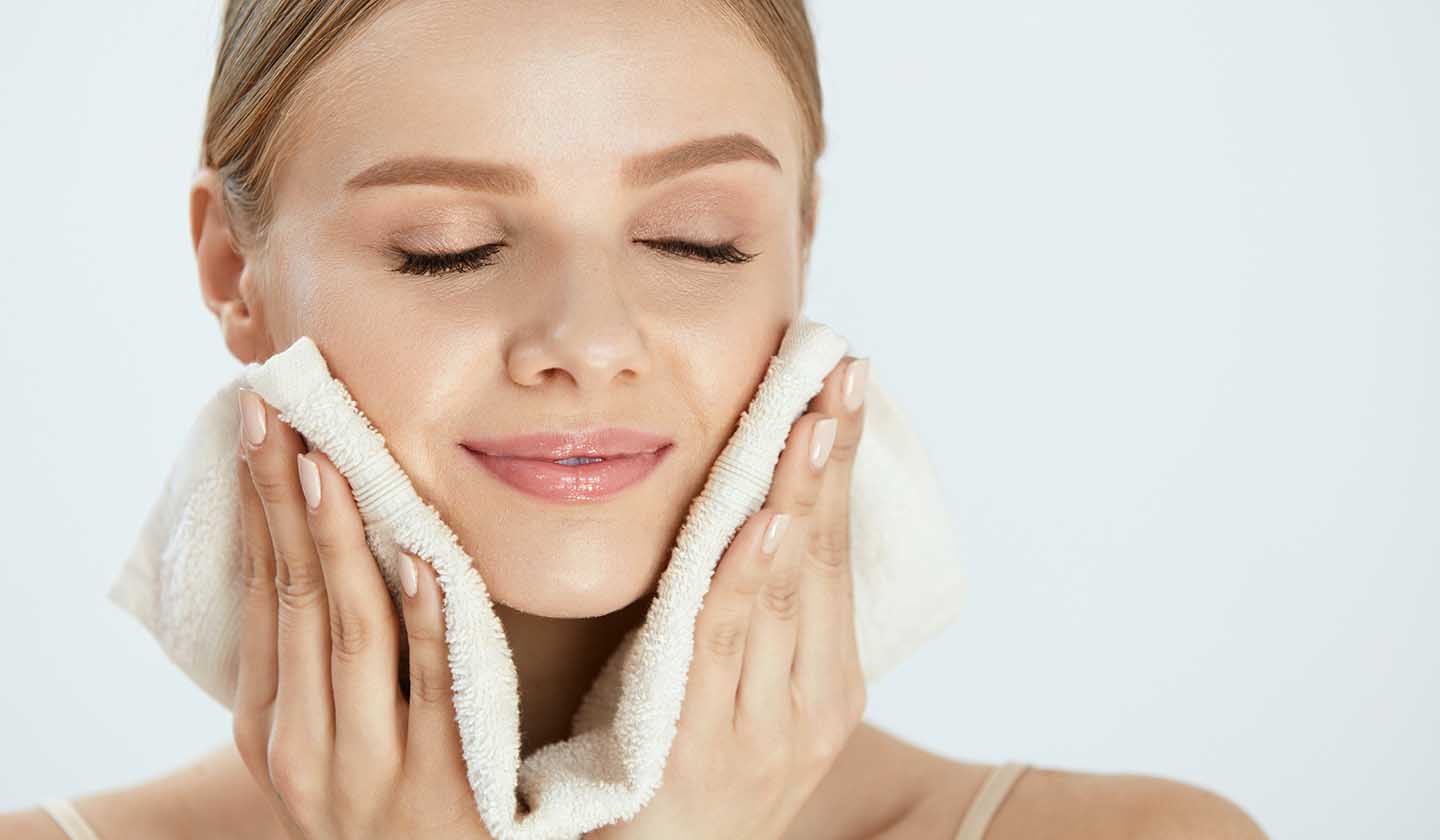

Skin care/Rosacea treatment
Dermo cosmetic care
They are intended to help repair and maintain the integrity of the skin barrier and reduce symptoms. They maintain adequate hydration and skin protection and camouflage redness.
- Gentle cleansing product - should have a neutral or slightly acidic pH (skin pH) that does not alter the skin barrier lipid membrane or normal flora (cleansing lotions, micellar waters);
- Thermal water - must be applied after cleaning and has a calming and soothing effect;
- Moisturizers - restore the skin barrier and must have soothing, vasoprotective and anti-inflammatory properties; formulations must be simple and free of perfumes and alcohol.
