Virus
Don't let this infection take your smile away
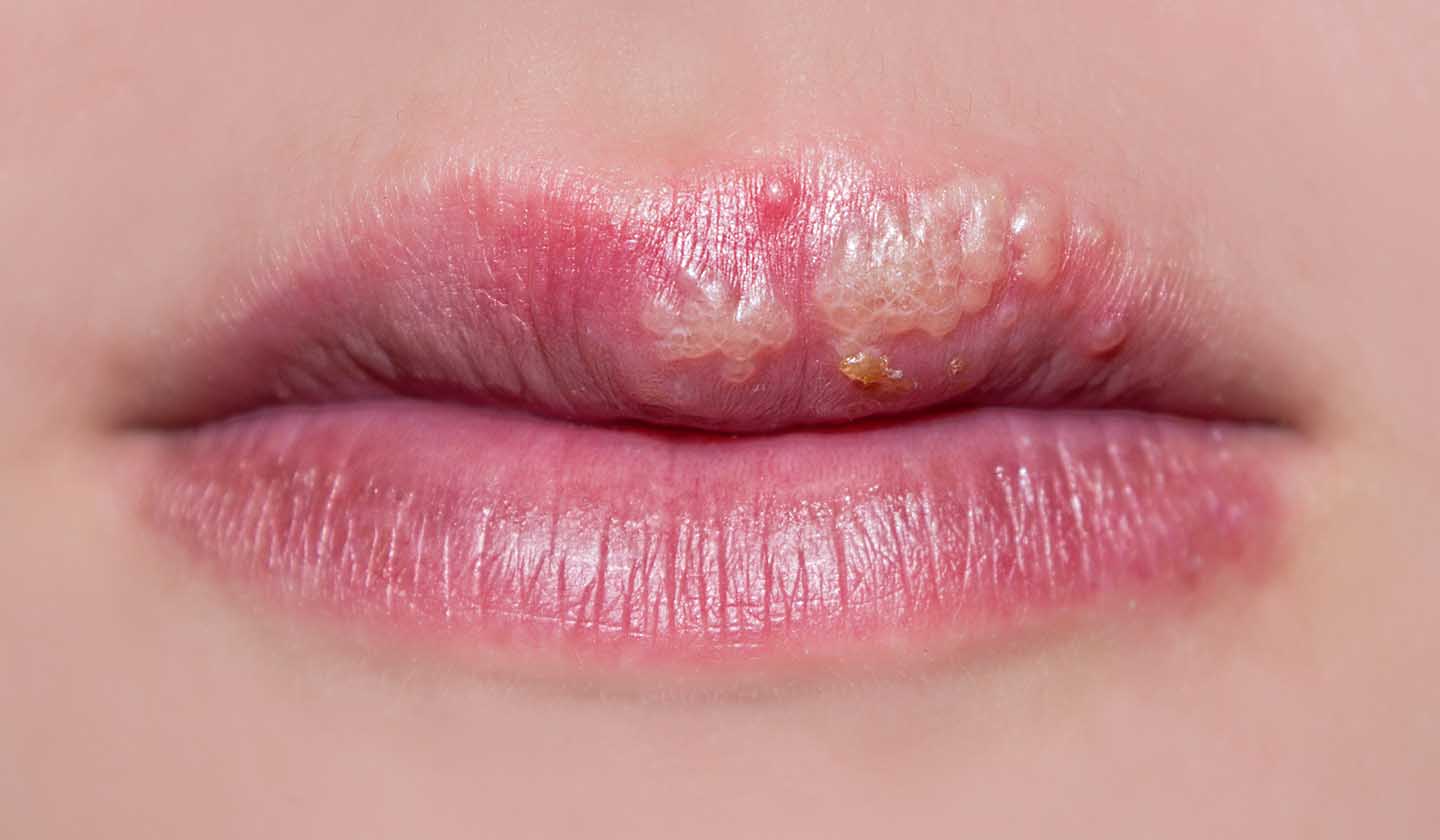
Small fluid-filled blisters, tingling, itching, or burning feeling on the lip (or around your lip)... If you have these symptoms you probably suffer from cold sores.
