Nourish your skin
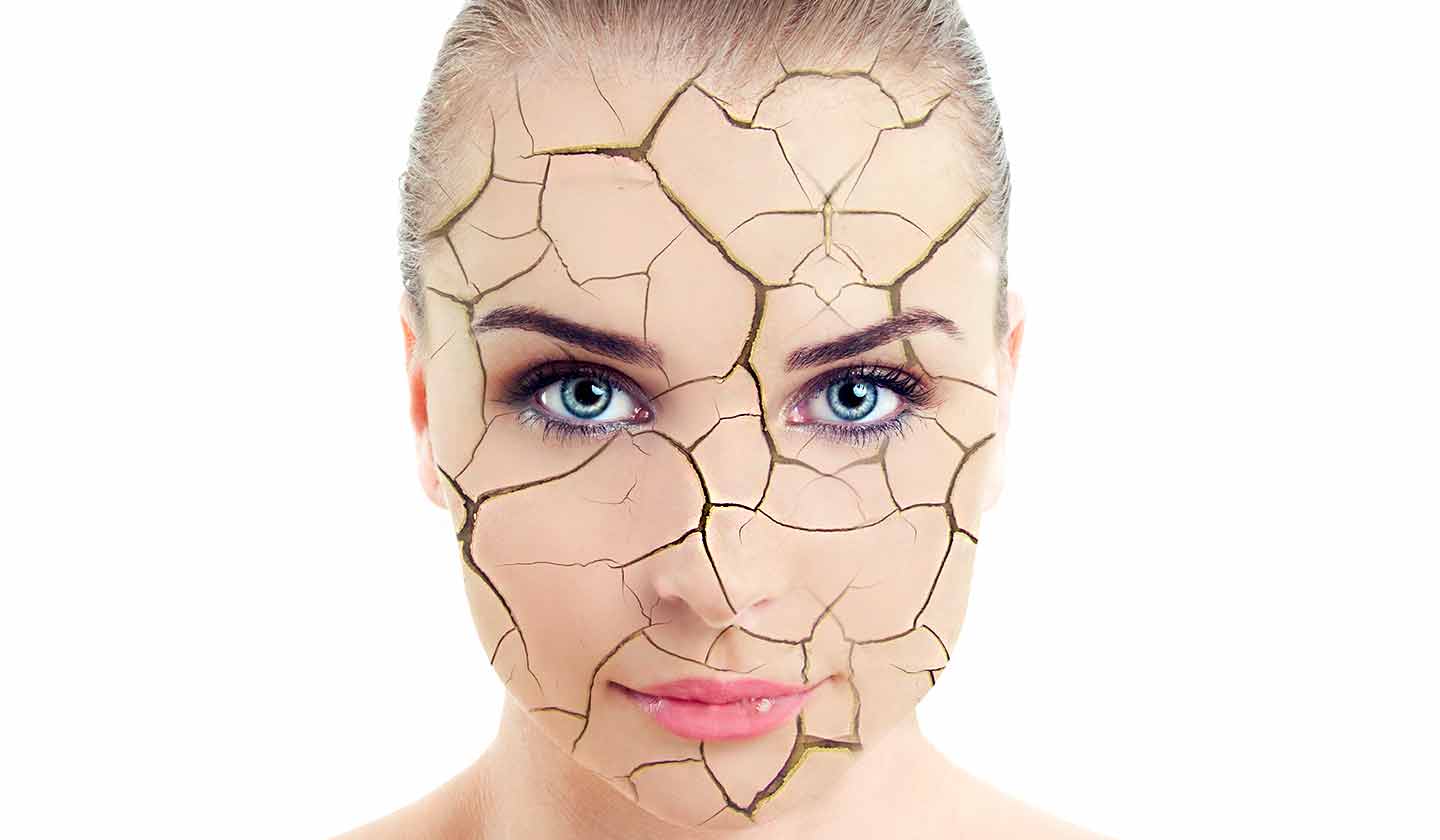

The skin, our largest organ, is often devalued. Because it protects us against the environment, it is always exposed to external aggression.
One of the main skin problems is dryness, which is caused by several factors.
