Dermatology
Contact Dermatitis - A Matter of Irritation
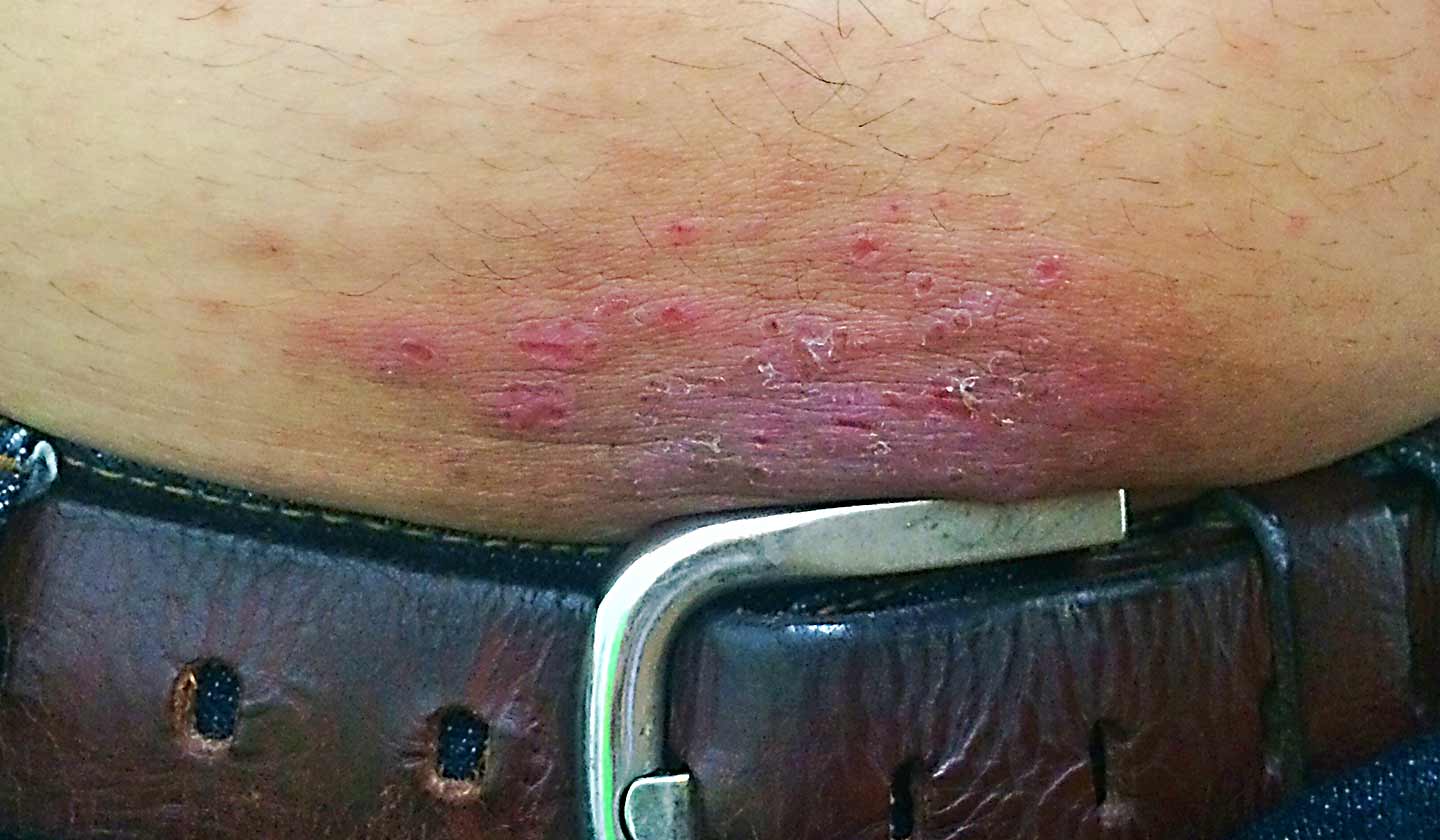
Contact dermatitis or contact eczema is an inflammatory reaction of the skin that occurs due to exposure to an agent capable of causing irritation or allergy.
It is not a contagious disease, however it can be very bothersome and interfere with the quality of life of sufferers.
Contact Dermatitis Types
There are two types of contact dermatitis, irritant and allergic:
- Irritant: caused by acid or alkaline substances (e.g. soaps, detergents). Lesions are restricted to the site of contact.
- Allergic: appears after repeated exposure to a product or substance (e.g. moisturising creams, perfumes, nail varnishes and topical medicines)
The allergic reaction appears within 24 to 48 hours after exposure.

