Prevention and treatment
Insect bite? After the slap comes torment
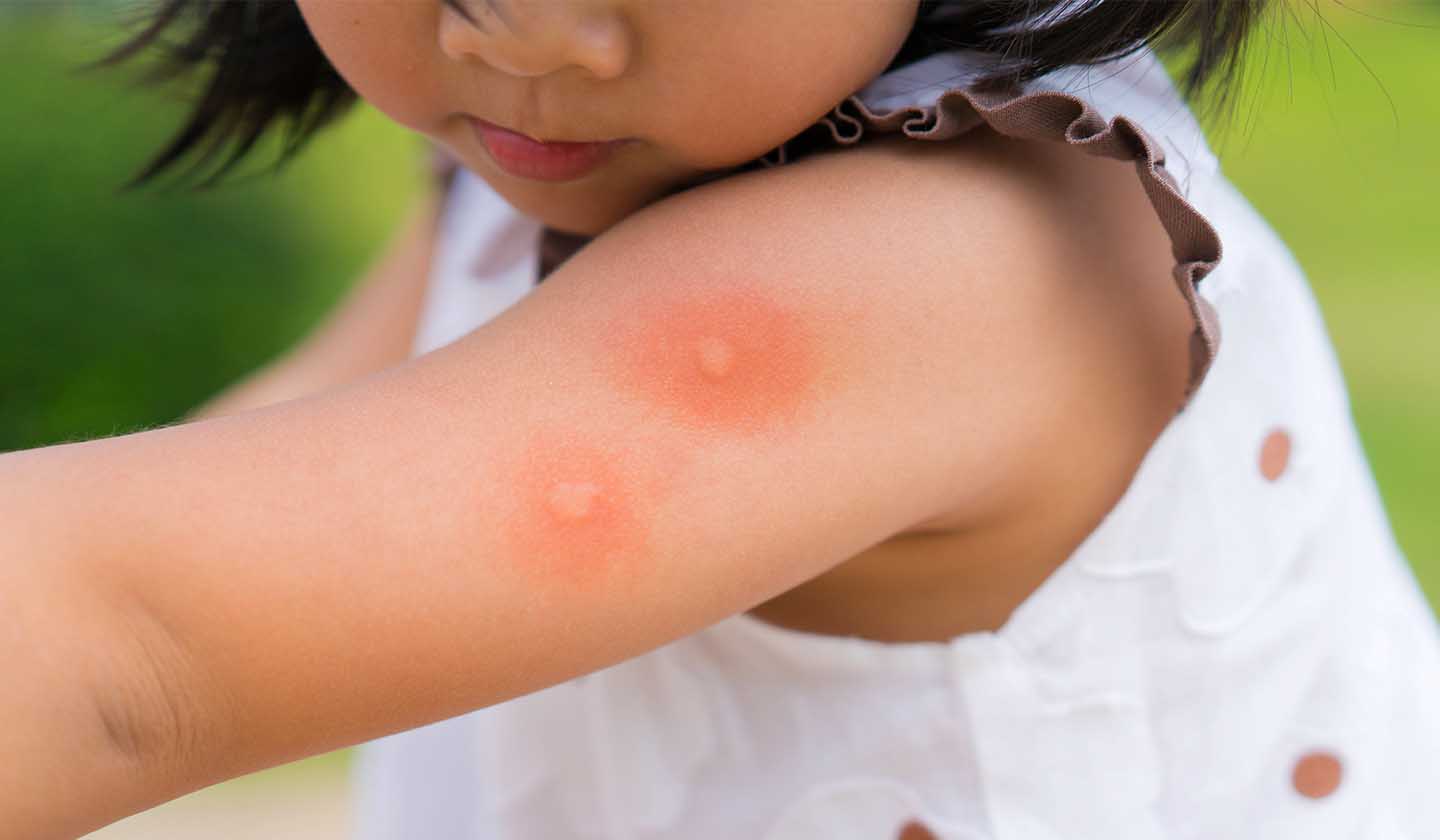

As the temperature rises, insects come up and chasing them away is always a challenge. Sometimes it is not possible to avoid their bites. They are not usually serious, but they can cause discomfort or transmit diseases such as malaria, dengue, and yellow fever, especially in endemic regions.