Cold sores are a common chronic cutaneous-mucosal infection usually caused by the Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1).
It is estimated that 67% of the world population under the age of 50 is known to be a carrier of the virus that causes cold sores and that the majority of infections are asymptomatic.
Although this kind of infection is extremely contagious when the symptoms are present, can be transmitted to other even when there are no symptoms.
This infection is benign and can often be cured without any treatment. Nonetheless, there are precautions that can diminish the feeling of discomfort and help prevent contagion.
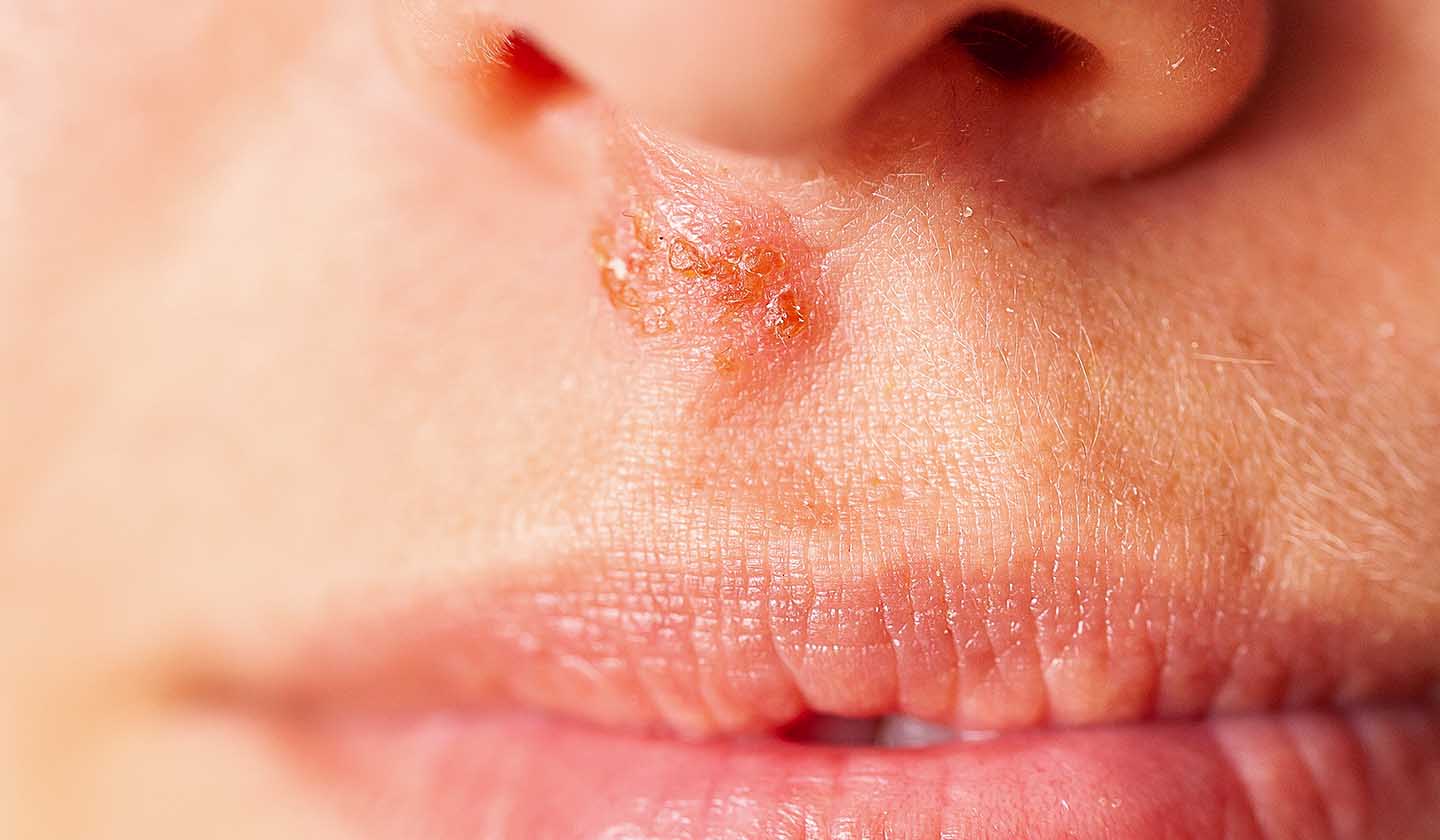
How do cold sores appear?