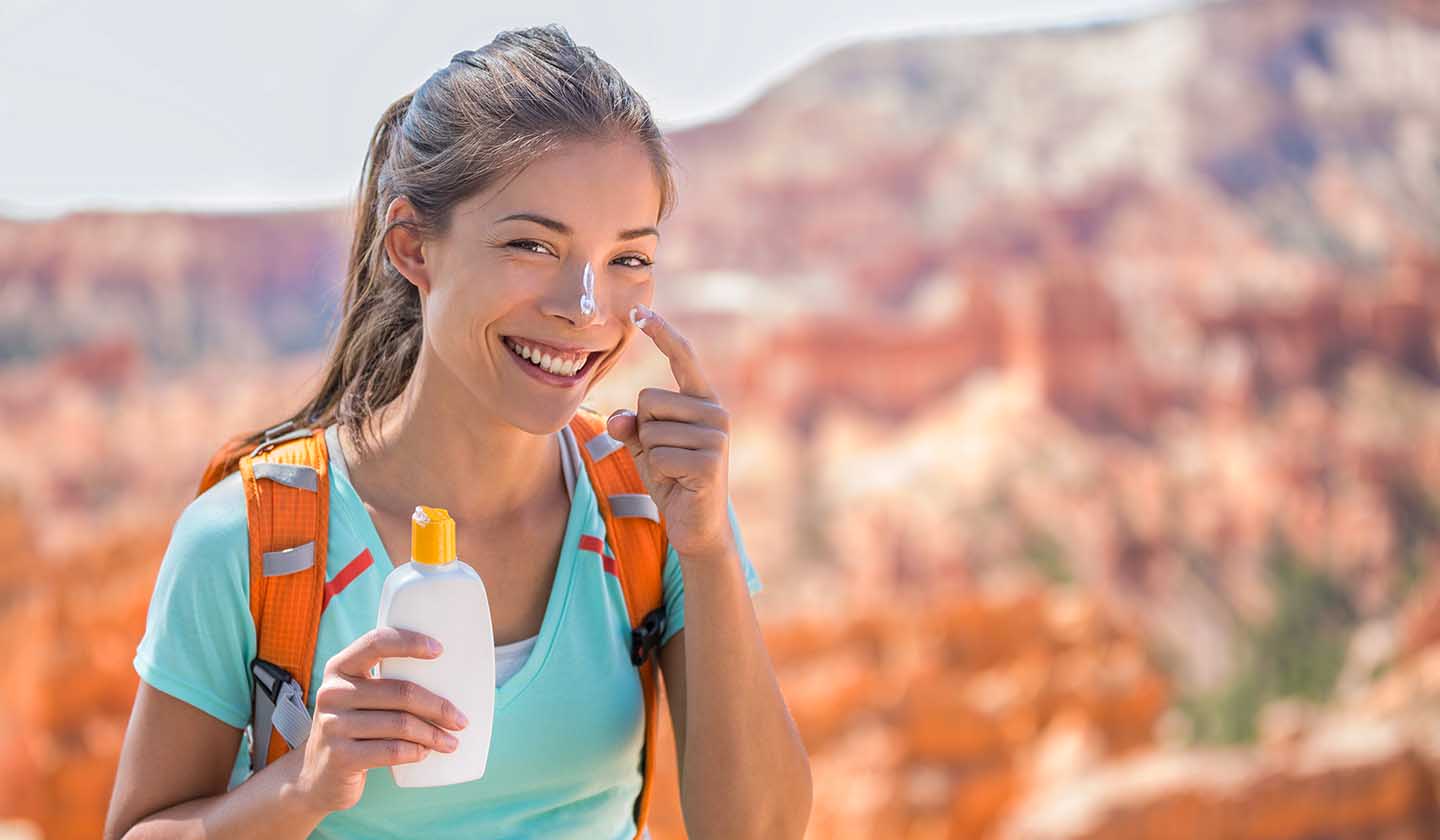
- Sunscreen - UV radiation is a trigger for rosacea, so daily use of high photoprotection (SPF 50+) is recommended; physical or mineral filters are best tolerated by rosacea skin;
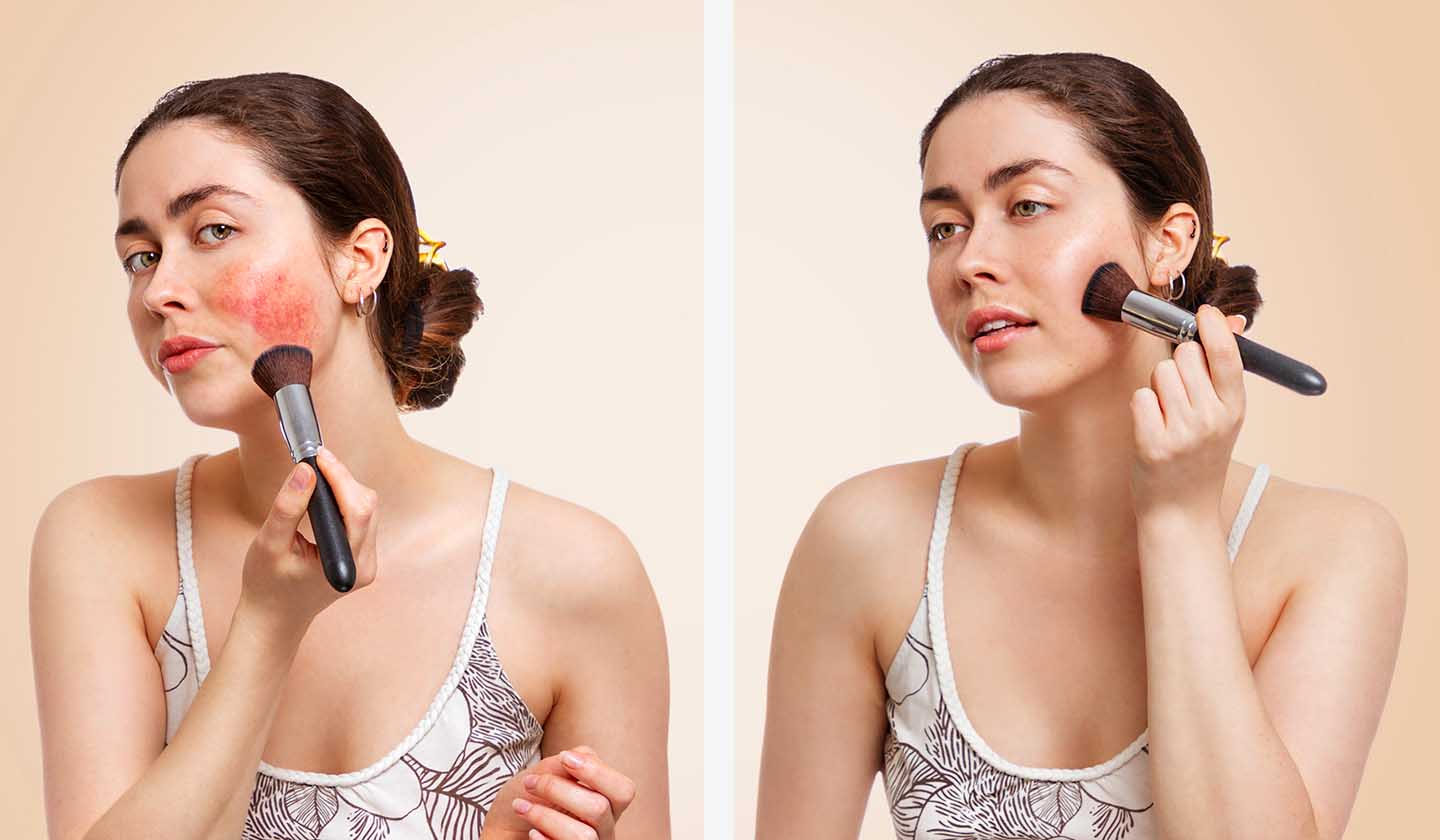
- Corrective makeup - camouflage redness, strokes, papules and pustules; this type of make-up uses the principle of colour opposition, that is, the redness can be disguised by applying a concealer with green pigments, which is the colour that neutralizes red, giving rise to a brown tone, which can be covered by a base.
