Dermatology
Bruises, behavioural medals!
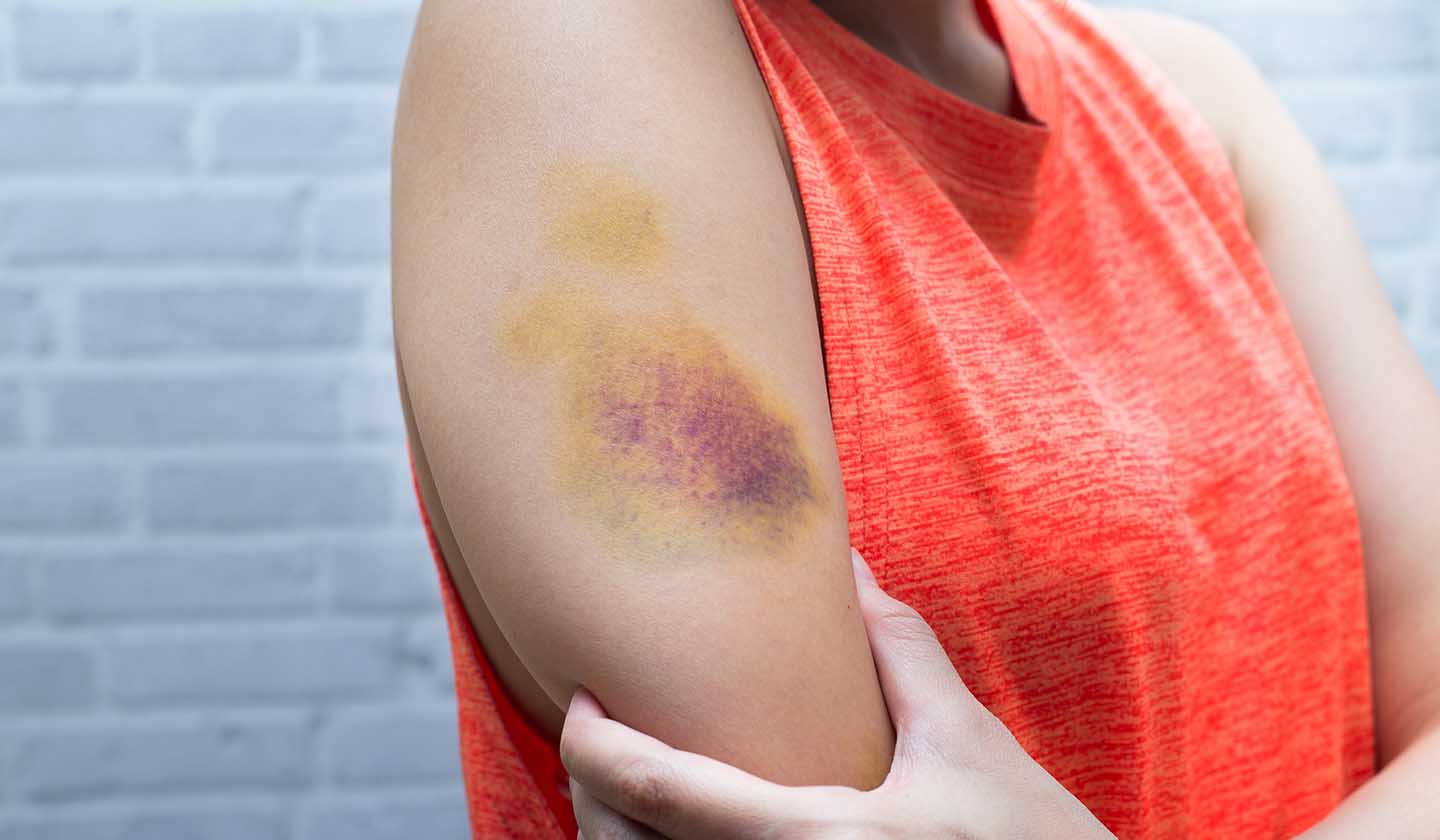
When there is a rupture of a blood vessel, haemorrhage occurs, and blood accumulates in the tissues resulting in the formation of a haematoma.
A small hematoma (1 to 2 centimetres in diameter) on the skin or mucous membranes is called ecchymosis, commonly known as "bruise".
Under normal conditions, hematomas and ecchymoses do not represent serious situations and disappear spontaneously within 2 weeks to 1 month.