Cold sores (herpes labialis) are a common chronic cutaneous-mucosal infection usually caused by the Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1).
The first infection occurs predominantly in childhood and it is often asymptomatic. After the initial infection the virus migrates through the sensory nerves to the closest ganglion, where it remains dormant throughout life. Periodically, it may be reactivated in certain circumstances.
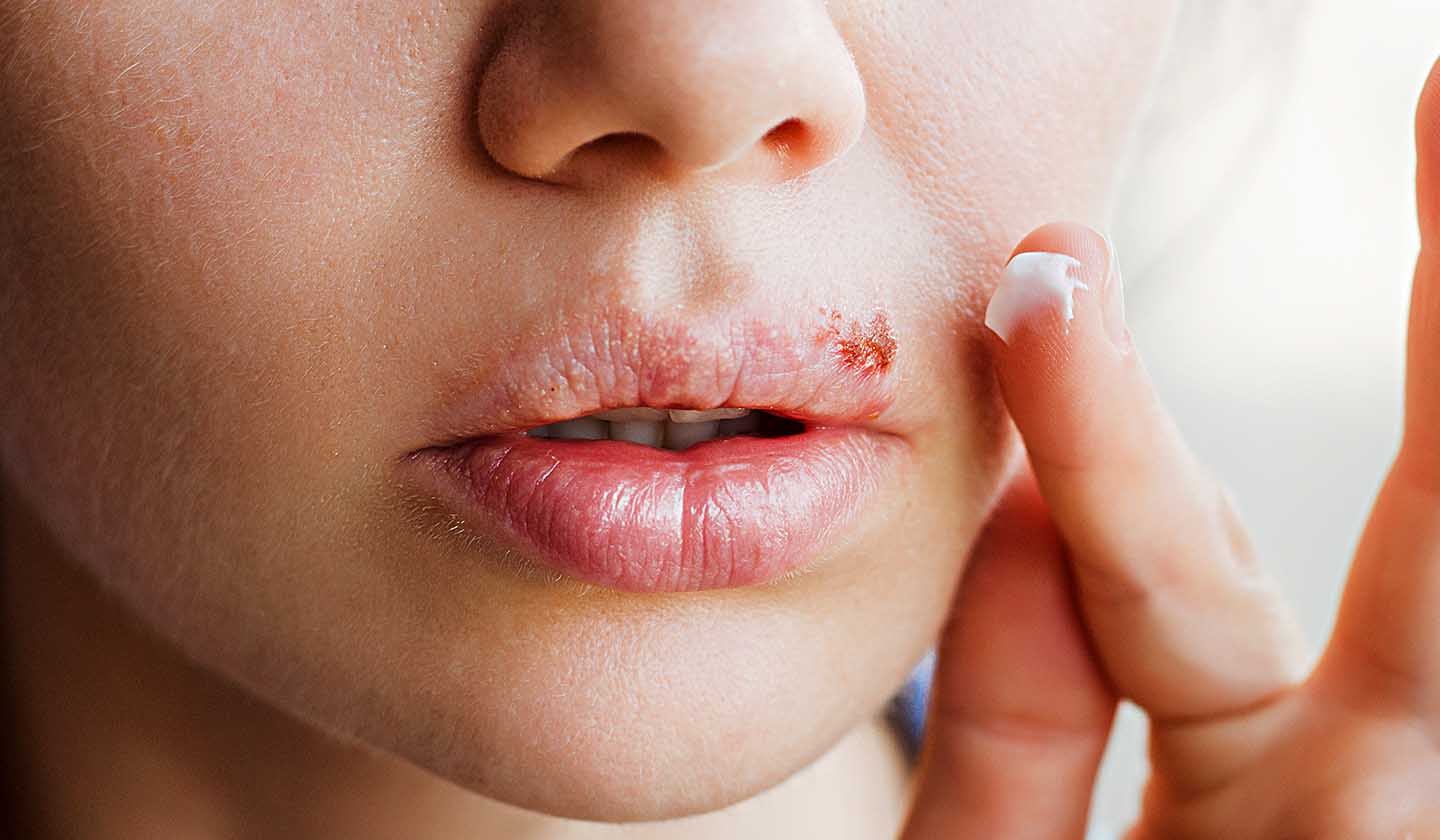

Factors that contribute to the virus reactivation
- Stress, fatigue;
- Fever, flu, cold;
- Menstrual period;
- Excessive sun exposure;
- Extreme weather conditions (cold, heat, wind);
