Bones and joints
When do we think we are rusty? That's arthrosis
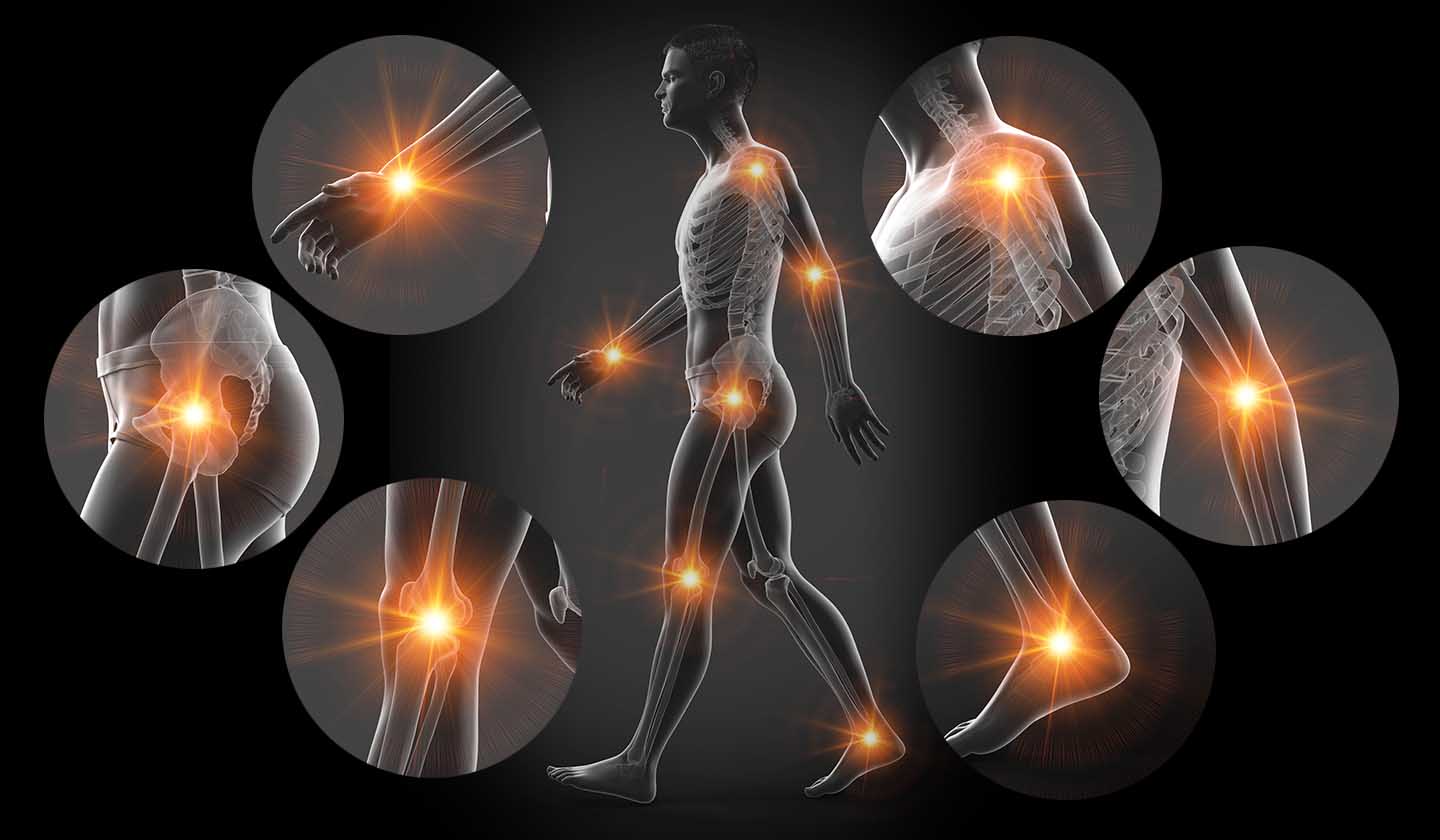
Osteoarthritis, or simply arthrosis, is a condition that mainly affects the articular cartilage, an elastic connective tissue found at the ends of the bones that articulate with each other.