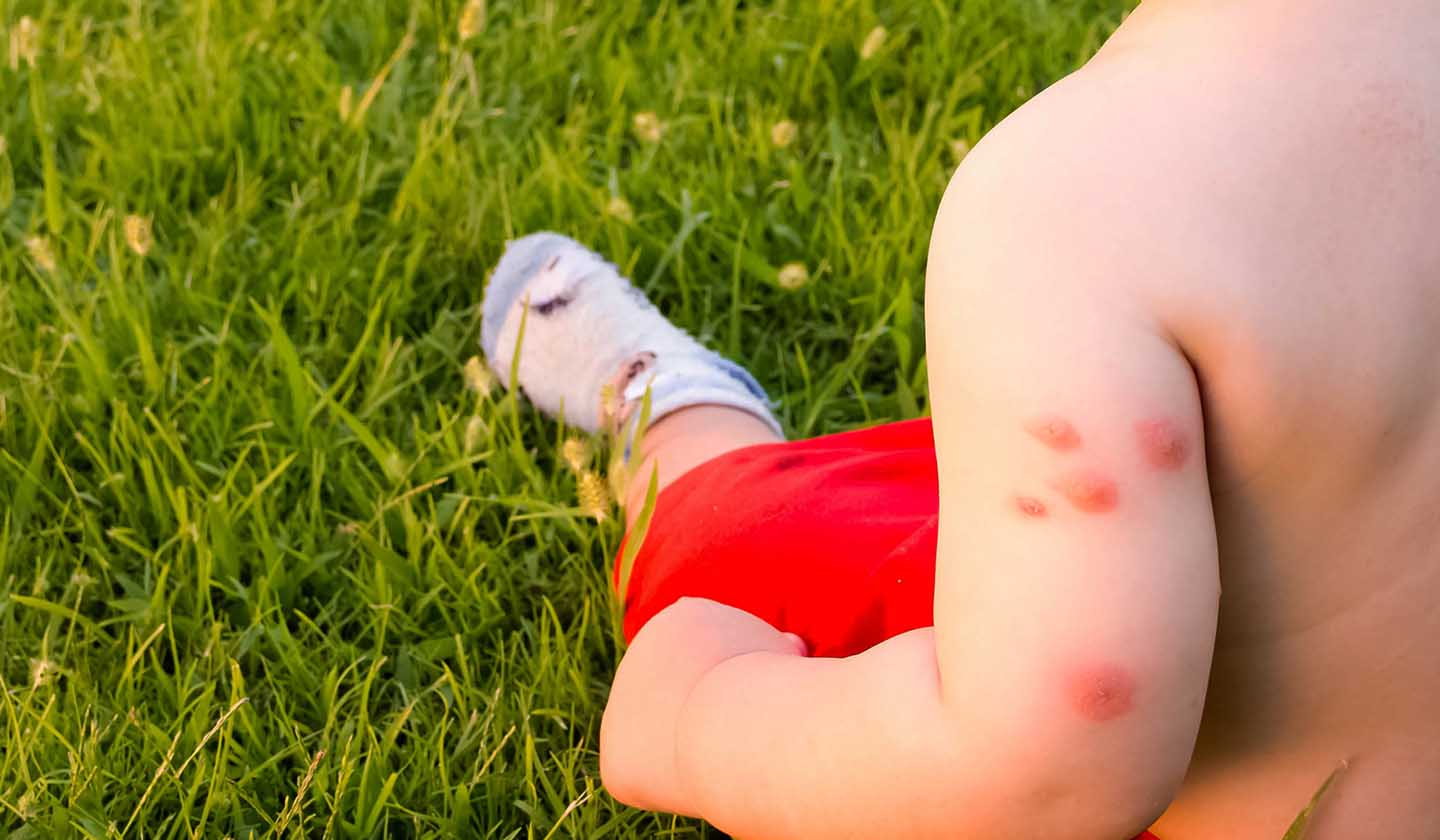

Symptoms
Some insect bites are not felt until a few hours later, but they can be bothersome and painful.
