Muscles
And suddenly the muscles hurt so much that you can't even move
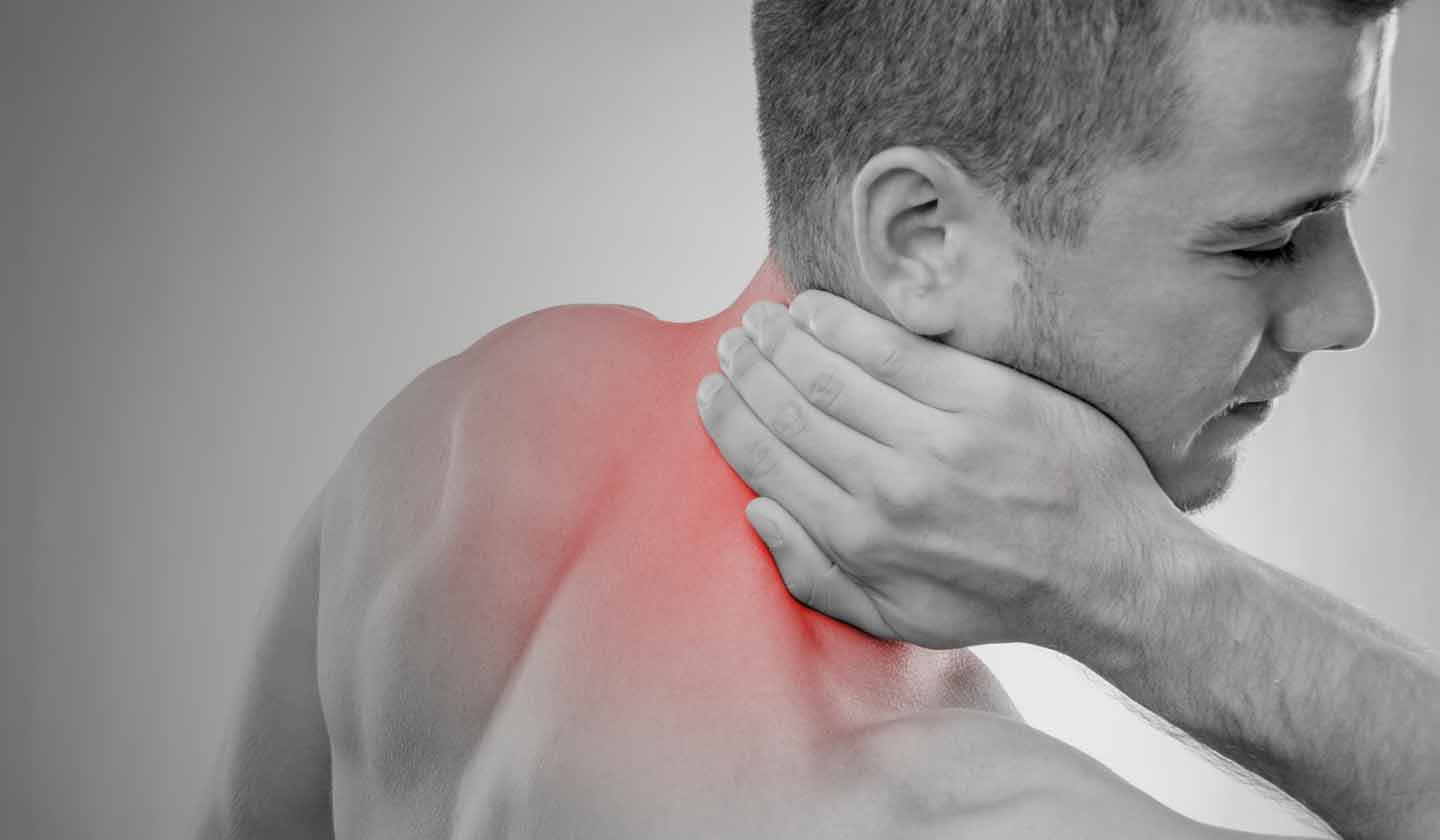
Muscle pain (Myalgia) is common and can be divided into 2 groups: the pain that affects the whole body (all muscles are affected) or the pain that affects a particular muscle (a part of the body). It may also involve ligaments, tendons, fascia, the soft tissues that connect to muscles, bones, and organs. It can affect many parts of the body such as the legs, thighs, shoulders, back, neck, among others.
Muscle pain can disappear in a short period of time, but it can persist for a longer period, lasting for months. People suffering from this condition, which may also affect normal daily life, experience a lot of discomfort.