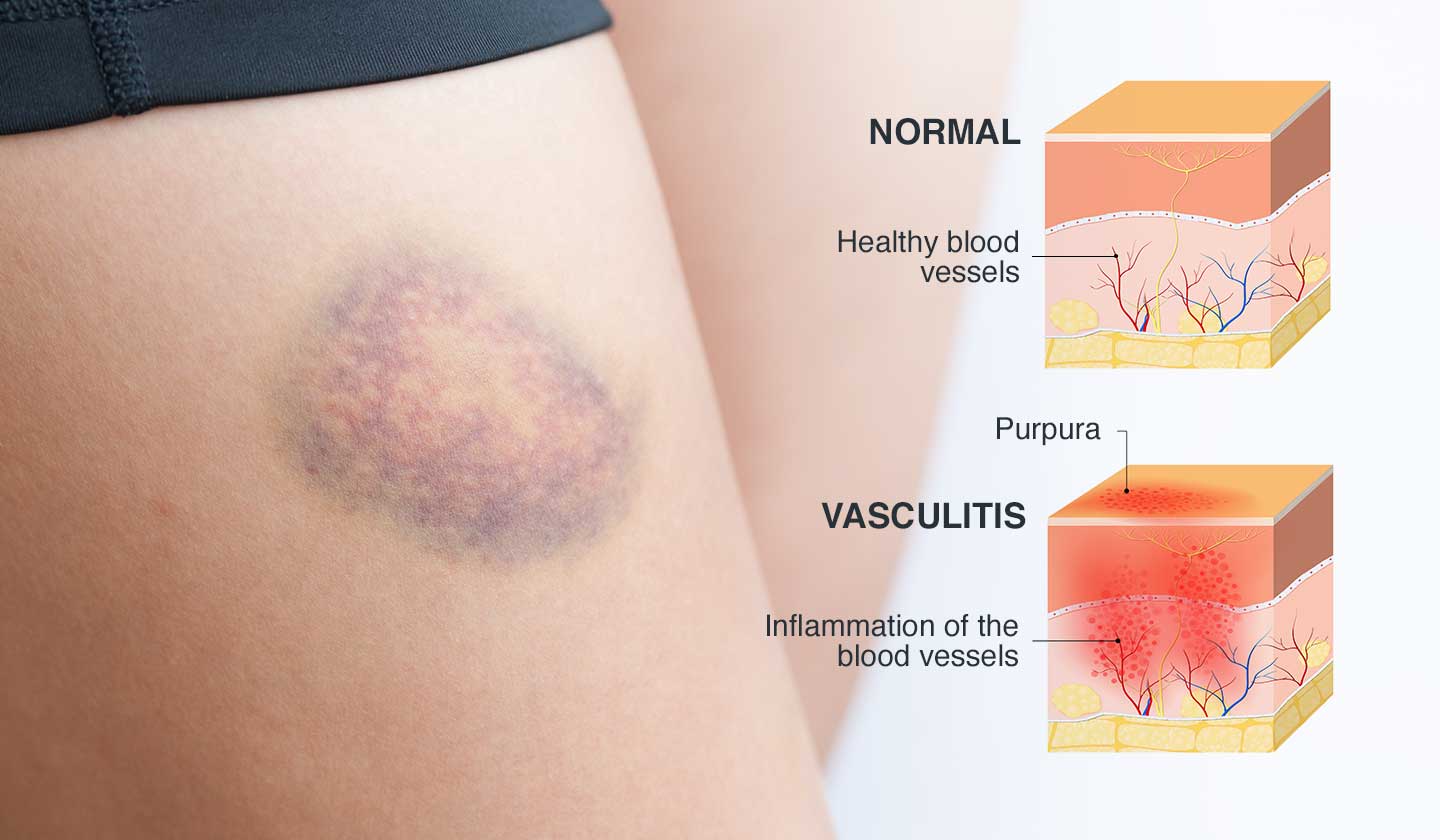
Symptoms
Symptoms will depend on the body area where the hematoma is formed. The main changes related to the presence of a hematoma are:
- Pain
- Local swelling
- Changes in skin colour - blue, red, or black skin at the injury site
Causes
- Falls
- Violent accidents, with direct or indirect knocks or shocks