- Depressed immune systems.
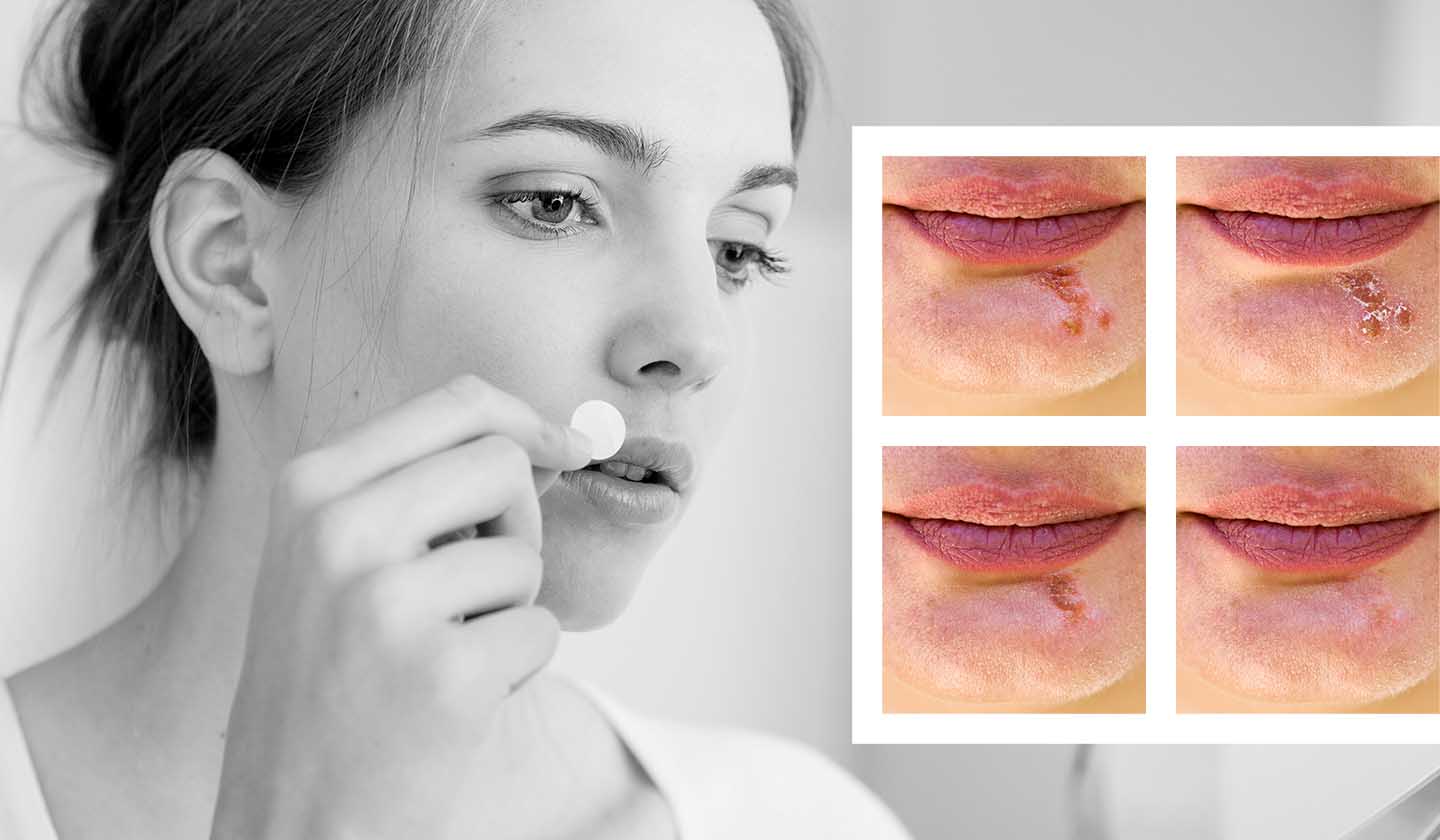
Classic symptoms
- Burning, tingling and itchy feeling;
- Inflammation, swelling;
- Slight pain.
Cold sores appear mainly in the external surface of the lip, around the lips or in the nose area. It starts with a red spot which rapidly (within 48h) becomes covered by small blisters (vesicles) that can break open giving way to a greater injury with a light-coloured fluid inside.
Afterwards, with the evolution of the injury, a yellow crust is formed. When this crust appears the contagion risk is significantly reduced but not eliminated. After approximately two weeks, this period can vary, the scabs will naturally fall off, leaving no scars.
