Viruses
Solutions for Molluscum contagiosum
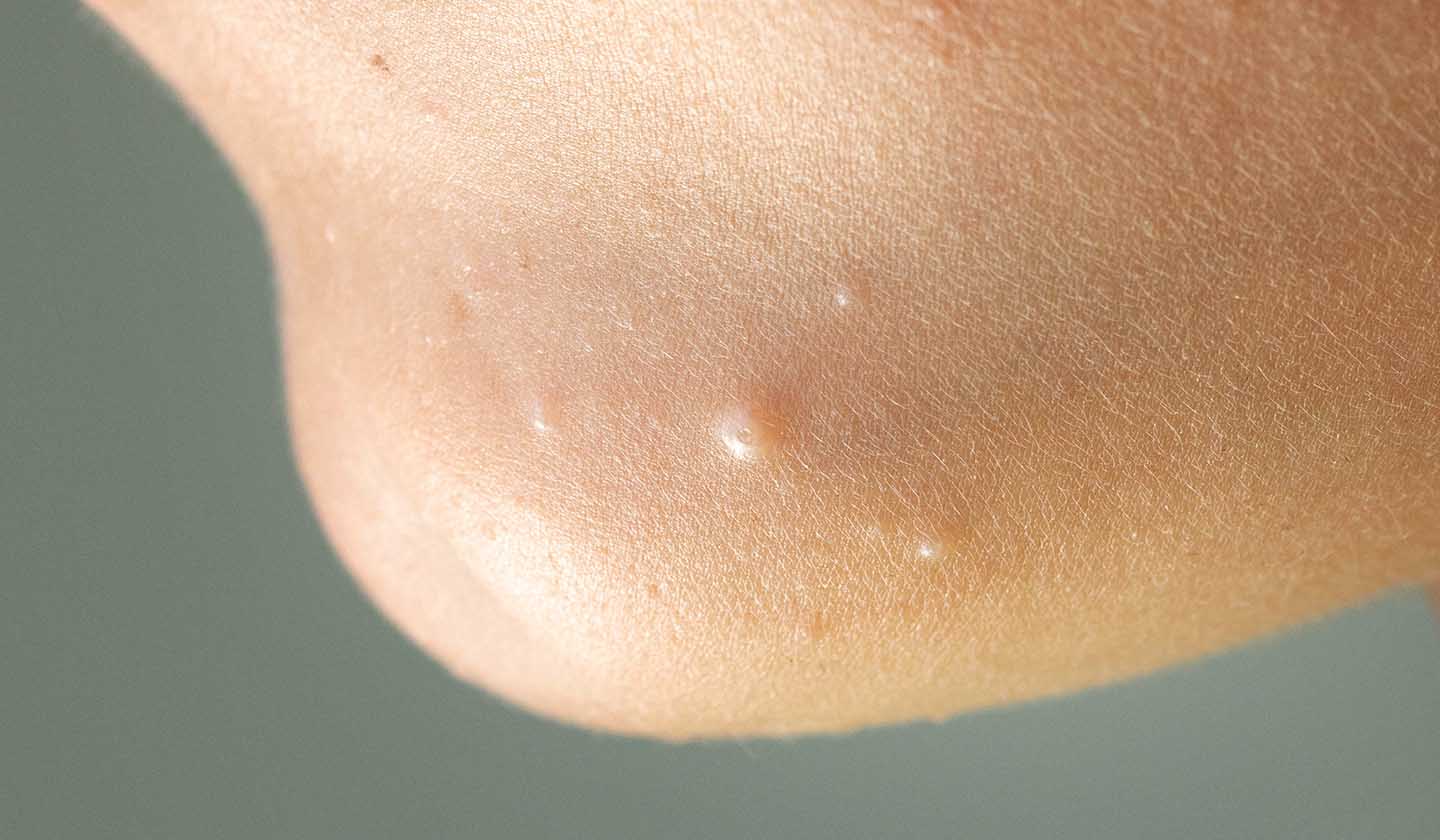
Molluscum contagiosum is a benign disease, characterised by the infection of cells on the skin surface by a virus of the family Poxviridae (smallpox family).
Molluscum contagiosum is common in children, especially those with eczema and atopic skin. It can also appear in individuals with a weakened immune system (e.g., chemotherapy, HIV ...).
Molluscum contagiosum is a self-limiting infection whose lesions, in some cases, may not even need specific treatment. Even where treatment is required, the healing of injuries, despite being an uncomfortable and sometimes prolonged process, is total and complete. In most severe situations, there is bacterial superinfection.