- Blood clotting disorders (e.g., haemophilia)
- Surgery complications
- Some medicines e.g., excess acetylsalicylic acid and anticoagulants
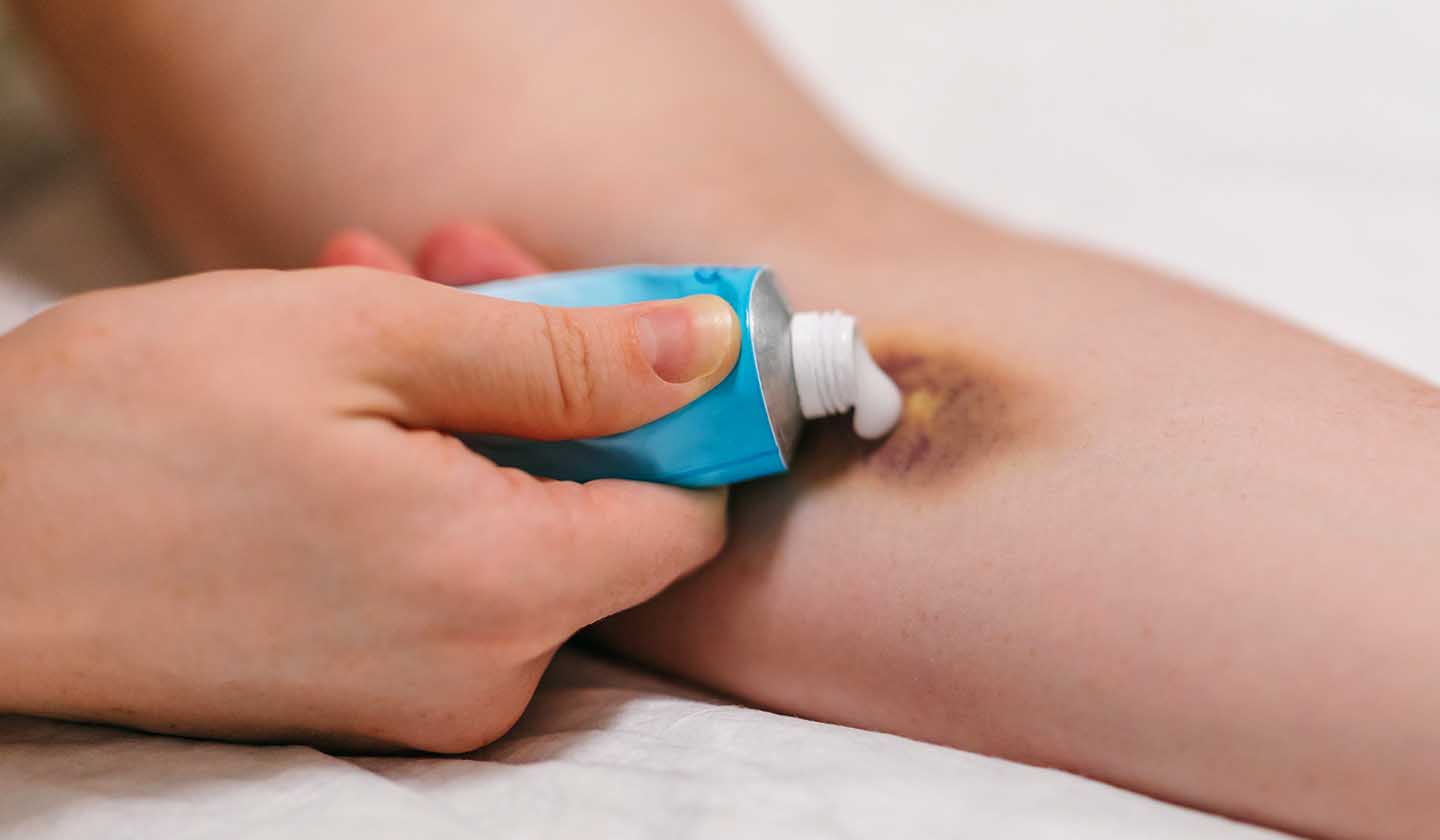
Treatments
To treat oedema (swelling) and bruising:
- Place ice or a cold gel bag on the affected area
- To relieve pain, apply a gel or cream with arnica which has anti-inflammatory and regenerating properties.