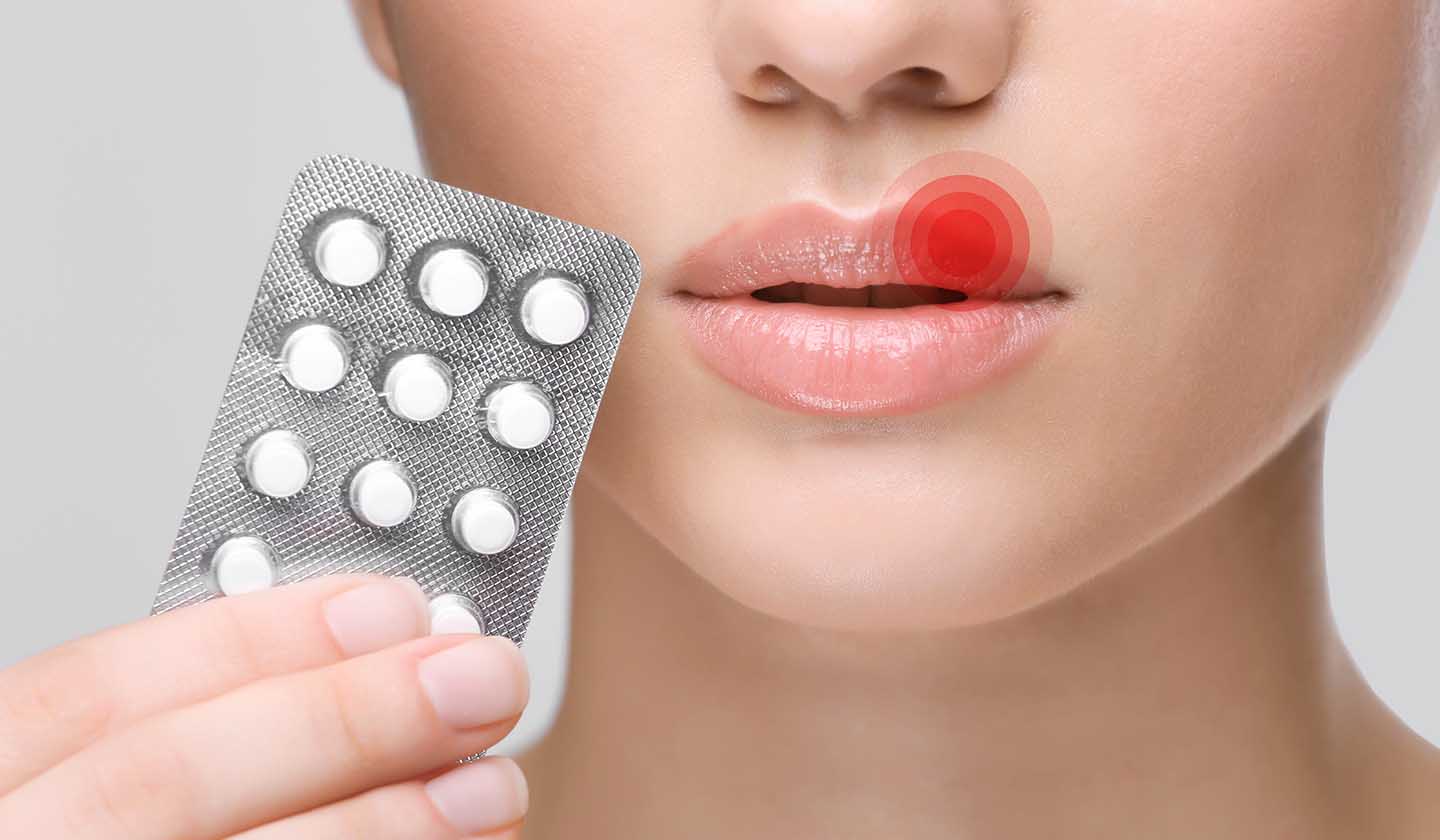
How to treat this problem?
Approximately 10 days after the appearance of herpetic eruptions these will eventually heal. However, this process can be uncomfortable, and you may require some help to speed up recovery and relieve the symptoms.
- Non-prescription medicinal products
- Antiviral creams (acyclovir, acyclovir with hydrocortisone, penciclovir): these should be used as soon as the first symptoms appear; they prevent viral replication, shortening symptom duration and speeding up the healing of lesions; the use of these creams in combination with hydrocortisone can be useful when the lesion is painful and inflammation spreads.
- Balms and creams (plant extract-based and emollient-based) liquid bandage
- Patches - the lesion becomes less visible; healing occurs adequately, and the risk of contagion is reduced.
- Prescription-only medicinal products
- Oral antiviral (acyclovir, valacyclovir): these should be used in more severe cases or in immunocompromised patients at risk of developing serious health complications.
- Oral antiviral (acyclovir, valacyclovir): these should be used in more severe cases or in immunocompromised patients at risk of developing serious health complications.
