Bones and joints
Gout - A guessing finger
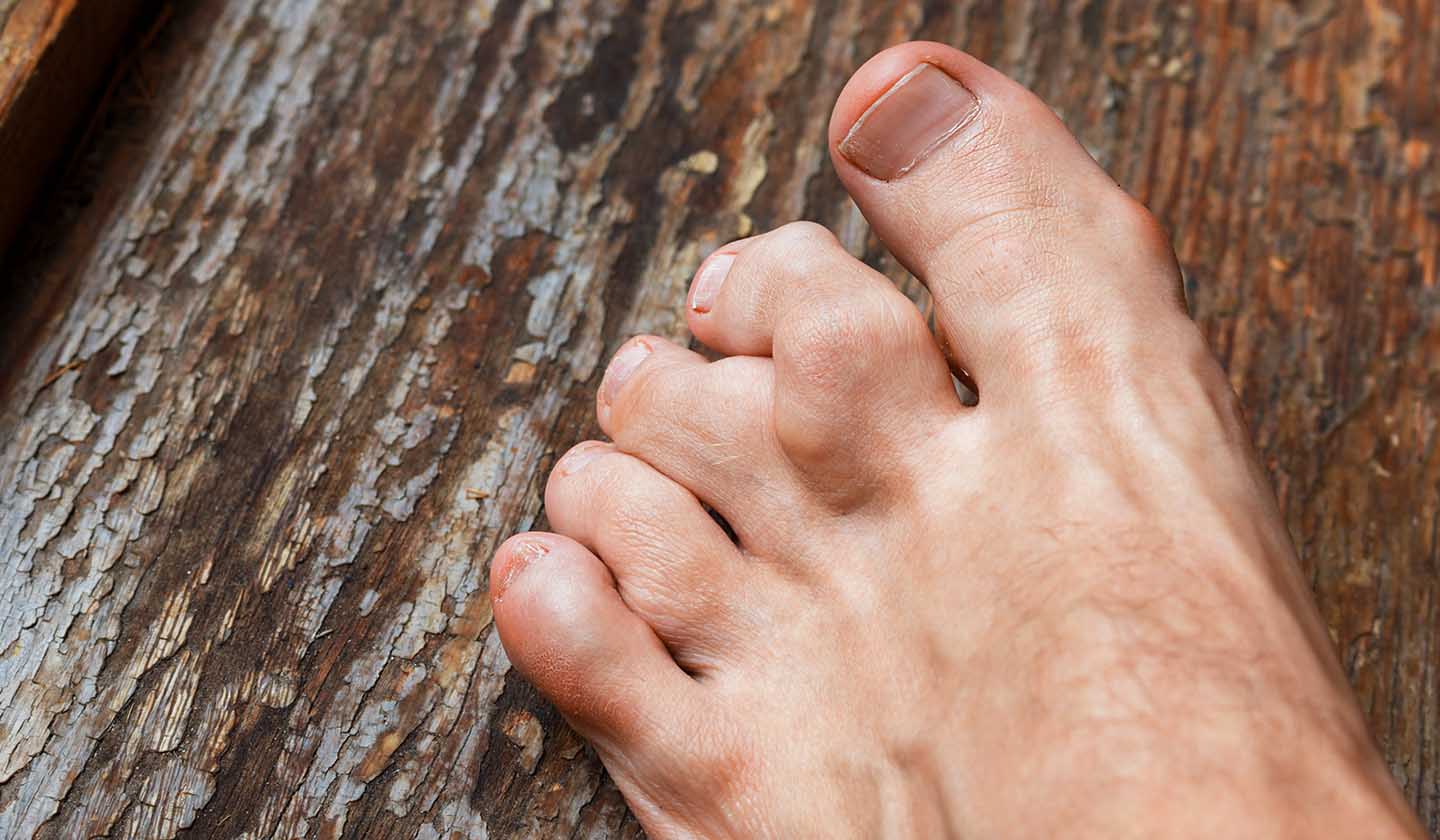