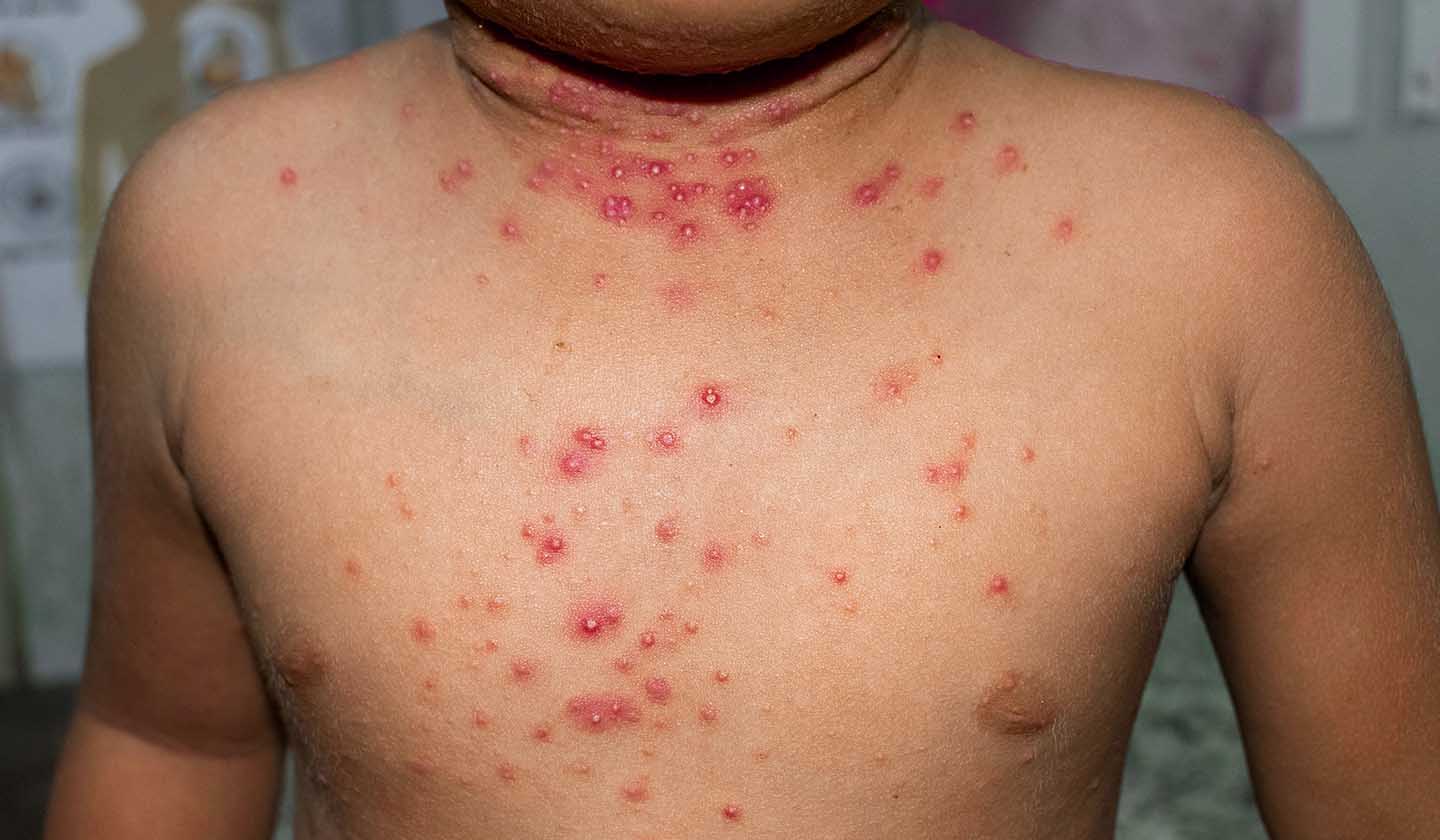
Transmission
Direct contact is the most common form of transmission for this type of infection.
It usually occurs in humid environments such as swimming pools or changing rooms, as moisture softens the skin and facilitates the penetration of the virus.