The articular cartilage is nourished by the joint or synovial fluid, promoting joint lubrication, and allowing the cartilages to slide without causing friction (wear). When the cartilage is worn out, there is friction between the bones and the movements can be painful.
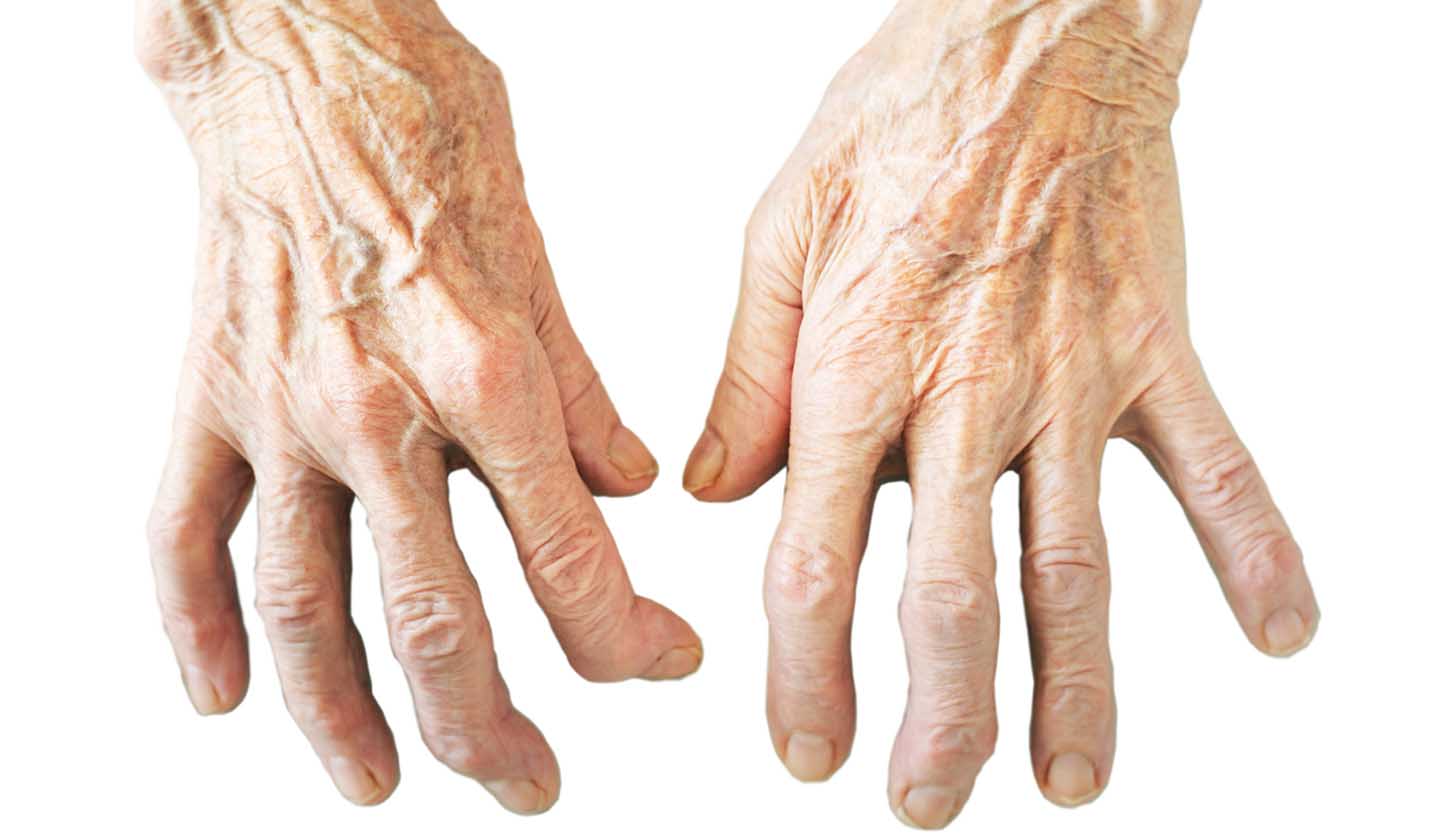
In osteoarthritis, the cartilage is injured, and the bone underneath (subchondral bone) reacts to this injury by getting thicker. These bony projections are called osteophytes, also known as "parrot beaks", and they are frequent in the spine.