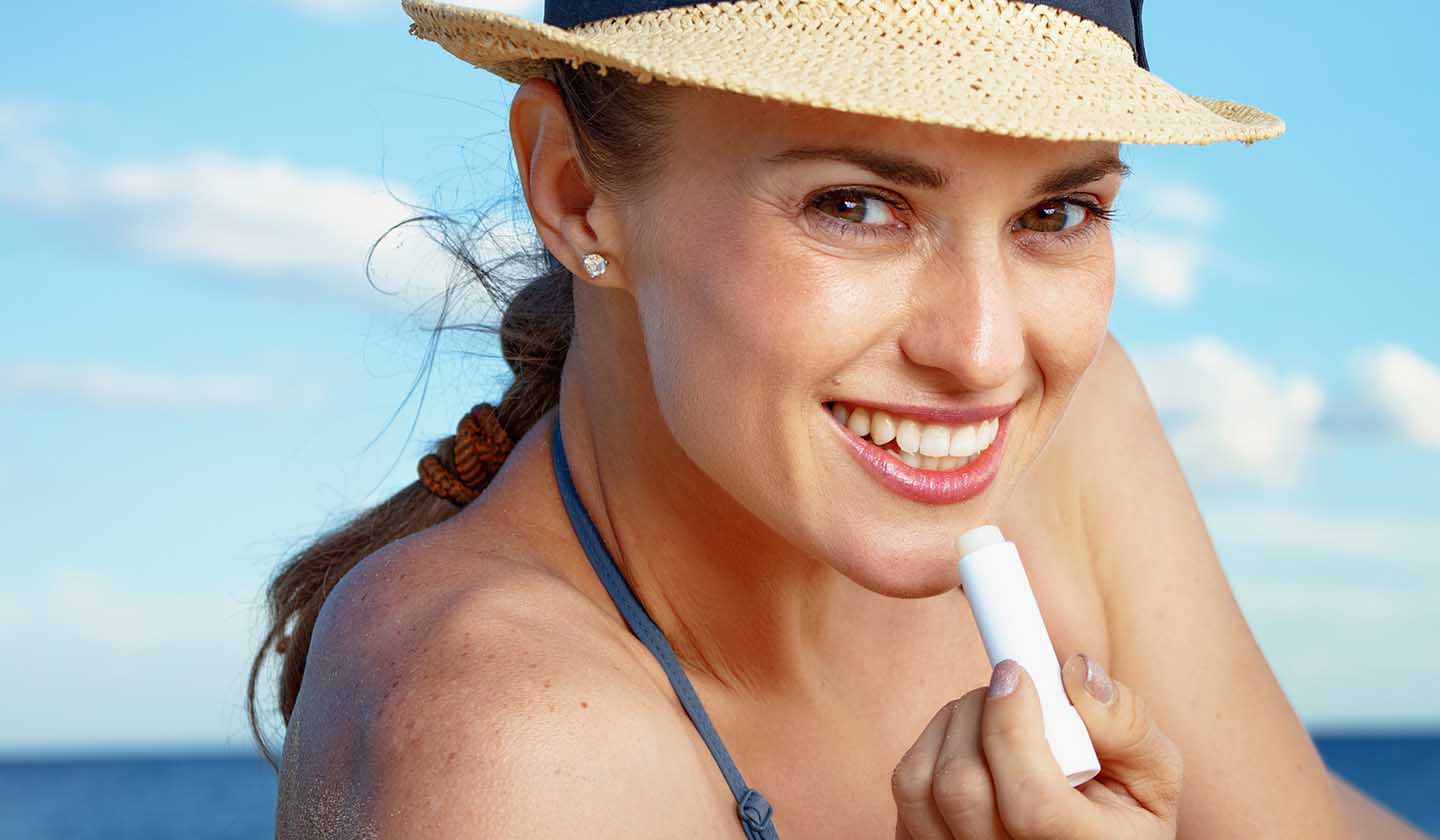

Preventing cold sores
- Keep the skin of your lips hydrated and moisturized;
- Use lip sunscreen, especially when there is a higher sun exposure;
- Avoid direct contact (avoid kissing) whenever lesions are visible and give particular attention to immunocompromised patients and children;
- Do not share personal use objects, such as glasses, cutlery, razor blades, towels, lipsticks, and other cosmetic products, like cream or makeup;
- Wash your hands often;
- Avoid touching your eyes and genitals because there is the risk of spreading the infection;
- Avoid the practice of oral sex, even when using condom;
- Avoid sports involving physical contact;
- Never pop blisters otherwise the infection will spread.
Sources
iSaúde
Farmácia Distribuição Magazine
Também lhe poderá interessar
Mouth and teeth






