Prevention and treatment
Are you travelling? Prepare before travelling

Travelling is an increasingly common practice these days, whether for professional, leisure or humanitarian reasons. Planning your trip is important so that you do not have to face unforeseen events, particularly regarding your health.
If you are chronically ill or undergoing treatment at the moment, many doubts related to the transport and storage of medication, adherence to therapy and the medication schedule may arise.
Write down some general recommendations for a more organized planning:
-
Make a detailed list of the medicines you take on a daily basis;
-
Make sure you travel with enough medication for the length of your trip; Include extra medication supplies to cover for any incident (for example, medication loss, possible travel delays or other event that makes you stay a few days longer at your destination);
-
Check if the expiration date of the drugs is compatible with the length of the trip;
-
Carry the medication in their original packaging with the respective labels;
-
If your medication requires the use of syringes, take enough syringes with you as well as a medical justification, if needed;
-
Take the medical prescriptions with you and make sure the name of the active substance can be read, as well as the dosage, pharmaceutical forms, and administration method (useful in the security check at the airport);
-
When you arrive at your destination, store medicines in a dry, cool place, away from heat and humidity (for example, the bathroom is not a suitable place).
If you are going by plane...
When flying, some precautions must be taken to carry medicines with you. If you are going to travel abroad, make sure you know the legal requirements for the transport of medicines, because there are countries with specific lists of restricted medicines, such as the United Arab Emirates, India, Pakistan or Turkey.
Travelling by plane with your medications requires you to:
-
Make a travel kit with your medicines, which can be carried in a hand luggage so that you can access them during the flight, if necessary;
-
Include extra doses of your medications in the hold baggage. However, be aware that extreme cargo hold temperatures can damage certain medications, so make sure your medications are not affected;
-
If you are travelling with someone else split the medication to minimize loss or theft;
-
Liquid medicines should be carried in bottles, in a transparent plastic bag, so that they can be opened by the authorities (for content checking). The medication must be accompanied by the respective prescription or doctor's declaration;
-
The transport of insulin, test strips, blood glucose meters, lancets, needles, and syringes is authorized in hand luggage;
-
Insulin must not be transported in the hold bag, as the extreme cold will denature the protein contained in insulin.
-
Medicines that need to be stored in a cool place (between 2 to 8.º C), must be transported in a refrigerated isothermal bag.
During your travel, make sure you follow the regular schedule of your medication.
In case of time zones changes, ask your doctor about the best way to adjust therapy.