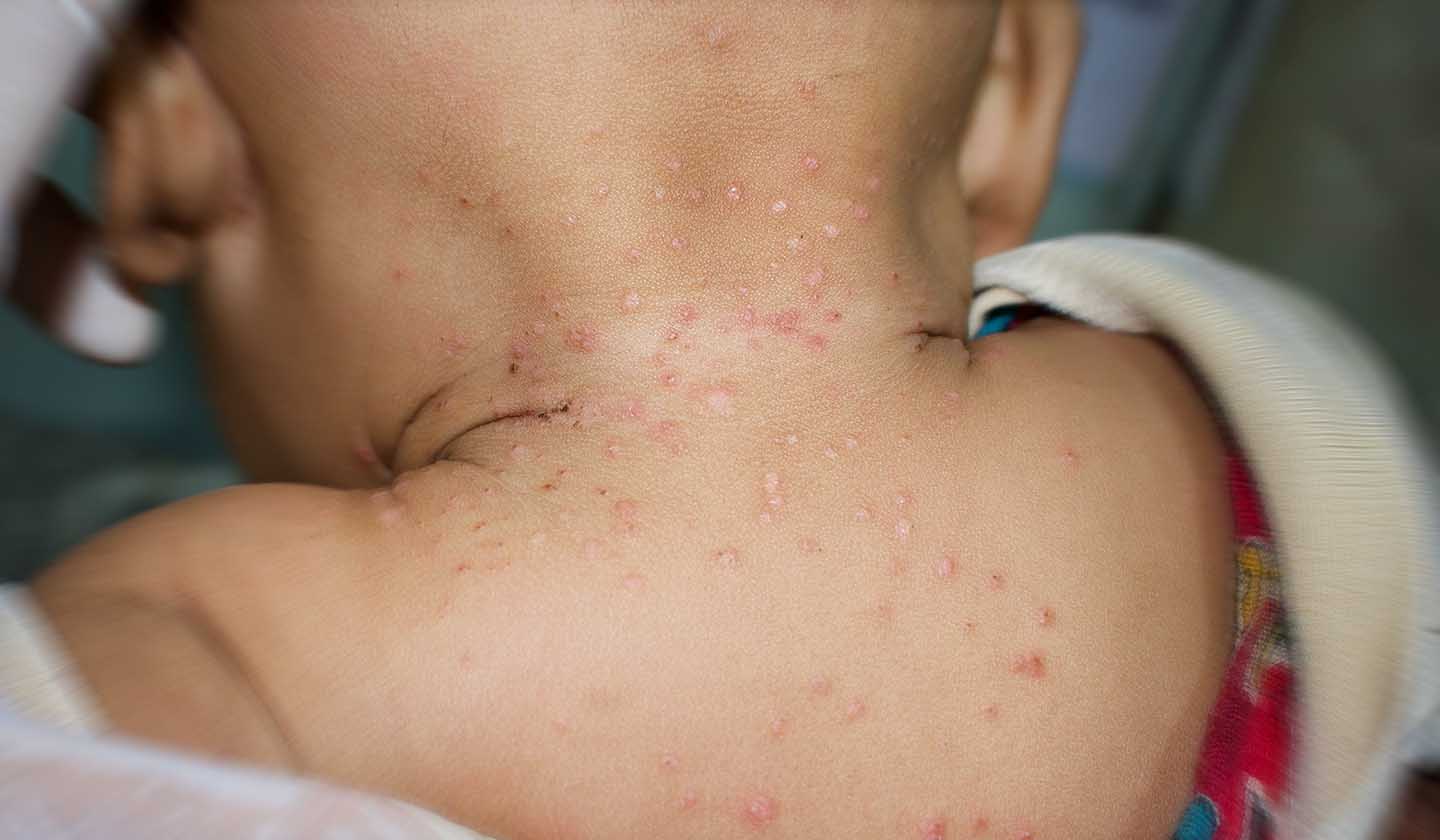
Signs and symptoms
Molluscum contagiosum
- It takes the form of small bumps or papules (similar to pearls), filled with a jelly-like, sticky fluid
- It can be white, pink, or yellow coloured
- It is painless and does not cause itching
- It is usually located on the trunk, arms, and legs, but can affect any area of the skin
- The size varies between a pinhead and 5 mm
- Injuries can be isolated or grouped, the number ranging from 6 to 10
- The appearance of lesions in the anal and genital areas does not mean there was sexual transmission. It may simply mean a self-inoculation event has occurred.