Skin symptoms associated with insect bites are:
-
Swelling;
-
Itching;
-
Redness;
-
Pain.
Usually, a local allergic reaction occurs (the area of skin around the bite or sting becomes swollen).
However, some people may develop a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis), a rare situation in which red spots appear on the body, swelling of the tongue and throat, pain, difficulty in breathing and swallowing, dizziness, and nausea.
Treatment
The symptoms caused by the insect bite (pain, swelling, itching) can last for a few days. There are some measures that can help minimize discomfort.
What to do?
-
In case of wasp stings, remove the sting with tweezers;
-
Wash the sting area with cold water and soap;
-
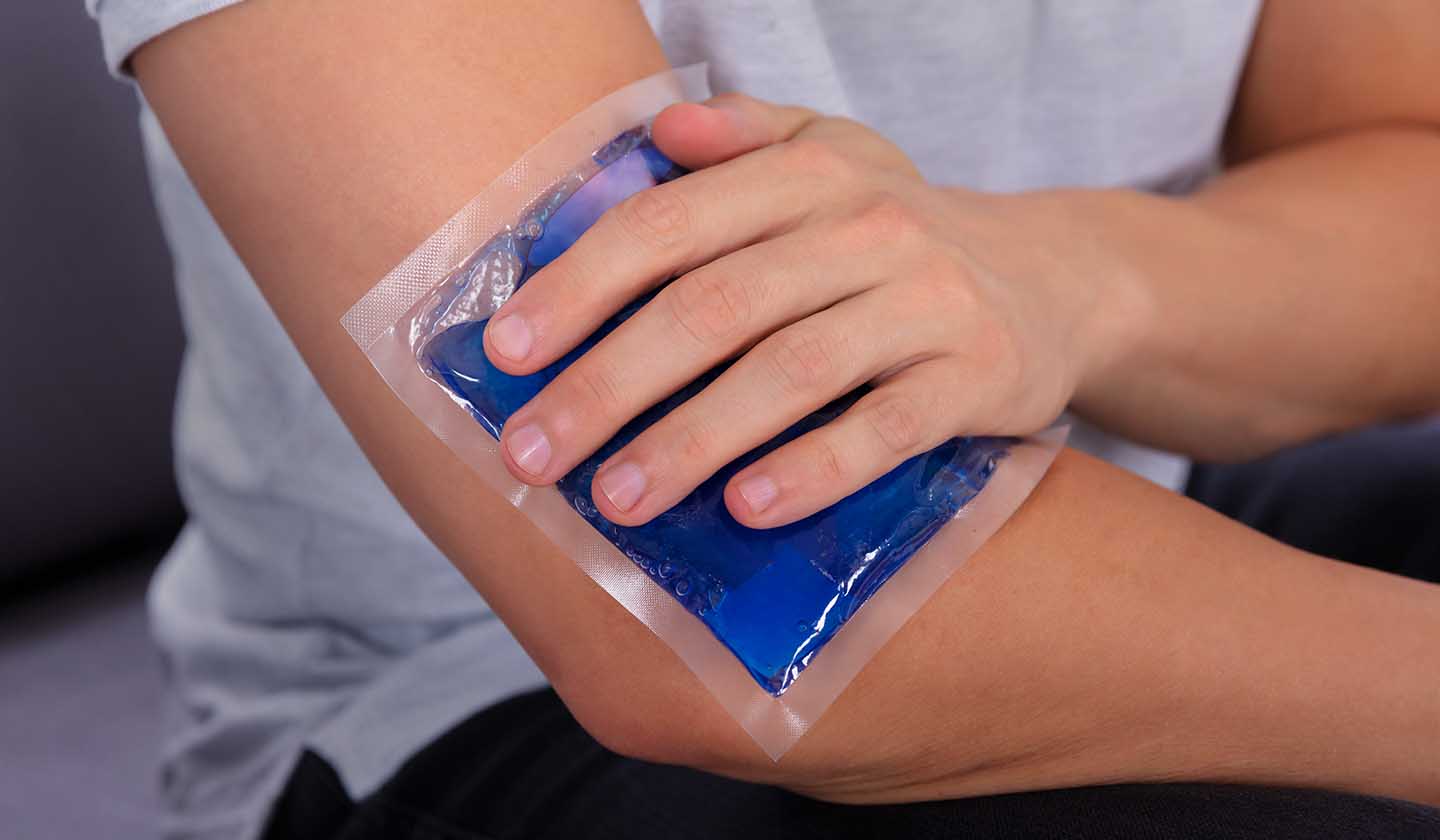
Apply an ice bag or cold compresses on the spot to relieve pain and itching (for 10 minutes);
-
If possible, keep the affected area in an elevated position, as it helps to reduce swelling;
-