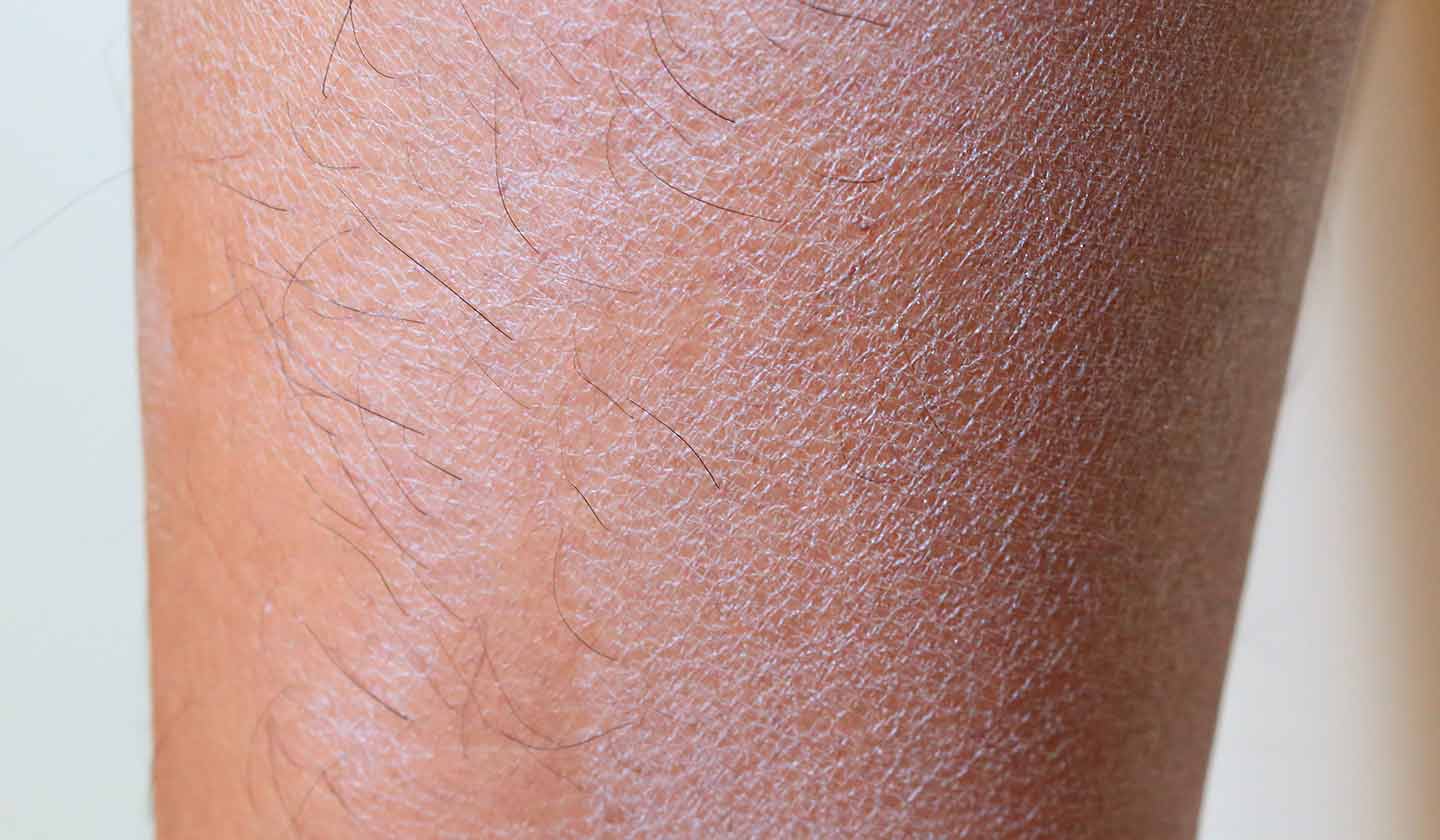
What is dry skin?
Dry skin (xerosis cutis) occurs when the skin natural lipid barrier, which prevents water from evaporating, is eliminated.
It often occurs in winter, due to temperature differences between the outside (cold) and the inside (heating) or in summer due to sun exposure and sea water, however it is not an exclusive situation of these seasons.
Dry skin is characterised by:
- Dehydrated, dull and rough appearance;
- Redness;
- Tightness;
- Flaking;
- Itching;
- Presence of small fine wrinkles;
- Fissures (cracks).