If you are travelling by car...
When travelling by car, you should pay attention to the following aspects:
-
Do not put medications in the glove compartment or in the luggage compartment (as high temperatures may damage them) ;
-
Medicines that need to be stored in a cool place (between 2 to 8.º C), must be transported in a refrigerated isothermal bag.
-
If high temperatures (higher than 25.º C) are expected, medicines should be transported in non-refrigerated isothermal bags.
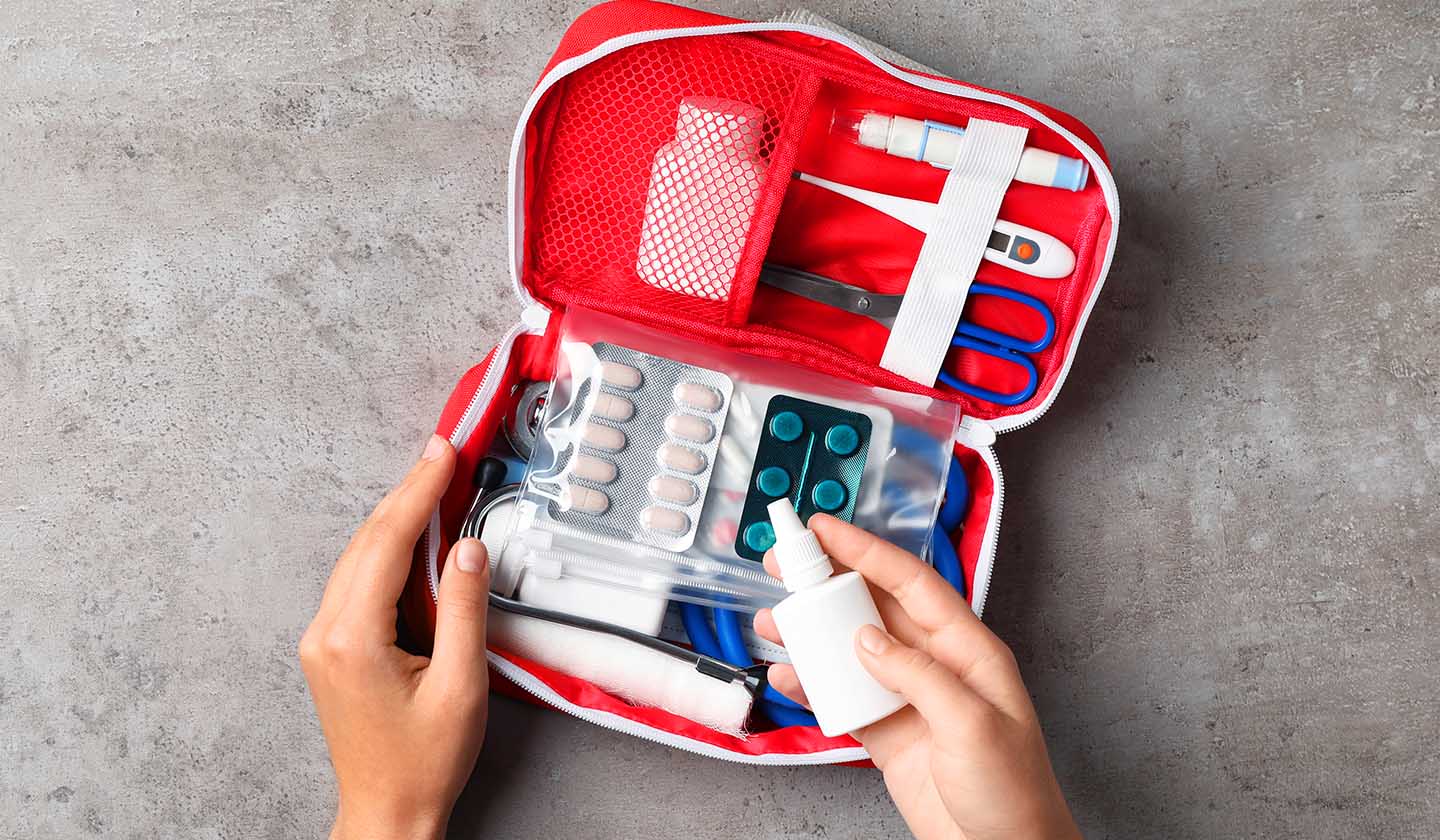

Make a holiday first aid kit
Unforeseen events may occur in any trip, regardless of the destination.
Therefore, in addition to your usual medications, you should take with you:
-
Analgesic and antipyretic (for the relief of fever or pain, for example headaches, ears, teeth or menstrual);
-
Nasal decongestant (relieves congestion);
-
Antiemetic (relieves nausea or vomiting symptoms);
-
Antidiarrheal (for watery diarrhoea without fever);
-
Oral rehydration solution (to prevent dehydration in situations of diarrhoea or vomiting);
-
Antacid (in case of malaise caused by food);
-
Antihistamine and/or topical corticosteroids (especially recommended for people with a history of allergic reactions, such as mosquito bites);
-
Insect repellent (for protection against mosquito bites);
-
Sunscreen (to protect from sunlight);
-
Unidose saline solution (for cleaning wounds or eyes);
-
Sterile compresses;
-
Adhesive plasters, adhesives, and bandages;
-
Antiseptic or disinfectant (to disinfect wounds)
-
Thermometer.
Sources
iSaúde
Farmácia Distribuição Magazine
Também lhe poderá interessar
Prevention
International destinations - Go, but go without worrying!
Prevention and treatment