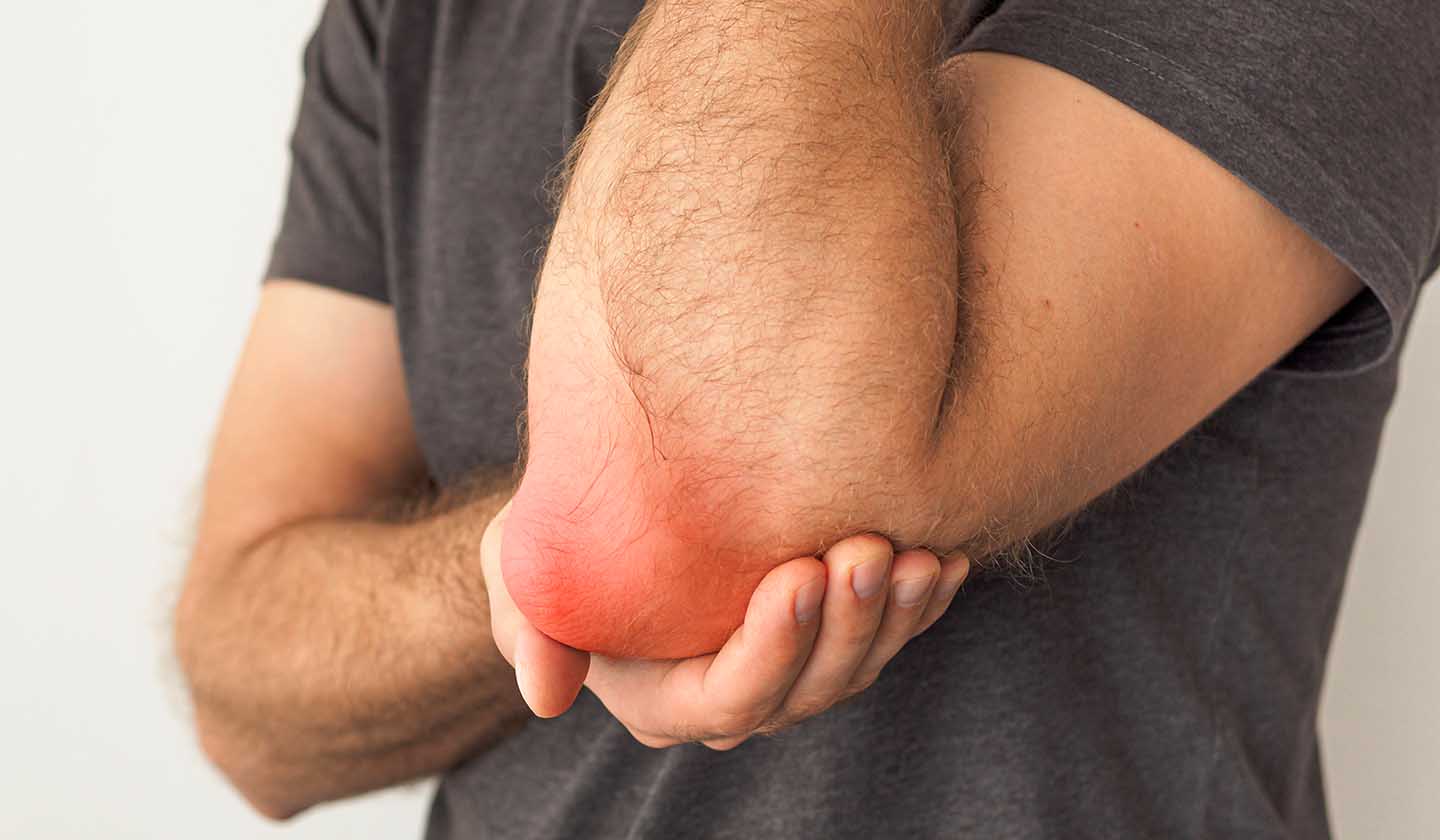
Symptoms:
Healthy cartilage allows bones to slide smoothly over each other during movement. Osteoarthritis occurs due to cartilage damage and leads to the appearance of different symptoms, such as:
-
Pain
-
Joint swelling and inflammation
-