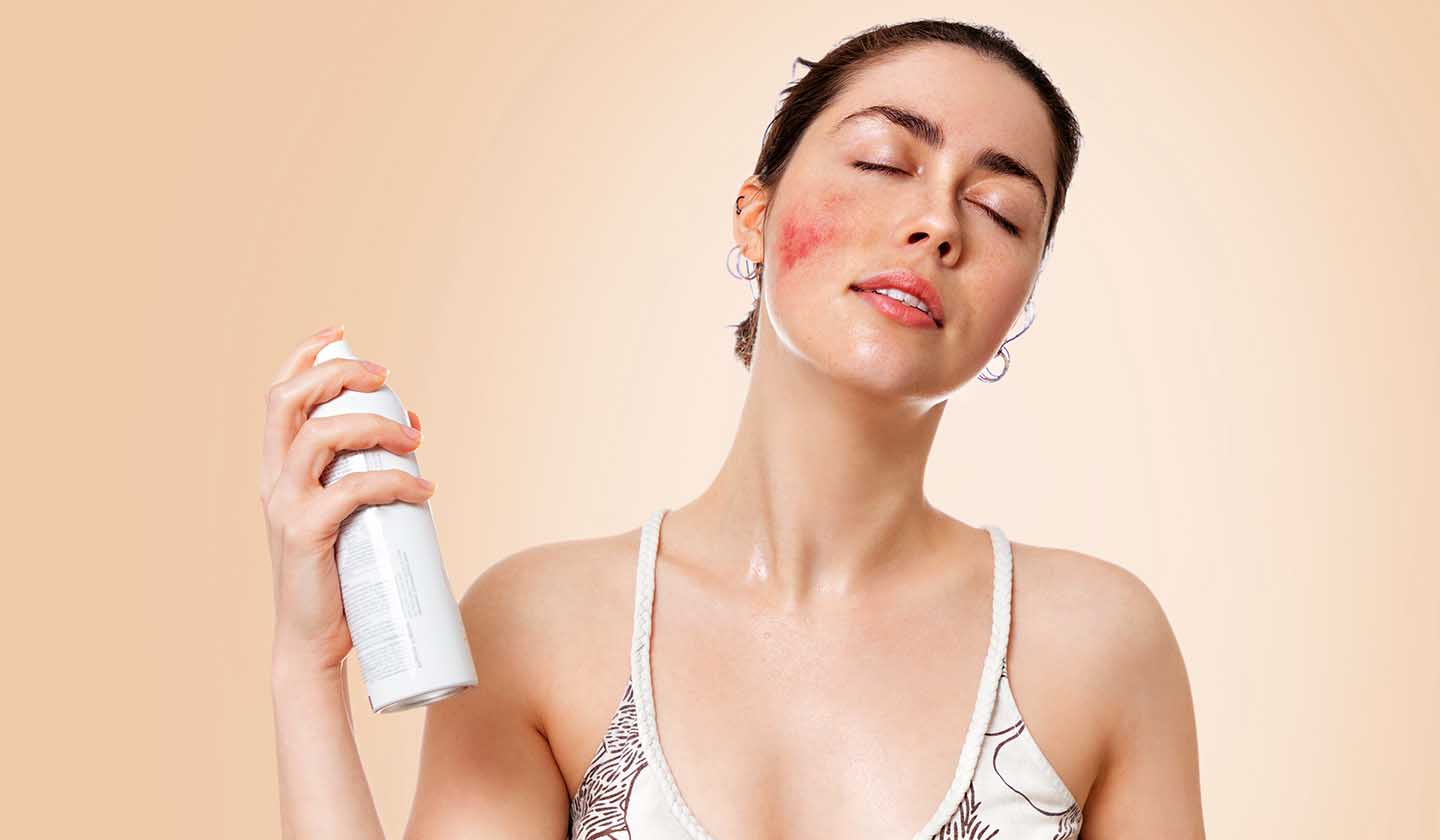

Pharmacological treatment (oral or topical therapy)
They do not cure rosacea, as it has no cure, but they help to manage the disease in more severe situations, improving the patient's quality of life. It aims to reduce symptoms, to spread crises and prevent the development of more advanced disease states.
- Oral or topical antibiotics (MSRM)

Laser Treatment
Reduces erythema and telangiectasias (strokes). IPL (intense pulsed light) or PDL (pulsed contrast laser) can be used.

Surgical treatment
Reserved for severe cases of the disease, as is the case of fimatous rosacea, which is characterized by a thickening of the skin with irregular nodules, especially in the nose, being more frequent in men.

Crisis prevention
- Avoid drinks and food that can trigger or aggravate rosacea situations;
- Clean the skin in the morning and at night, drying gently with a soft cotton towel and without rubbing;
- Drink water (staying hydrated is essential for your skin);
- For men, avoid using a razor blade and prefer an electric shaver.
- Use thermal water;
- Choose products suitable for your skin (ask your pharmacist for advice);
- Use a sunscreen (SPF 50+) daily;
- Adopt a healthy diet and sleep 7-8h;
- Reduce your stress levels.
The cause of rosacea is unknown, but it is thought that its appearance may be related to a genetic predisposition, skin phototype and environmental factors. Although this pathology has no cure, it is possible to manage the disease by adopting daily care that will reduce discomfort and prevent its worsening. Medical diagnosis is essential so that you can properly address your skin problem.
Sources
iSaúde
Farmácia Distribuição Magazine
Também lhe poderá interessar
Prevention and treatment