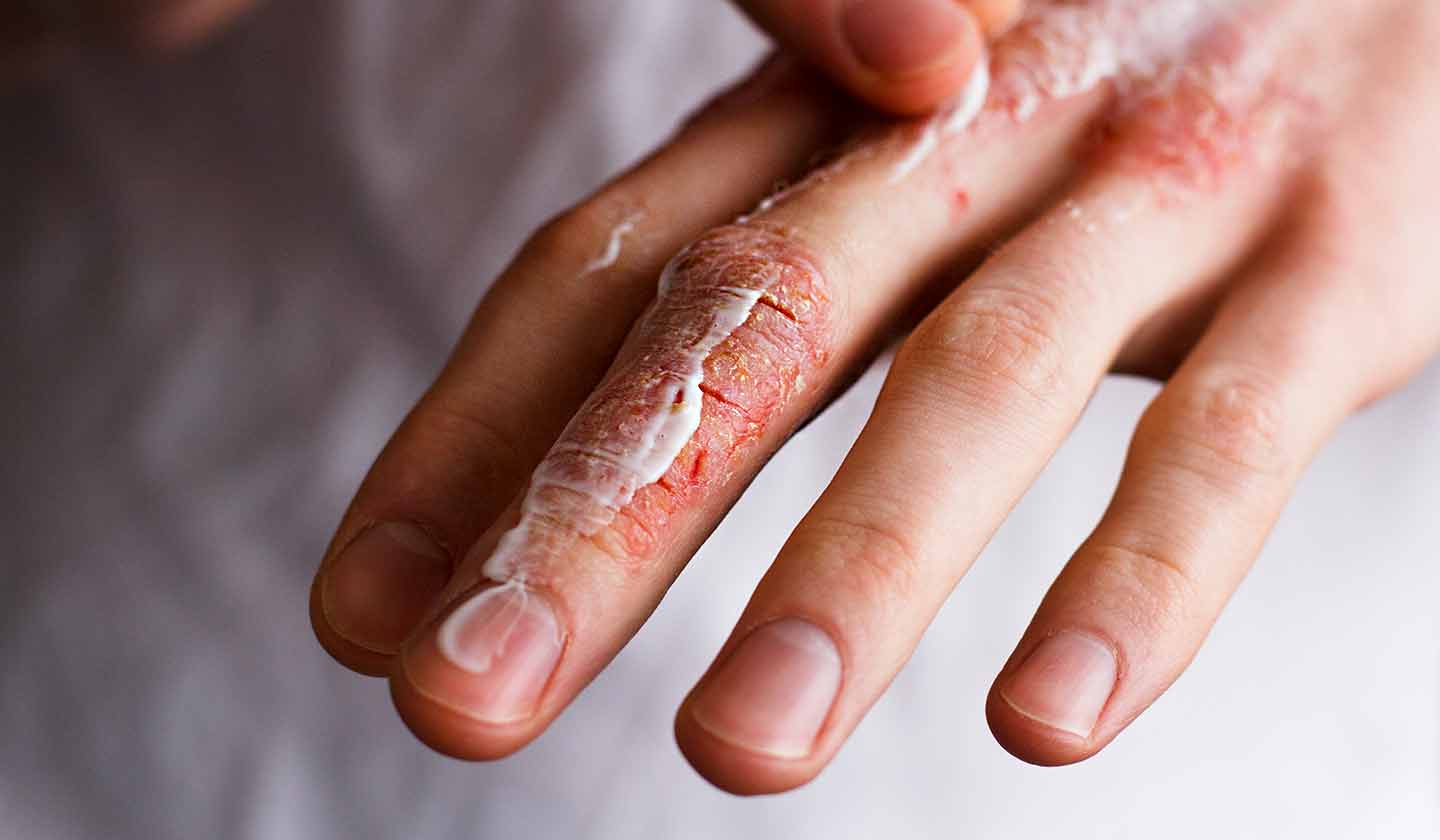
What causes dry skin?
Sometimes the skin starts to get rough, peeled and dehydrated. This situation essentially occurs as a result of several external and internal factors that influence the skin ability to retain water.
External Factors
- Climatic conditions - hot, cold air and dry heat (with low humidity);
- Air conditioning and heating - they reduce the humidity present in the air, which contributes to drier skin;
- Long, frequent, hot showers and baths - they remove the lipid layer of which the skin barrier is composed of;
- Sun exposure;
- Medications - medications can cause skin dryness
- Smoking excessive amounts of tobacco.
Internal Factors
- Age - with ageing, sebaceous glands have less activity, which contributes to dry skin;
- Diseases - some medical conditions, such as eczema, psoriasis, hypothyroidism, atopic dermatitis, and diabetes, can cause dry skin;
- Hormonal influences - pregnancy as well as menopause can influence dry skin;
- Gender - dry skin is more common in women, especially in post-menopausal women.