Joint stiffness, especially in the morning
-
Loss of joint mobility
-
Increased joint volume
-
Joint deformation
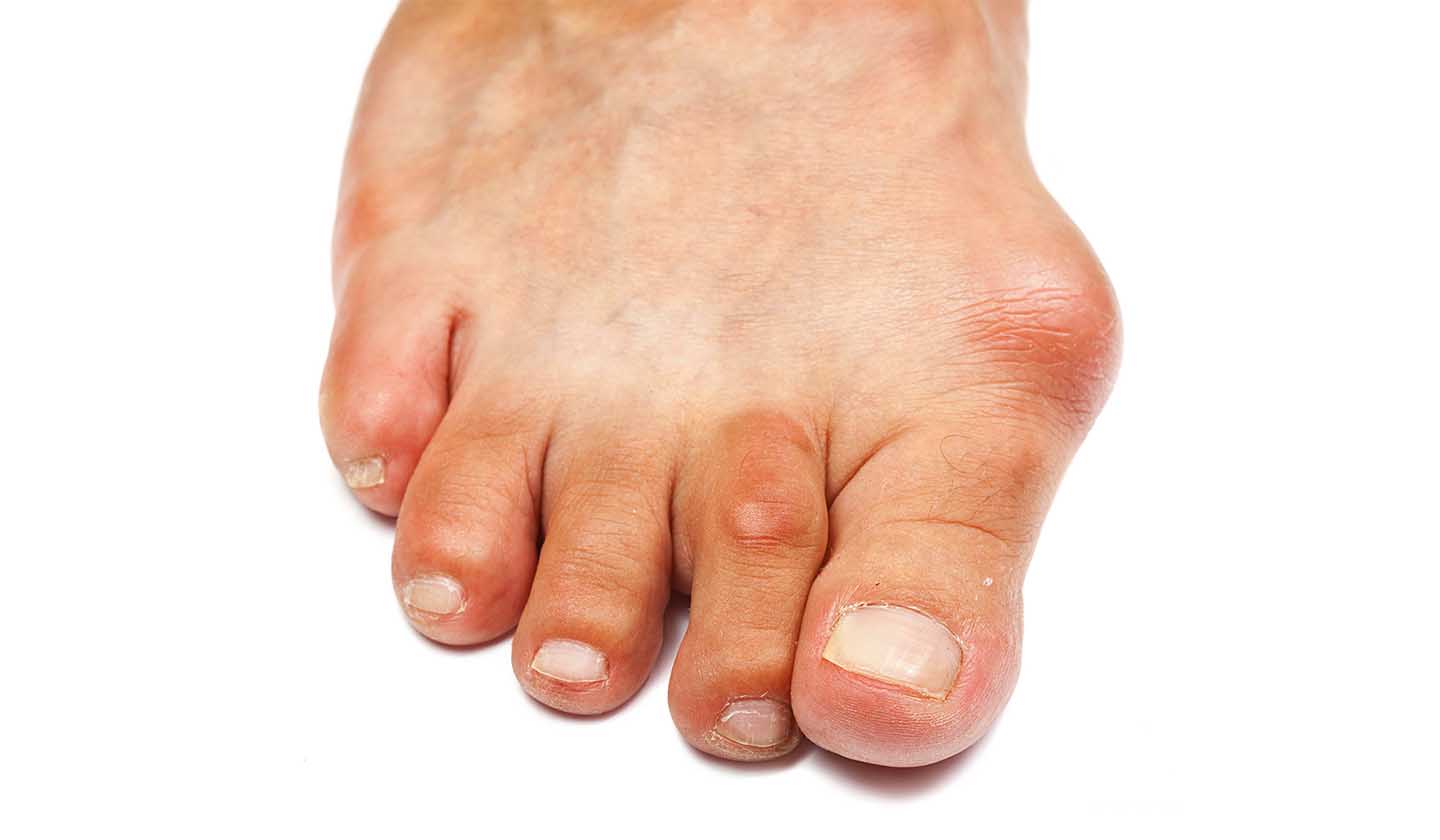
Risk factors:
Osteoarthritis affects functional joints, such as those of the hands, knee, hip, spine, and foot, being one of the main causes of disability.