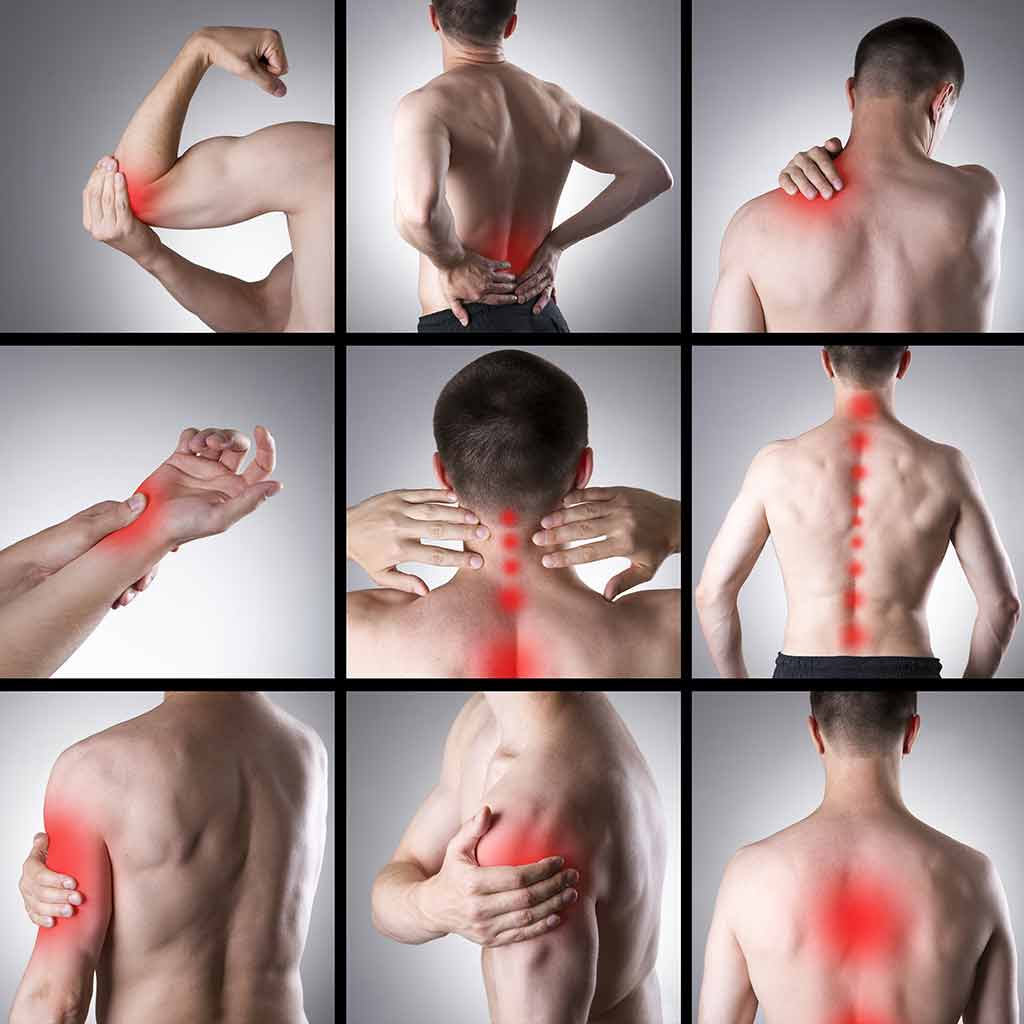
Symptoms
- Pain
- Headache
- Sleep disorders
- Inflammation
- Redness/inflammation
- Swelling
- Moving unsteadily or with difficulty
Muscle pain associated with mild trauma or muscle exertion usually goes away within 3 to 5 days.