Gout is an inflammatory rheumatic disease that results from hyperuricemia, that is, from excess uric acid in the blood and from its accumulation in the joints in the form of sodium monourate crystals (similar to needles).
Gout appears as a sudden and intense pain in the joints, particularly in the big toe. Its prevalence is higher in men and it is a cardiovascular risk factor, which can trigger serious diseases. In addition, it can cause disability.
Risk factors:
- Genetics
- Food, especially if it is rich in red meat, offal, and seafood;
- Excessive consumption of alcoholic beverages (mainly white drinks and beer)
- Medicines that interfere with the natural excretion of uric acid by the body (e.g., some diuretics)
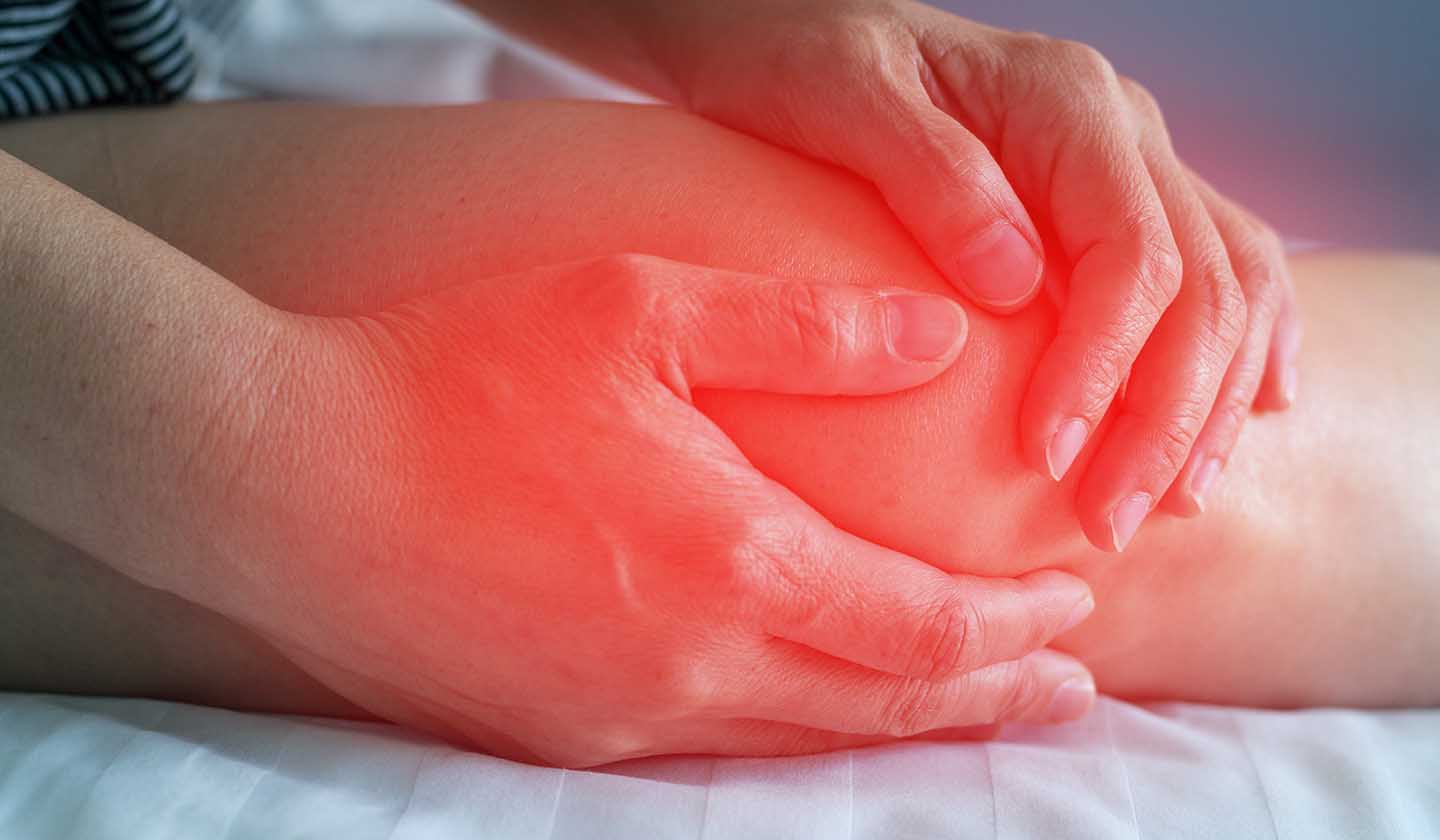
Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms vary depending on the stage of the disease and include:
- Pain
- Fever
- Inflammation in the joints, with heat, redness, and oedema (swelling), particularly in the lower limbs (feet, ankles, knees), but also in the upper limbs (hands, wrists, and elbows)
- Kidney problems (renal calculi, known as “kidney stones”, and kidney failure) and metabolic problems (e.g., hypertension)
Stages of the disease:
- Initial stage: In this stage, gout may not present any symptoms
- Crisis: Over time, inflammation appears, intermittently, with symptoms in the affected joints, it can last 1 or 2 weeks
- Chronic: In the absence of treatment, in the long term, chronic gout installs itself, with continuous symptoms, without interruption, with the presence of tophi (agglomeration of crystals) in the joints, which can cause deformations of the hands, feet, elbows and knees. In an advanced state, gout can affect bones and kidneys.

Prevention / Care:
- Avoid being overweight
- Balanced diet
- Avoid purine rich foods (e.g., viscera, sausages, seafood, young animal meat)
- Drink water (> or = 1.5L)
- Consume lean milk and dairy products (they reduce uric acid)
- Practice physical exercise regularly
- Avoid alcoholic beverages
- Avoid certain medications and supplements that increase uric acid
- Control uric acid levels: these can be determined through a blood test, quick test, done at your pharmacy (finger prick where a drop of blood is drawn)
These precautions help to control the risk factors for uric acid and also bring a better metabolic control, reducing the risk of other diseases and improving the quality of life.

Treatment
The treatment main goal is to control the acute gout crisis and prevent it from recurring. To this end, the following care may be prescribed:
- medicines that relieve joint pain and inflammation (anti-inflammatory drugs)
- medicines to lower uric acid
- rest
- applying ice (e.g., reusable gel bags)
- food supplements to help prevent uric acid accumulation and others that help to eliminate it from the body (e.g., artichoke, vitamin C, omega 3, heather and bearberry)
To find out what is the most appropriate care for the prevention and treatment of gout, talk to your pharmacist.
Sources
iSaúde
Farmácia Distribuição Magazine
Também lhe poderá interessar
Bones and joints
When do we think we are rusty? That's arthrosis
Urinary tract