-
Age > 50 years
-
Genetic factors
-
Female sex - menopause
-
Obesity
-
Sportsmen and sportswomen
-
Overload - incorrect movements and postures
-
Trauma/joint injury
-
Metabolic and endocrine disorders
-
Inflammatory joint diseases
Prevention/treatment
-
Weight loss
-
Rest
-
Sedentary lifestyle - Whenever your work involves sitting for long periods of time, you should avoid incorrect postures.
-
Physical exercise -strengthens periarticular muscles, increases range of motion, and decreases friction between bones, thus relieving pain and reducing inflammation.
-
Orthoses - externally applied devices used to correct or prevent structural joint deviation, promoting the function of the body. There are several types of orthoses (available at your pharmacy) that splint joints and can reduce pain and inflammation.
-
Technical aids for movement - aids used to reduce effort, for instance, walking sticks, crutches, walkers, and bath supports.
-
Moist heat - decreases muscle spasm and protects the skin, avoiding local burns by direct contact. Can be applied several times a day for periods of 10 minutes and with a minimum interval of 2 hours.
-
Balanced diet - rich in the necessary nutrients and promoting a healthy weight. This diet should be rich in fibres, vegetables, and greens, and also include fish, lean meats, and dairy products.
-
Clothing: should be simple and practical, avoid wearing tight clothes, back zips, or small buttons.
-
Shoes: wear resistant 3-4 cm high heels shoes, choose shoes with wide toe caps and insoles made of material that reduces the impact when walking (you can find these at your pharmacy).
-
Food supplements - either alone or in combination, such as certain vitamins (K, C, D and E), minerals (calcium, magnesium, zinc, phosphorus and manganese), omega 3 and curcuma, can relieve pain symptoms and prevent the worsening of the structural injury.
-
Drugs:
-
-
Painkillers and/or anti-inflammatory drugs are used to relieve pain and inflammation; these drugs are available as creams, lotions and gels, so they can be applied directly to the affected region, and they can also be found in the pill form.
-
Glucosamine sulphate and chondroitin sulphate stimulate the production of cartilage components, relieve pain and function, and may have a beneficial effect on structural damage. These medicinal products should be taken for long periods of time given that their effect is not immediate.
- Hyaluronic acid injected in the joint to help lubricate it.
-
- Physiotherapy and hydrotherapy - therapeutic exercises alleviate discomfort and promote mobility.
- Surgery - in patients with knee or hip arthrosis, where treatment was not effective, who experience major physical limitations in their daily activity.