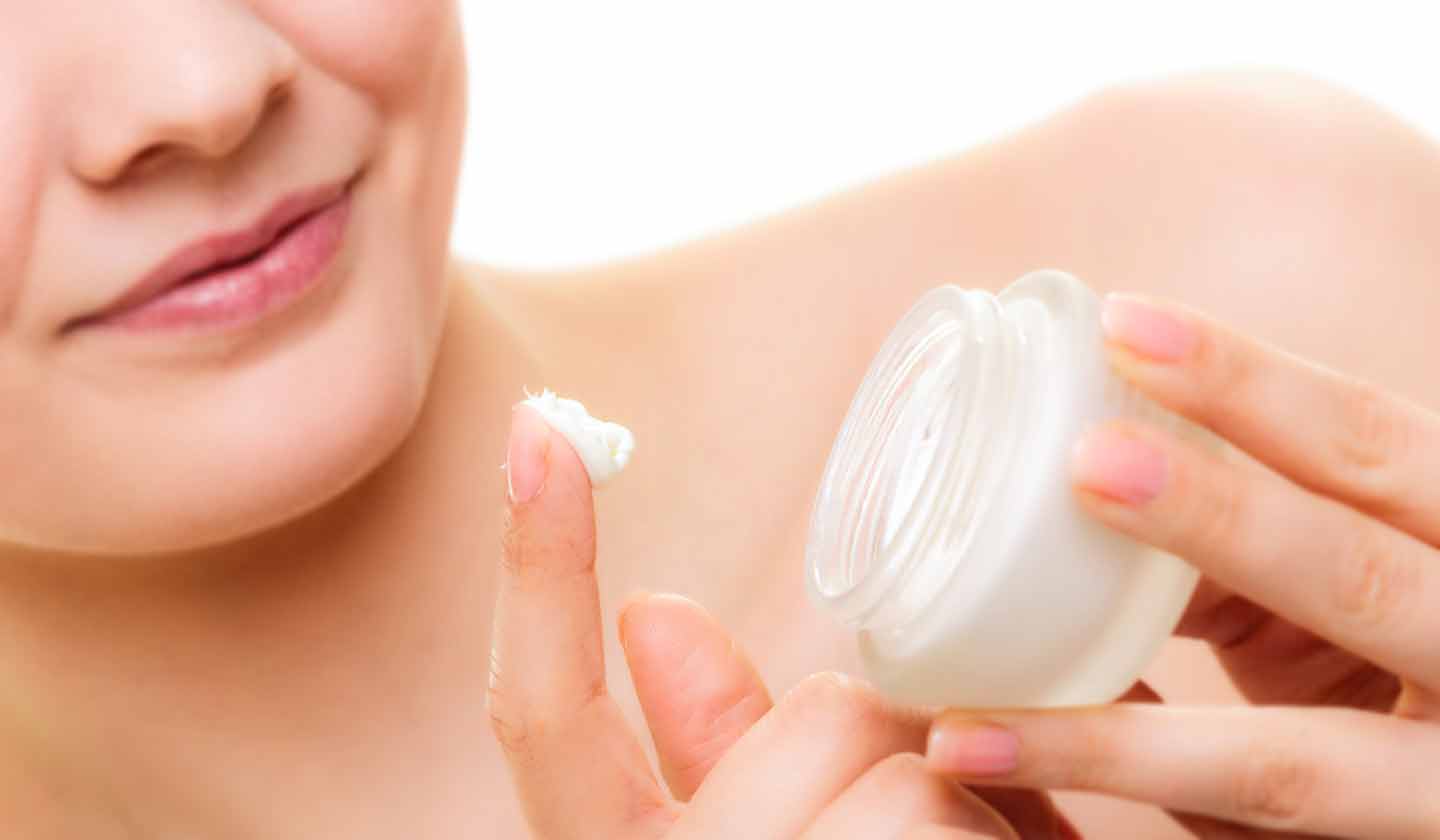

How to treat dry skin?
This condition occurs when the skin gets dehydrated due to the loss of the lipid layer. Small daily routines can make a difference:
- Take a warm water shower for 10 to 15 minutes;
- Use mild cleansing products - avoid those containing perfumes and alcohol;
- You can use shower oil instead of shower gel - it cleans, restores the skin barrier, and moisturises the skin (be careful as the oil can make the bathtub slippery);
- Moisturise your skin after the shower - use a moisturiser that contains urea, lactic acid, or lanolin.