In case of pruritus (itching) symptoms, you can apply a topical antihistamine to calm it down;
-
You can apply thermal water on the affected area (as it softens and soothes the skin);
-
Avoid scratching the area and/or bursting the blister (to reduce the risk of infection).
Pain symptoms can be relieved with a painkiller (such as paracetamol).
If the itching is severe, you can opt for an oral antihistamine for relief.
When inflammation associated with insect bites occurs, the use of a topical corticosteroid may be indicated.
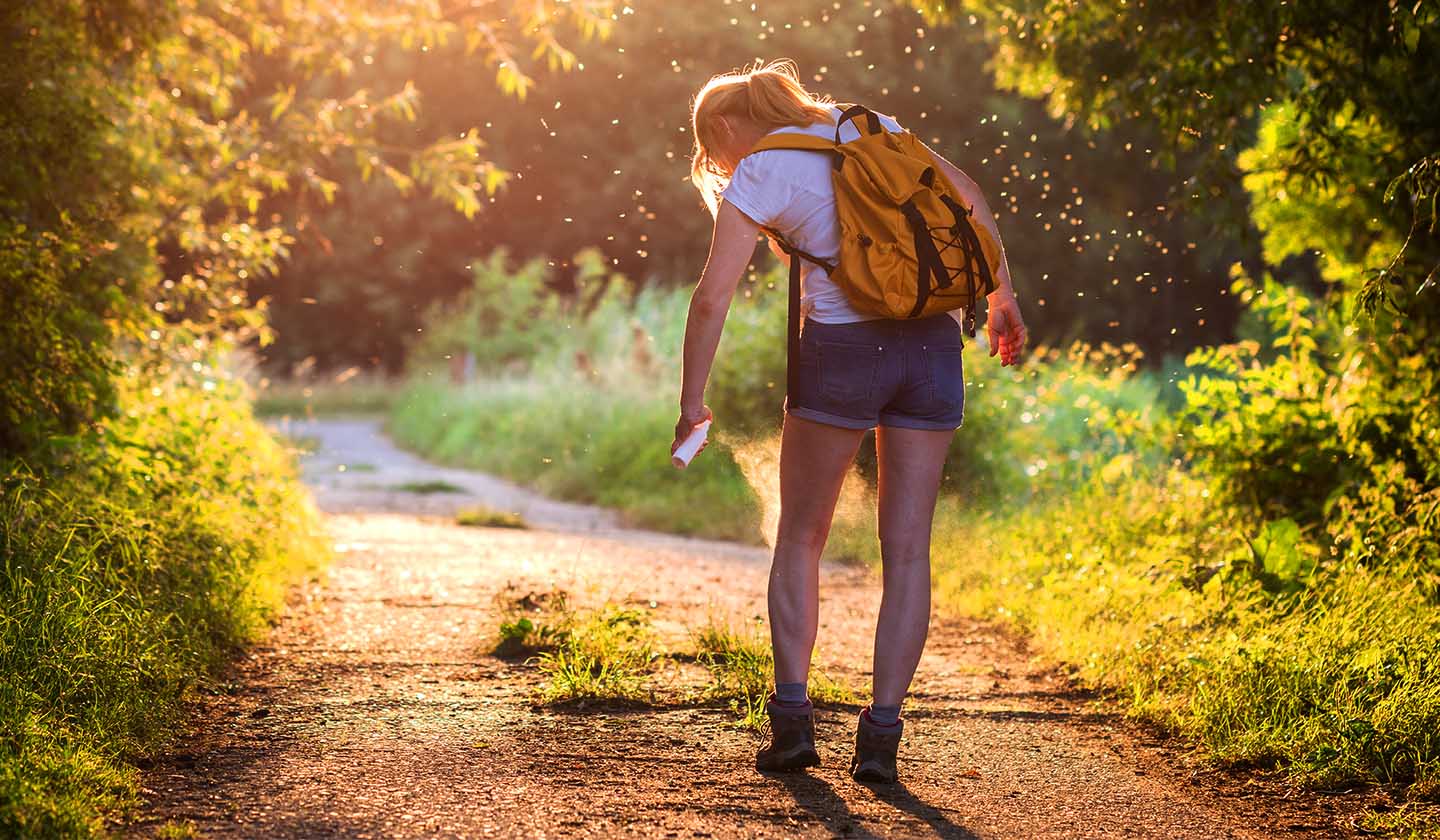

Preventing insect bites
To reduce the risk of an insect, bite some measures can be considered.
What to do:
-
When wasps or bees appear, keep calm, and move away slowly without swinging your arms;
-
Apply insect repellent on the exposed areas of your body (arms, legs, ankles, neck, and face);
-
In tropical regions, apply a bug spray every four hours;
-
