Allergies
Urticaria - To nettles with it
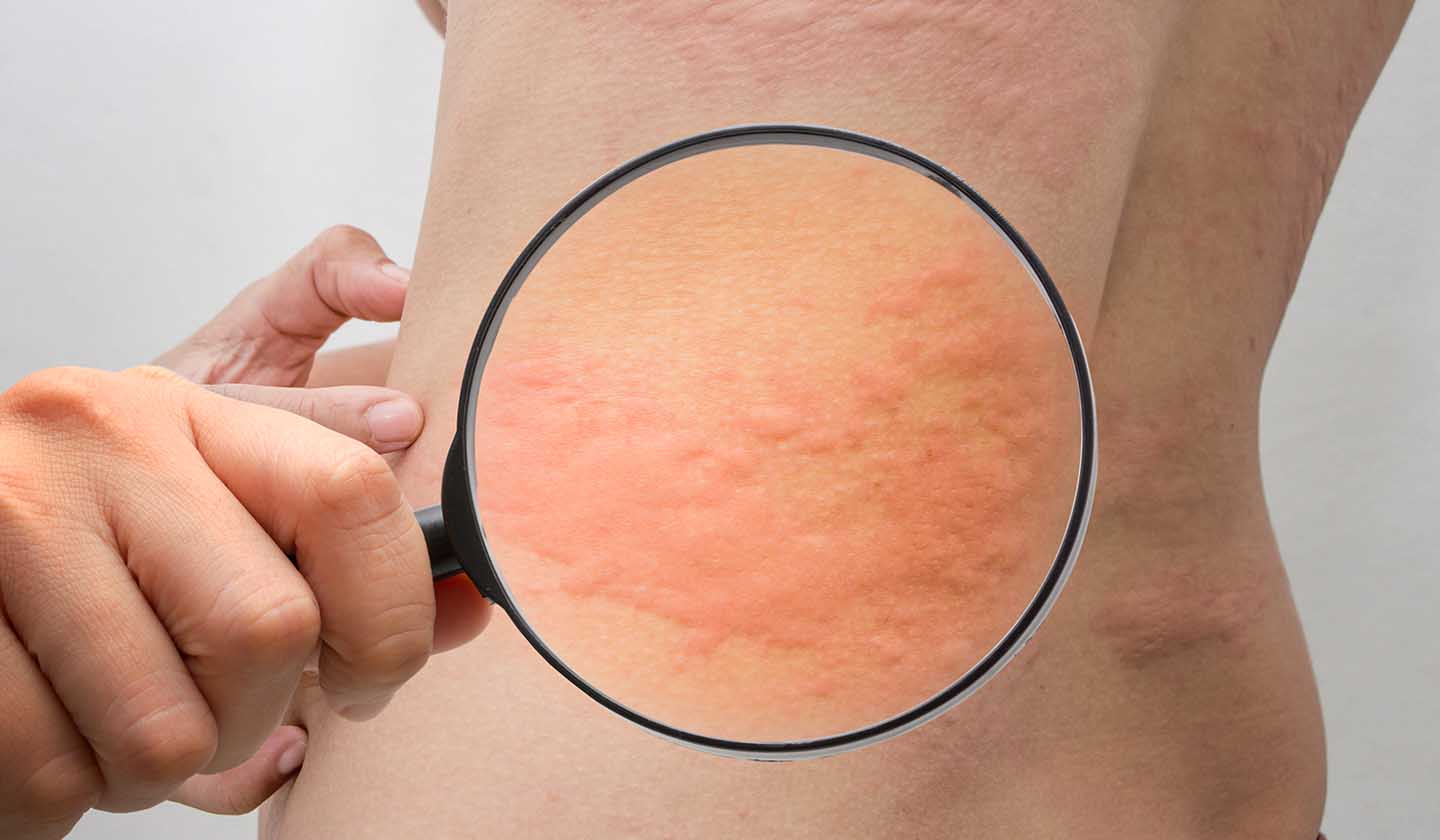
When itching arises it is not always easy to control. The situation can be more uncomfortable when it is accompanied by swollen reddish spots.