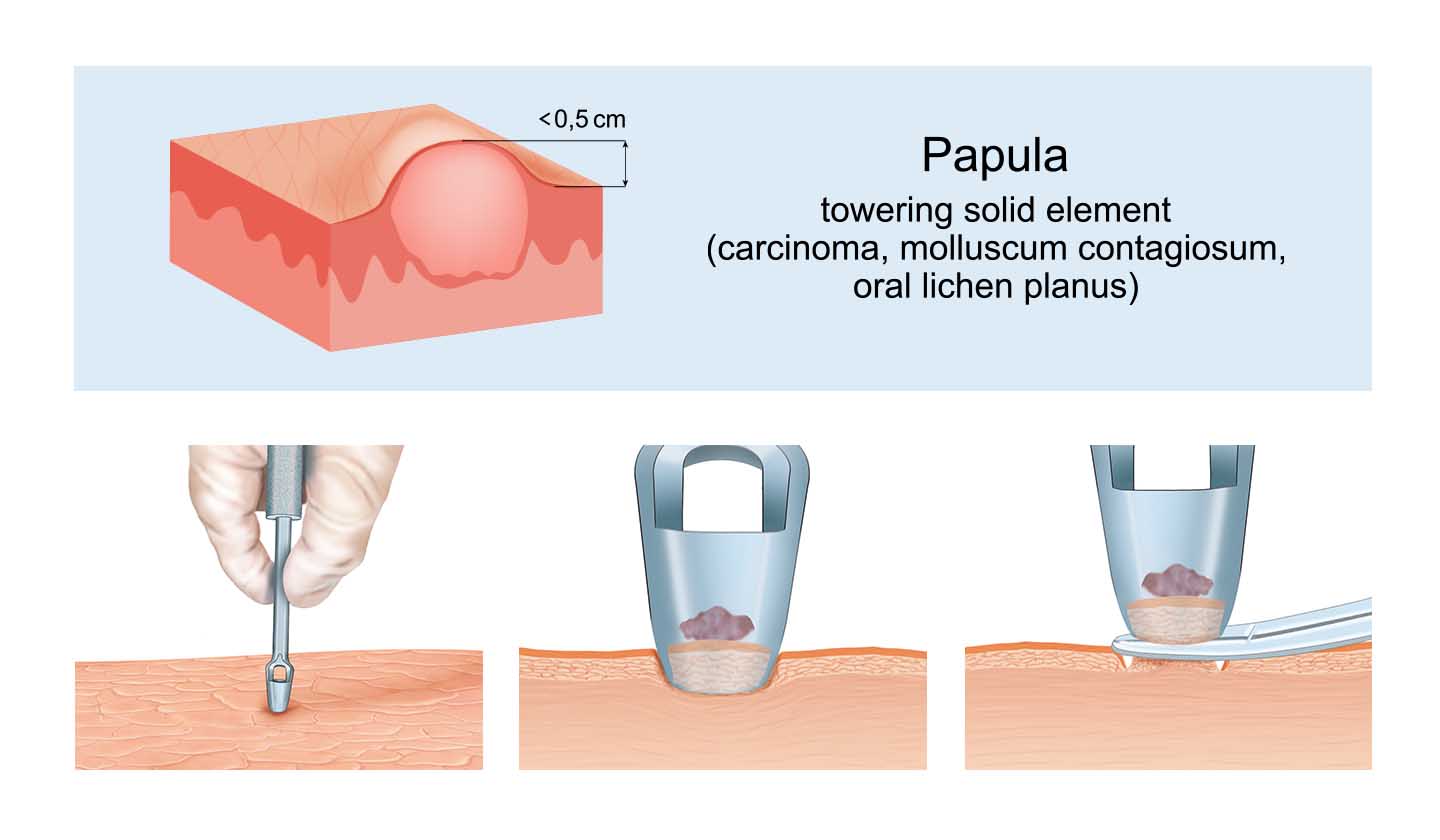
Treatment
First-line treatment - application of creams and / or lotions containing substances such as salicylic acid, lactic acid, potassium hydroxide, retinoic acid (vitamin A), among others to destroy molluscum
Surgical removal:
- Scraping
- Freezing
- Electrosurgery - extraction of the central core with a needle, using local anaesthesia through the application of anaesthetic creams
Prevention:
- Keep lesions clean and dry using antiseptic products
- Avoid direct contact with the skin lesions of an infected person
- Do not scratch / scrape
- The treatment of eczema in children helps to prevent the spread of molluscum contagiosum, therefore, you should:
-
- Avoid warm and lasting baths
- Use hypoallergenic shower gel
- Keep your skin hydrated - use specific creams for atopic skin
- Avoid sharing towels, bathing suits, bath sponges
- Avoid swimming pools and saunas
- To avoid sexual transmission, prevention should include the use of condoms
- Children do not need to stop going to school or nursery, however, the papules must be covered (e.g., with dressings) to reduce the risk of transmission
Talk to your pharmacist and find out what is the most appropriate care in the prevention and treatment of Molluscum contagiosum, as well as in the care of atopic skin.
Sources
iSaúde
Farmácia Distribuição Magazine