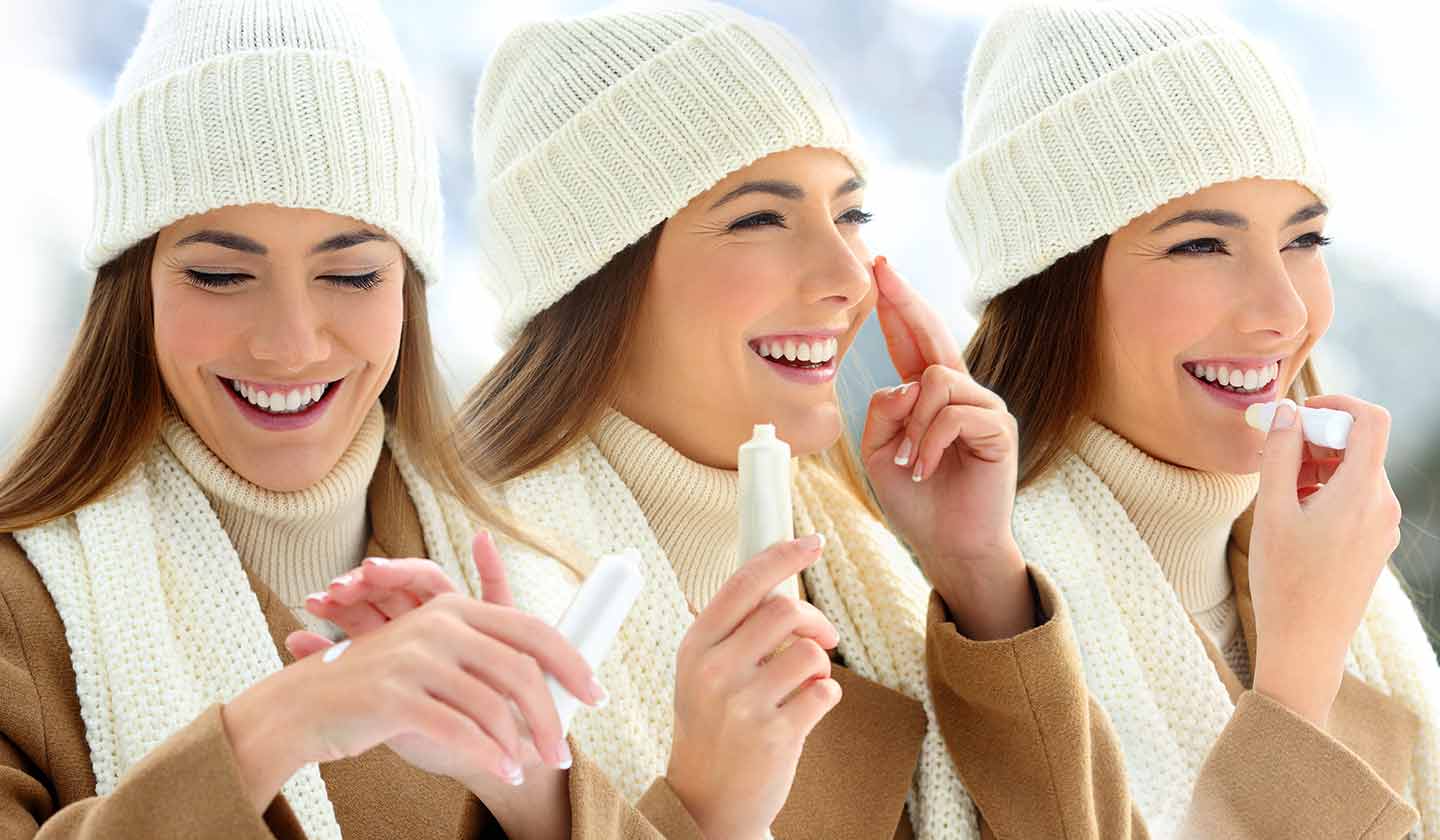

How to prevent it?
- Avoid prolonged hot water showers or baths;
- Prefer cream or ointment for skin hydration - the ointment forms an occlusive barrier that protects the skin allowing the moisturising ingredients to be more effective;
- Moisturise your hands - apply a moisturising cream suitable for hands after washing them and before bedtime;
- Wear gloves during housework chores - detergents remove the skin barrier thus causing the skin to dry;
- In winter, wear gloves to protect your hands from the cold;
- Use a moisturising lipstick - lip hydration prevents cracks;
- Use sunscreen in summer and winter to prevent photoaging.
Sources
iSaúde
Farmácia Distribuição Magazine
Também lhe poderá interessar
Prevention and treatment
Hyperpigmentation - When melanin stimuli need correction
Dermatology