Avoid using perfumes and cosmetics (deodorant, moisturiser, among others) with strong smells, as they can attract insects;
-
Stay away from flowering plants, trash, and stagnant water (where mosquitoes breed);
-
Opt for light coloured clothing and wide pieces that cover arms and legs;
-
Protect doors and windows with mosquito nets or, if these are not available, just keep them closed.
-
Avoid going out at dawn and dusk to places with vegetation or close to rivers, lakes, and dams;
-
Keep food and drinks covered when you are outdoors.
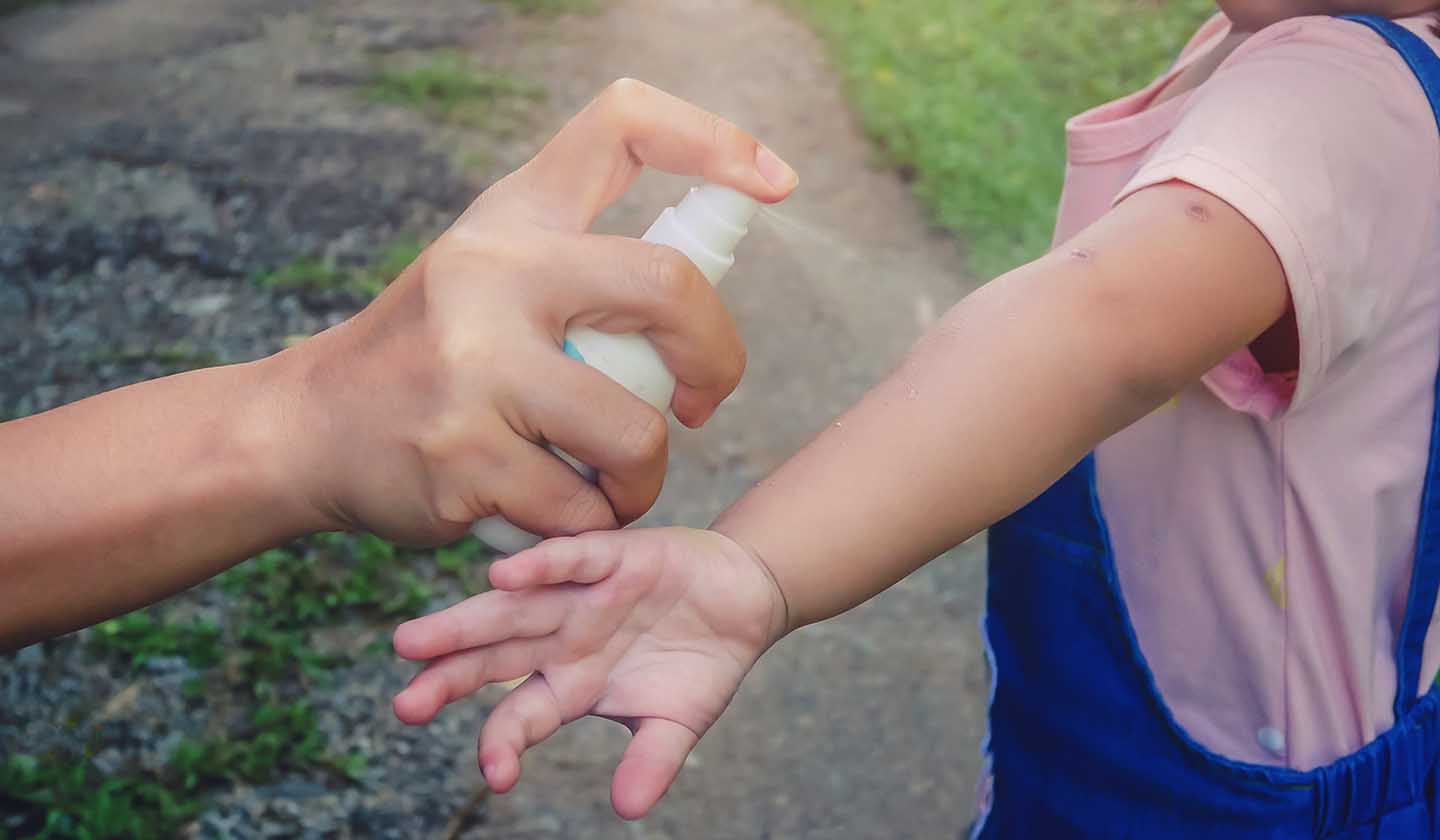

Using insect repellents safely
The repellent prevents insects, such as mosquitoes and others, from approaching, providing protection for a few hours. They are available in the form of bracelets, roll-on, spray, adhesives, wipes, and cream.
For the correct and safe use of insect repellents, please note:
-
Apply to exposed skin and over clothing;
-
Do not put it directly on the face;
-
Do not apply on wounds or irritated skin;
-
Avoid contact with the mouth and eyes;
-
Reapply according to the manufacturer's instructions;
-
If you are using sunscreen, apply it before the repellent.
As for children, choose an age-specific repellent, which should always be applied by an adult. If the repellent contains DEET (diethyltoluamide) or icaridine, the concentration should not be greater than 10%.
Are you going on a travel? Extra care to be taken
If you are travelling to countries where there is a high risk of contracting a serious disease through an insect bite (such as malaria or yellow fever), go to a travel medicine consultation. In this consultation you will be advised on how to plan your trip in terms of health care (vaccines, medications, and necessary care) and you can clear up any doubts you might have.
Sources
iSaúde
Farmácia Distribuição Magazine
Também lhe poderá interessar
Dermatology
Mycosis? Let's get on with it
Prevention and treatment