The quality of life can be influenced by both the discomfort caused and the negative impact it can have on the person’s looks.
This situation is an allergic reaction that arises as the response of the body to an allergen (factor that causes allergy).
What is urticaria?
Urticaria is an allergic reaction with symptoms at the skin level characterised by acute (lasting less than 6 weeks) or chronic rash (lasting more than 6 weeks).
Despite causing a lot of itching (pruritus), sometimes unbearable, it does not cause pain. It can appear anywhere on the body.
Urticaria can be classified according to its triggering factors:
- Contact urticaria - it appears immediately after skin contact with a substance (food, cosmetics, medicines, latex);
- Physical urticaria - it appears after exposure to physical factors (pressure, heat, sunlight);
- Cholinergic urticaria - it occurs when there is a slight increase in body temperature (stress, physical exercise, a hot bath);
- Spontaneous chronic urticaria - it is characterised by the sudden appearance of raised reddish lesions on the skin lasting for more than six weeks.
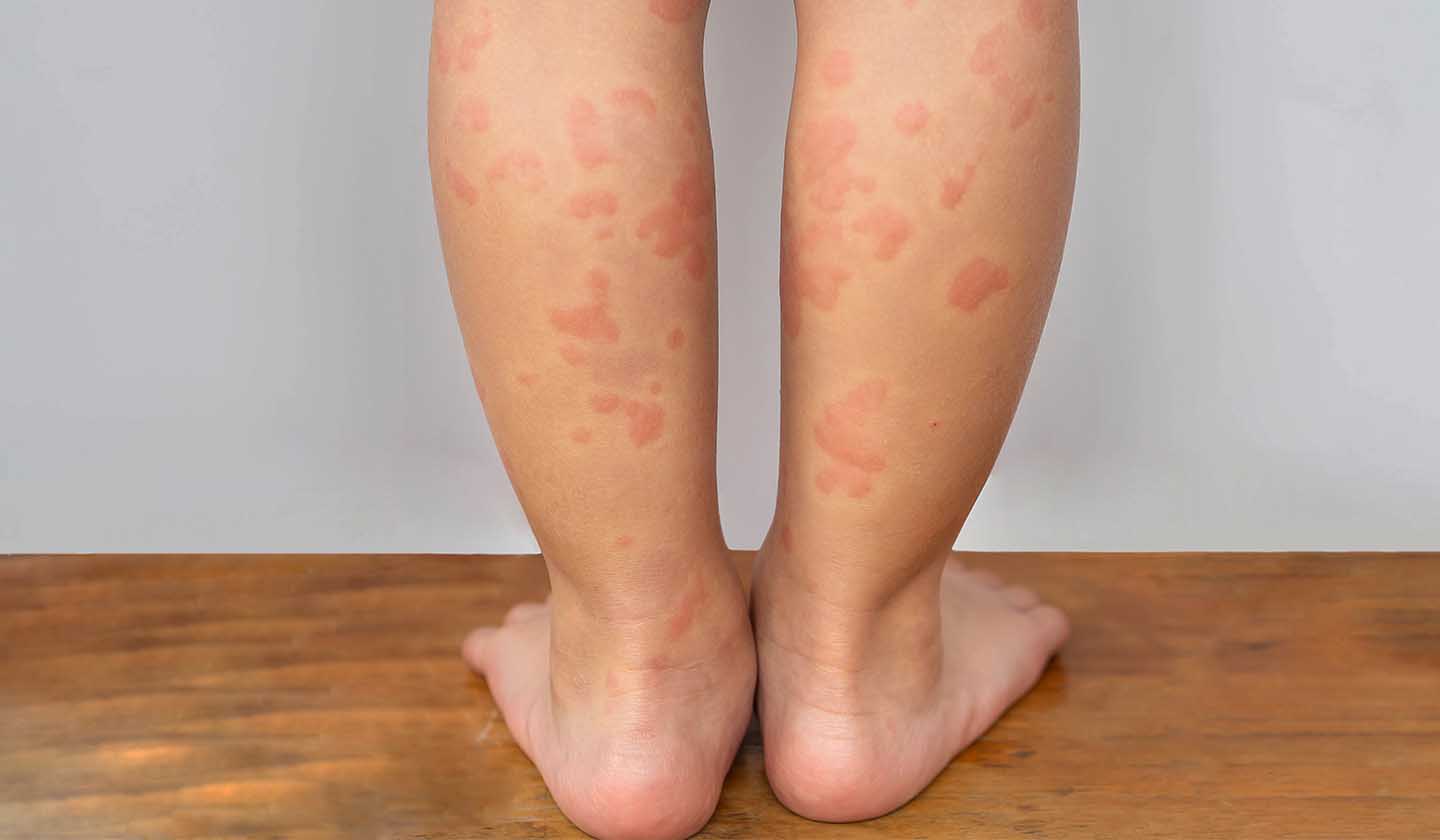
Clinical manifestations
Urticaria is characterised by the appearance of red bumps on the skin, very varied in shape and size, accompanied by intense itching.
The spots tend to disappear spontaneously in 2 - 3 hours (it can take up to 1 day), without leaving marks on the skin.
Usually, when the spots disappear, new spots appear in other areas of the body.
Causes of hives:
Urticaria may appear occasionally in the presence of an allergen (element that triggers an allergic reaction) or it can be a chronic spontaneous pathology, that is, for no specific reason.
Some factors can contribute to the appearance of hives:
- Food (nuts, eggs, cow milk, seafood, chocolate, fruits, mushrooms, among others);
- Medicines: any medication can cause hives. The most frequent being penicillin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (for example: ibuprofen), diuretics;
- Insect bites;
- Pollen, mites;