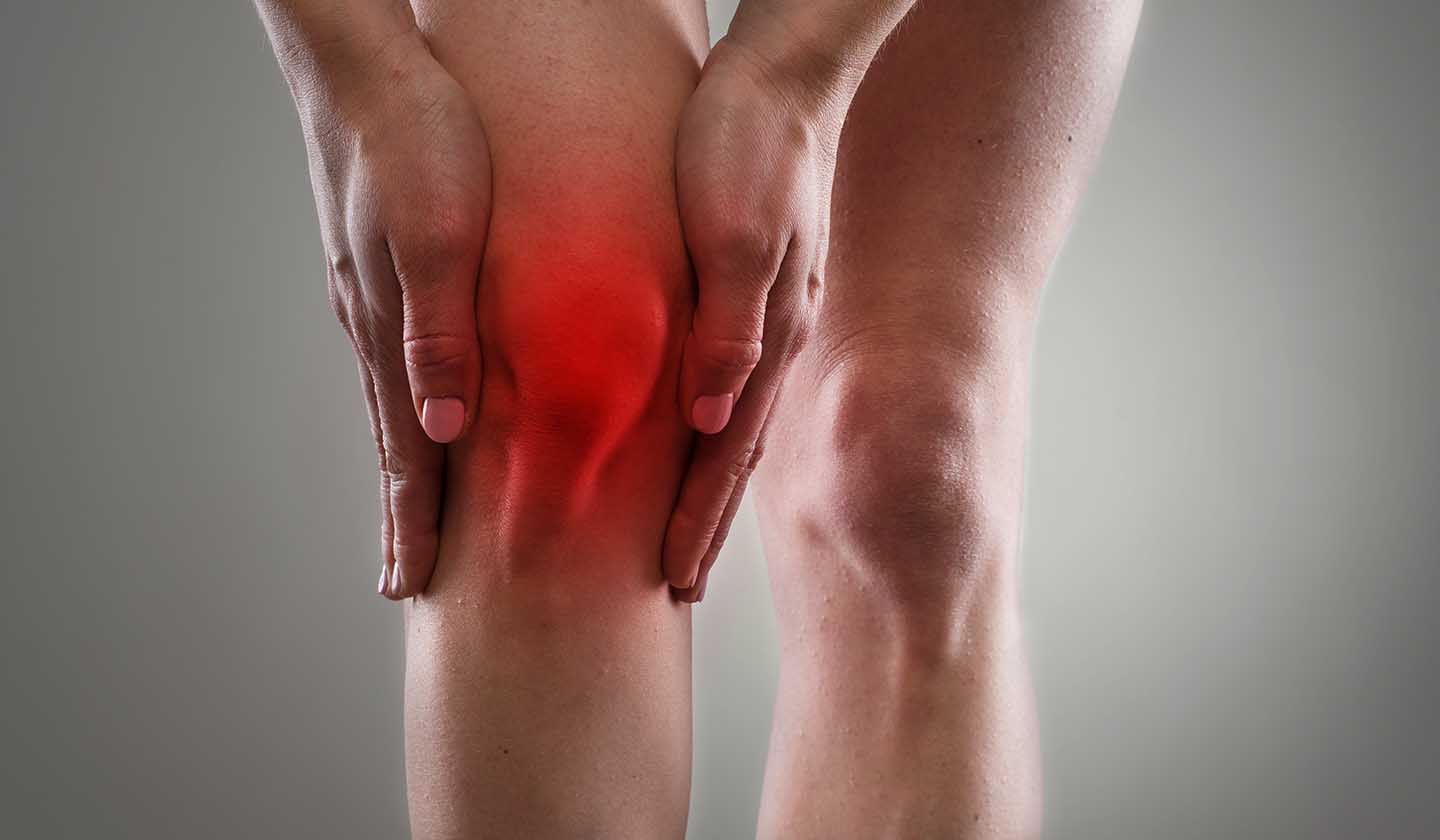
Osteoarticular pain can be associated with inflammation (arthritis). In case of severe pain and sudden swelling the patient should be immediately referred to the doctor.
Sources
iSaúde
Farmácia Distribuição Magazine
Também lhe poderá interessar
Bones and joints
Heel spur - On tiptoes
Bones and joints