Prevention
- do not leave a baby alone on the bed, bathroom counter, tables, or sofas
- take special care of the elderly as they have a higher risk of falling and have more sensitive skin
- contact sports athletes must wear protective equipment
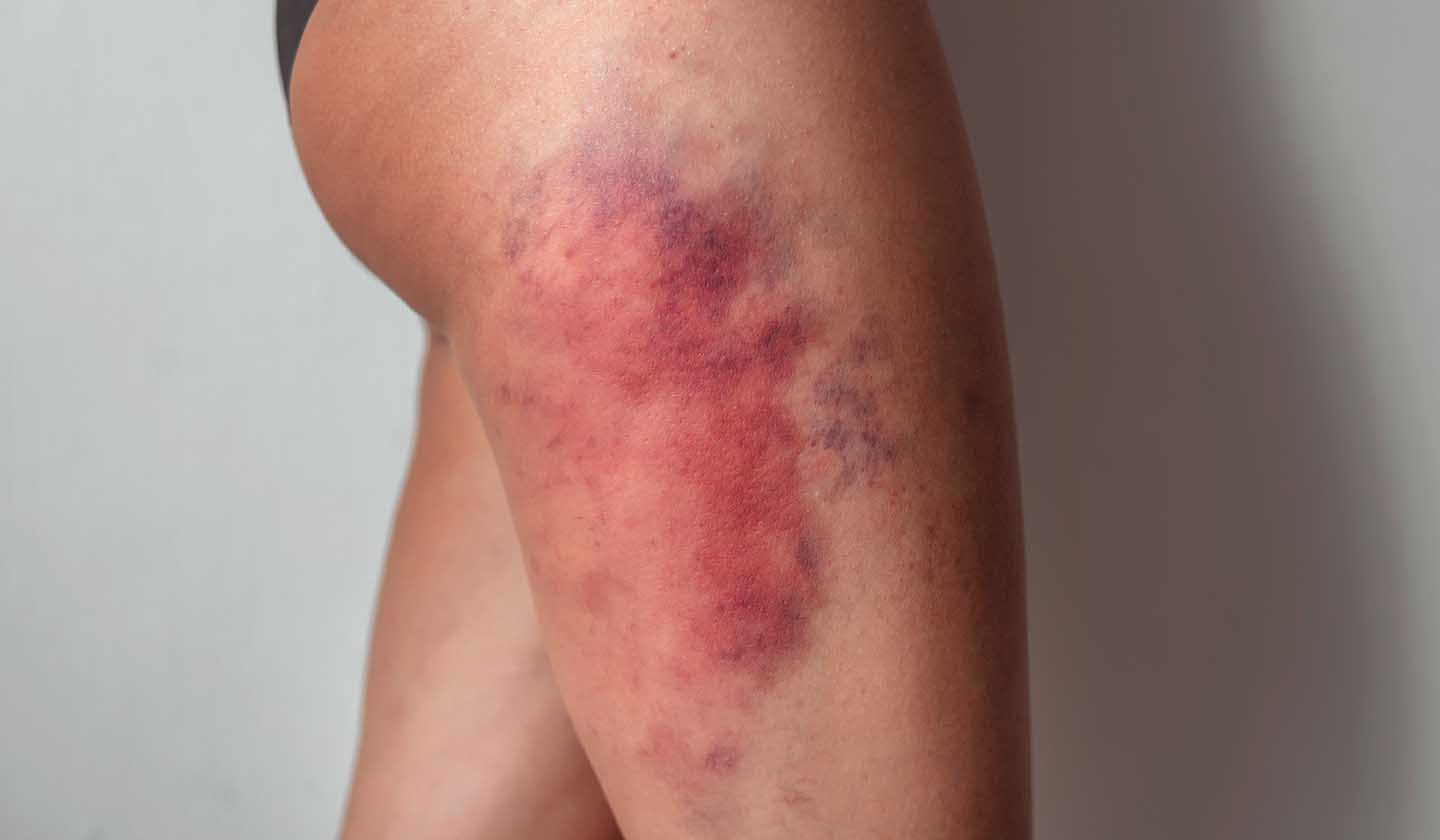
When should I see a doctor?
- if the swelling persists and the child or adult has difficulty moving
- when wounds and bruises have no apparent cause and / or are located in unusual body regions (e.g., neck, ears, buttocks, abdomen)
- presence of headache, confusion or other sudden symptoms related to the brain or nervous system
- pregnancy
- signs of infection, such as fever, tremors, and diarrhoea
In the presence of a hematoma, your pharmacist can help you choose the most suitable product to apply, as well as the measures to be taken to relieve symptoms.
Sources
iSaúde
Farmácia Distribuição Magazine
Também lhe poderá interessar
Muscles