- Tobacco smoke;
- Contact with chemicals;
- Latex;
- Exposure to the sun, heat, cold, water;
- Infections (respiratory infections such as sinusitis, tonsillitis, and parasites);
- Physical exercise;
- Emotional changes (stress).
In situations of spontaneous urticaria it is not possible to predict when it will occur, since there is no specific triggering factor.
If it is found that urticaria arises following a specific situation, such as eating a certain food, exposure to the urticaria triggering factor should be avoided.

Treatment
The first step of treatment is to avoid or eliminate the factors that trigger urticaria.
During an attack, treatment aims to relieve symptoms, especially to relieve itching.
In mild and moderate cases, the 1st line treatment is the use of 2nd generation oral antihistamines (the so-called “anti-allergy” that do not cause drowsiness as a side effect). These drugs relieve itching (pruritus) and prevent the formation of red bumps.
In more complex or severe cases, it may be necessary to include cortisone in the treatment.

Advice for relieving discomfort
- Bathing with tepid water (avoid hot water as it increases itching);
- Avoid wearing too many layers of clothes and avoid tight clothing. Opt for light and loose clothing;
- Apply a moisturising cream for sensitive skin daily, preferably without perfume (as it helps prevent skin dehydration);
- Use a shower gel for sensitive skin;
- You can apply thermal water to the affected area (as it softens and soothes the skin);
- Keep calm. Hives are not caused by stress, but stress can make hives worse.
What should you avoid doing?
- Scratching the reddened areas;
- Bathing in hot water;
- Wearing tight clothing;
- Exposing to factors that can trigger hives;
- Exposing to tobacco smoke (which is irritating to the skin).
Keep in mind that:
If urticaria spreads throughout the body and is accompanied by pain, fever and / or difficulty breathing or swallowing, immediate medical care should be sought.
Sources
iSaúde
Farmácia Distribuição Magazine






