Medicines and Devices
Antibiotic and Doctor an inseparable combination
Antibiotics are drugs used to eliminate microorganisms, namely bacteria, which cause infections, such as cystitis (urinary tract infection), tonsillitis, ear infections or more serious conditions, such as meningitis and encephalitis.
However, they only act against infections caused by specific bacteria which are sensitive to the action of a certain antibiotic and therefore, not all of them are able to fight the various infection situations. For example, they are not effective against other infections caused by viruses, parasites or fungi. For those agents that also cause diseases, there are specific medications, such as antivirals, antiparasitic and antifungal agents, respectively.
What are bacteria and viruses?
Bacteria and viruses exist everywhere in nature.
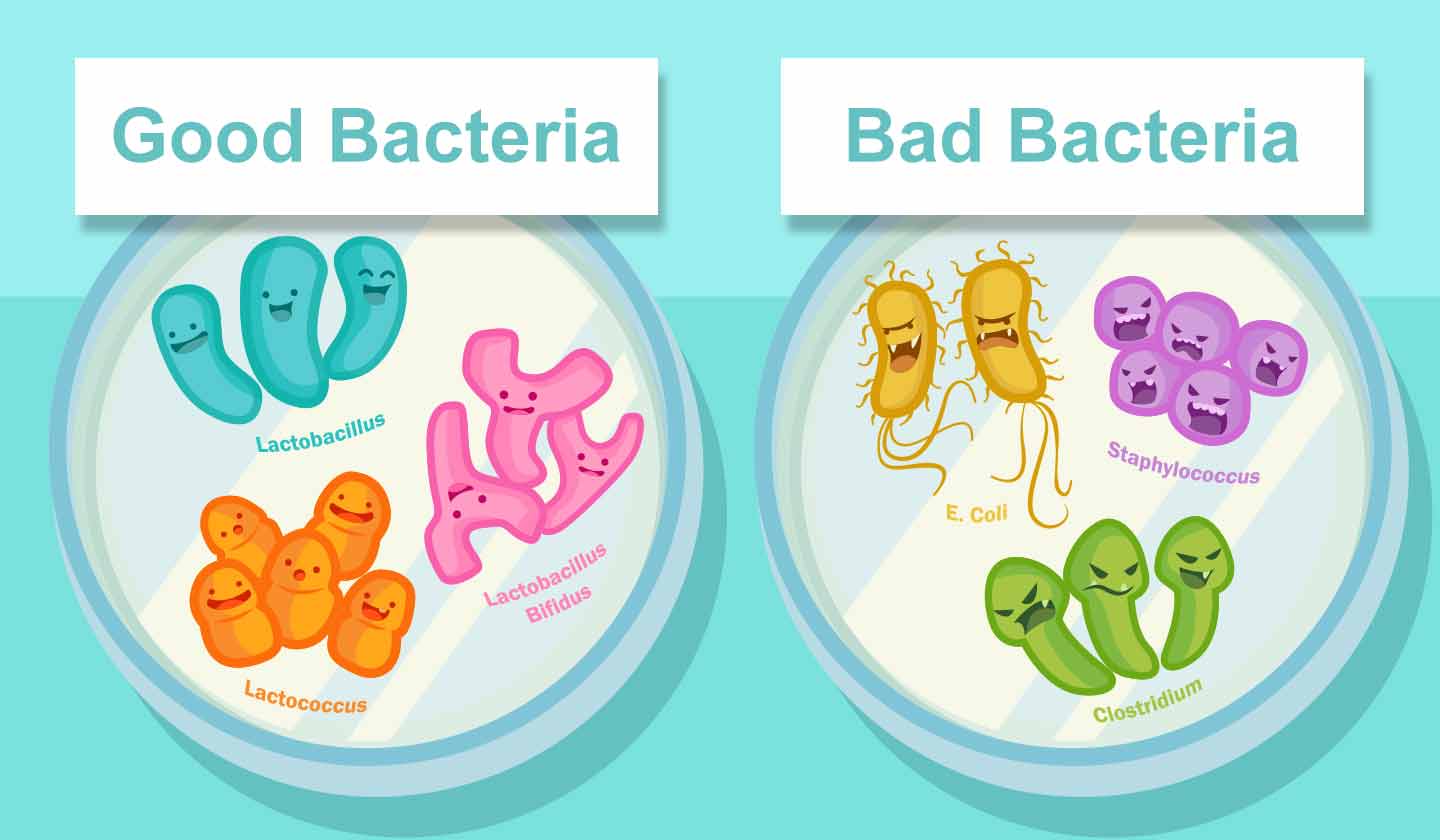
Bacteria are microscopic living beings made up of a single cell. Our body has usually as many bacteria as human cells. Most of them do not have any harmful effect, and when they do, they cause mild diseases and can even contribute, for example, to the manufacture of cheese or yoghurt. They multiply quickly, every twenty minutes.
Viruses are simpler living beings, only visible under the electron microscope (which has much more magnifying power than the traditional microscope). To multiply, they need to infect other cells.
What is the risk of using antibiotics?
The indiscriminate use of antibiotics can cause a phenomenon called bacterial resistance, which is caused by the use of substances in the composition of these drugs that have a higher bacterial elimination power than would be necessary.
This allows the possibility for some bacteria to resist treatment with these same antibiotics in the future, thus rendering the medicine ineffective. In addition to making treatment more difficult, it can also affect other bacteria that usually help our bodies to function properly, and that are mostly present in the intestine.
The fact that bacteria become resistant to the antibiotic is normal and expected in medical treatments, but the way antibiotics are indiscriminately used can accelerate the time it takes for these microorganisms to become resistant and stop responding to treatment. Antibiotics are not able to act on viruses.

When should we use antibiotics?
Antibiotics are prescription drugs that require a medical prescription. Only a doctor can indicate the most appropriate medication, dosage and treatment time for each case.

What precautions should be taken when using antibiotics?
- Use antibiotics strictly, that is, as prescribed by your doctor or as indicated by your pharmacist. Comply scrupulously with treatment duration and administration times. If you happen to miss a dose, start over as soon as possible.
- Do not use antibiotics left over from previous treatments or from other people. If you have leftovers at home, deposit them in the ValorMed container at your pharmacy.
- When you have a fever, headache or sore throat do not use antibiotics right away. Most fever situations are caused by viruses and they break in 3 to 4 days. When in doubt, talk to your doctor or call the Portuguese Health Helpline SNS24 - 808 24 24 24.
- Cook meat and fish well, avoid eating them raw. The heat inactivates the residues of antibiotics that may be present in these foods. Wash vegetables well to eliminate possible residues.
- Wash your hands thoroughly before meals, after using the bathroom, after touching surfaces of public use or being in contact with animals.
- In hospitals, health centres, dialysis units, day centres, homes for the elderly and nursing homes, always wash your hands after contacting patients or residents or surfaces.

António Hipólito de Aguiar
(Pharmacist; University Professor)
Também lhe poderá interessar
Urinary tract
A constant urge to urinate can be desperate
Drugs and devices