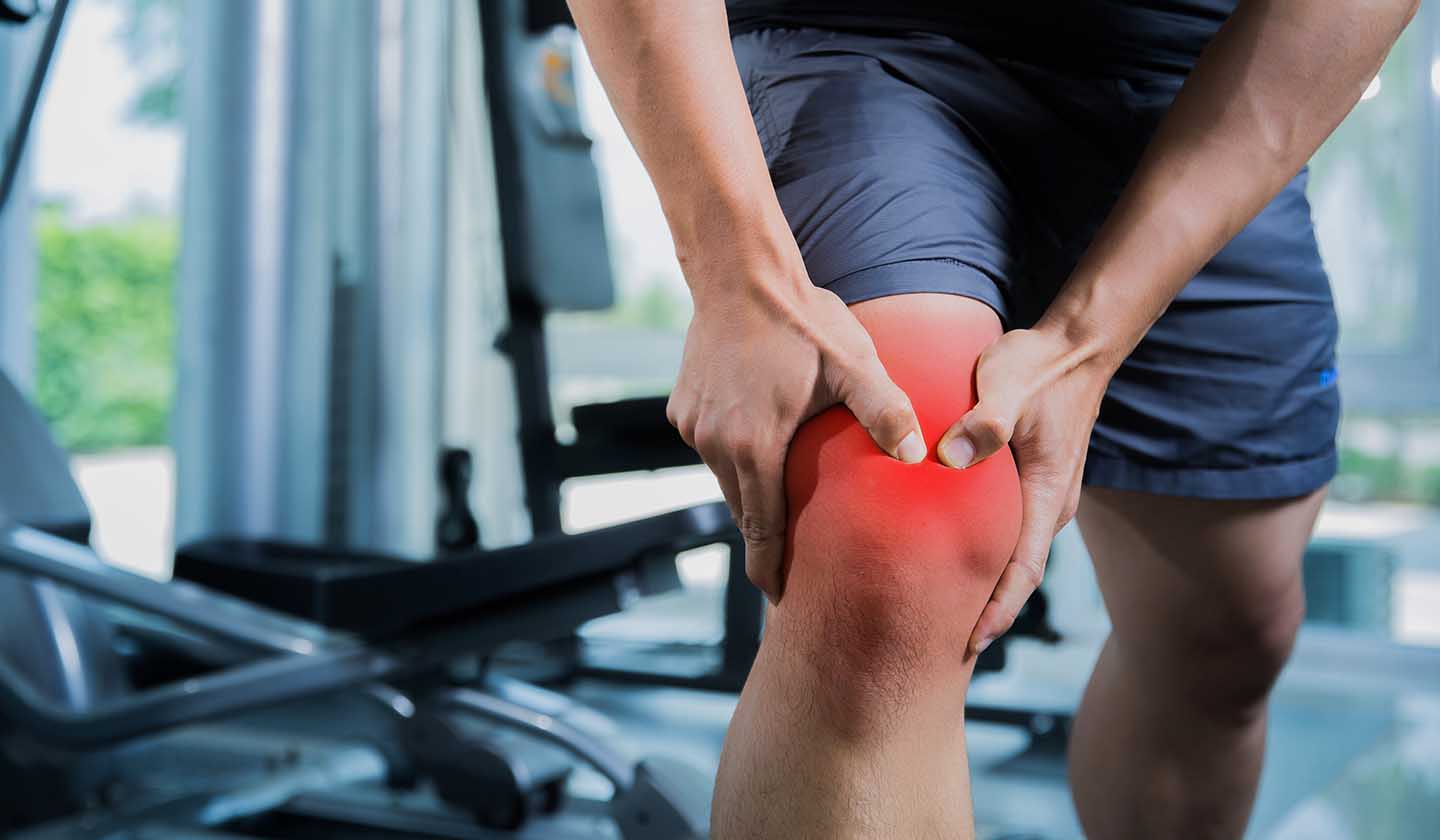
Causes/risk factors
Muscle pain can occur due to:
- Muscle injury: in sport
- Muscle cramps:often due to lack of magnesium, for instance, muscle spasms in the calves
- Muscle tension: the affected area becomes painful and stiff, for instance, incorrect body posture
- Muscle diseases: pathogenic agents can trigger a muscle inflammation, which can be caused by bacteria (tetanus) or viruses (flu). Muscle pain can also be caused by diseases such as: hypothyroidism, Malaria, Dengue, dermatomyositis, lupus
- Medicinal products:for example, cholesterol-lowering drugs cholesterol (statins) and high blood pressure medications (ACE inhibitors)
- Obesity and age
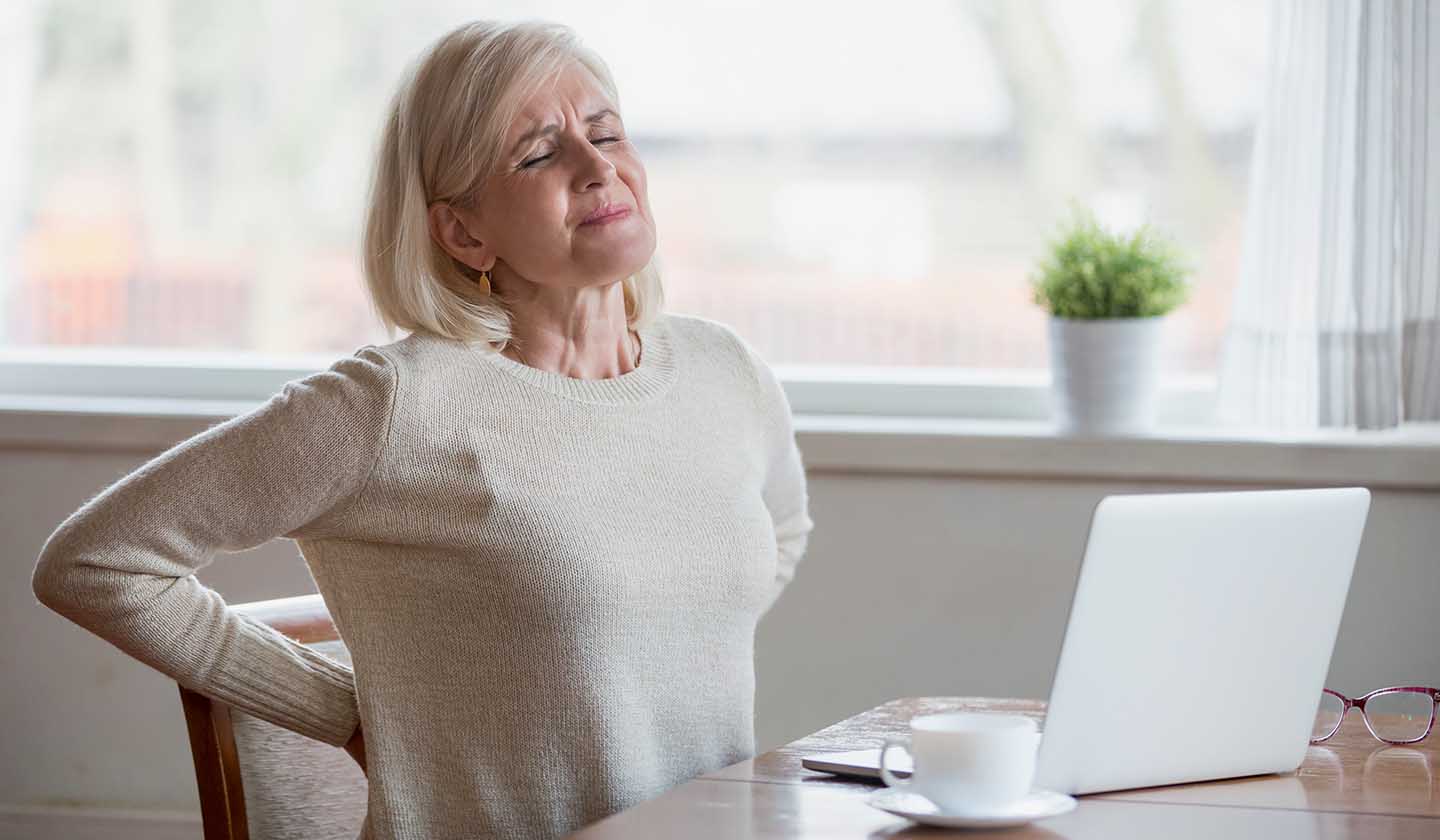

Prevention/care to be taken:
There are several ways to prevent muscle pain:
- Physical exercise: warm up before exercising; stretch at the end; drink water before, during and after exercise, as it helps to oxygenate muscles and practice regular physical exercise.
- Sedentary lifestyle: if you spend a lot of time sitting, stretch/stand up every hour.
- Rest - avoid intense efforts in the affected area
- Ice application - ice can help to relieve pain, as well as reduce inflammation during the first few hours after the trauma (for instance, reusable gel bags)
- Massage - the pain occurs due to muscle fibre damage and to the release of inflammatory enzymes, thus massaging the area affected helps to reduce those toxins. At the same time, massages promote a faster muscle oxygenation. Using anti-inflammatory products (cream/ointments and lotions)
- Physiotherapy (prescribed by the doctor)
- Heat application - when there is no swelling and inflammation, heat can be applied to help relax the muscle. A hot water bag, or reusable gel heating pads, can be used)
- Food supplements: either alone or in combination, can contribute to the reduction and treatment of symptoms, such as: magnesium, glucosamine, and curcuma.
The use of medicinal products to relieve pain and inflammation (painkillers and/or anti-inflammatory drugs) whether for application on the affected area or for oral intake, should be advised by the pharmacist.
Sudden-onset and severe muscle pain should be evaluated by the doctor.
Sources
iSaúde
Farmácia Distribuição Magazine
Também lhe poderá interessar
Nervous system
Preventing sciatica - A matter of nerve
Muscles






