Cardiovascular system
Anti-coagulants, what precautions?
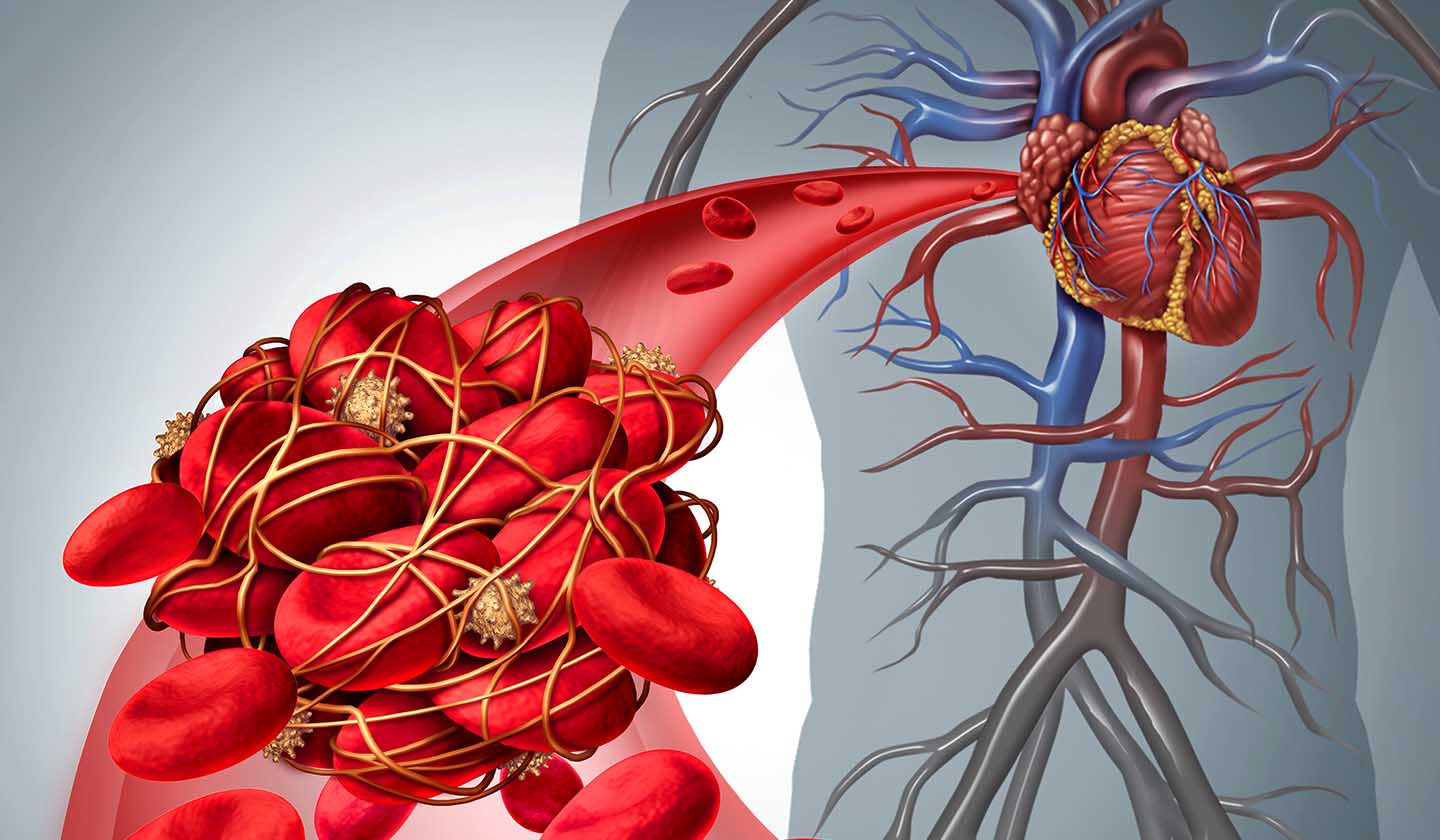
Oral anticoagulants (OACs) are medications that inhibit the blood’s ability to form blood clots by making it thinner.
OACs are used to treat and prevent thromboembolic and heart diseases, such as acute myocardial infarction, stroke, and pulmonary embolism.
The clotting mechanism is quite complex, involving several factors that contribute to blood clotting. Some of these factors are controlled by vitamin K.
There are 2 groups of OACs: the ones that have the opposite effect of vitamin K, preventing the formation of clotting factors, and the new OACs.
When compared to the first ones, the new OACs have the advantage of not requiring a regular monitoring of blood “thickness”, and they interact less with other medicines and foods. Older OACs require periodic laboratory analysis of INR* values in order to adjust the dose to be taken and have many interactions with food and other drugs, which makes them not so safe to take.
The main side effect of OACs is the increased risk of bleeding.
Vitamin K participates not only in blood clotting but also in bone metabolism, being therefore an essential vitamin in our body. Patients who use medication with OAC should not stop eating foods rich in vitamin K, however they should monitor their INR levels in order to adjust their therapy.

Foods rich in vitamin K that can interfere with blood clotting:
- Fruit
- Kiwi
- Blackberries
- Grapes
- Avocado
- Figs
- Vegetables
- Broccoli
- Spinach
- Cabbage
- Lettuce
- Grain legumes
- Grain
- Lentils
- Soy
- Egg yolk
- Bovine liver
Patients taking medication with OAC should also pay attention to the other drugs they are using, especially those that are not prescribed by the doctor. Medicines can interfere with blood clotting, including anti-inflammatory drugs, which can increase the risk of bleeding.
The patient undergoing OAC must be more careful when using drugs purchased without medical prescription.
INR* - laboratory parameter used to monitor patients undergoing therapy with anticoagulants.
Sources
iSaúde
Farmácia Distribuição Magazine
Também lhe poderá interessar
Cardiovascular system
The dangerous and silent hypertension
Cardiovascular system