Substances which may cause allergy
- Certain plants;
- Metals such as nickel and cobalt in jewellery, watches and belt buckles
- Topical medicines: ointments with antibiotics, anaesthetics, antifungals and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Cosmetics: perfumes, shampoos, moisturizing creams, varnishes and sunscreens
- Clothes and synthetic fabrics;
- Detergents and solvents;
- Adhesives;
- Cement, latex oils, greases and wall paint.
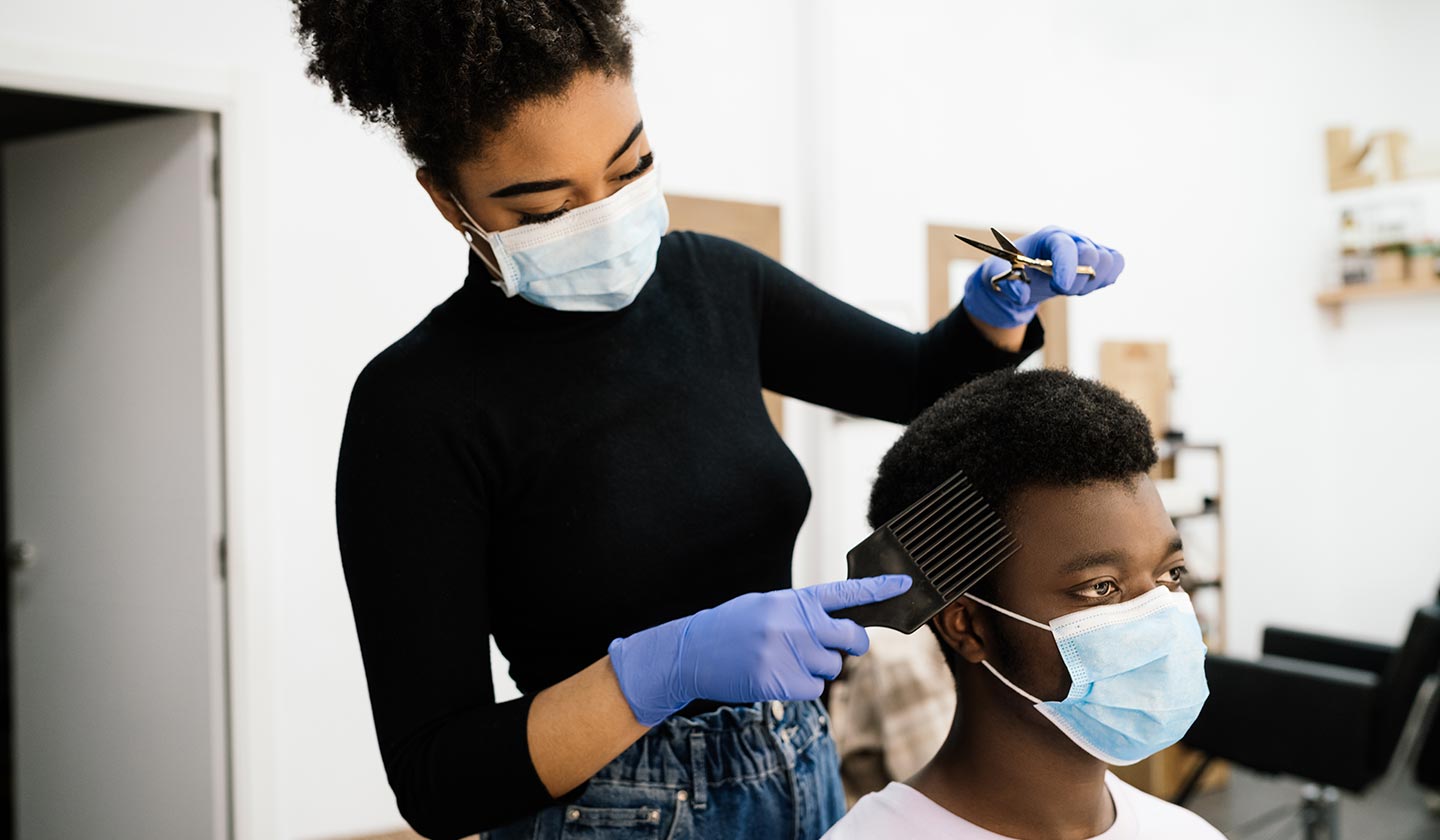

Professions most at risk of Contact Dermatitis
The professions most susceptible to developing this disease are: hairdressers, beauticians, painters, locksmiths, metalworkers, bakers, florists, cleaning auxiliaries and carers of children and the elderly.
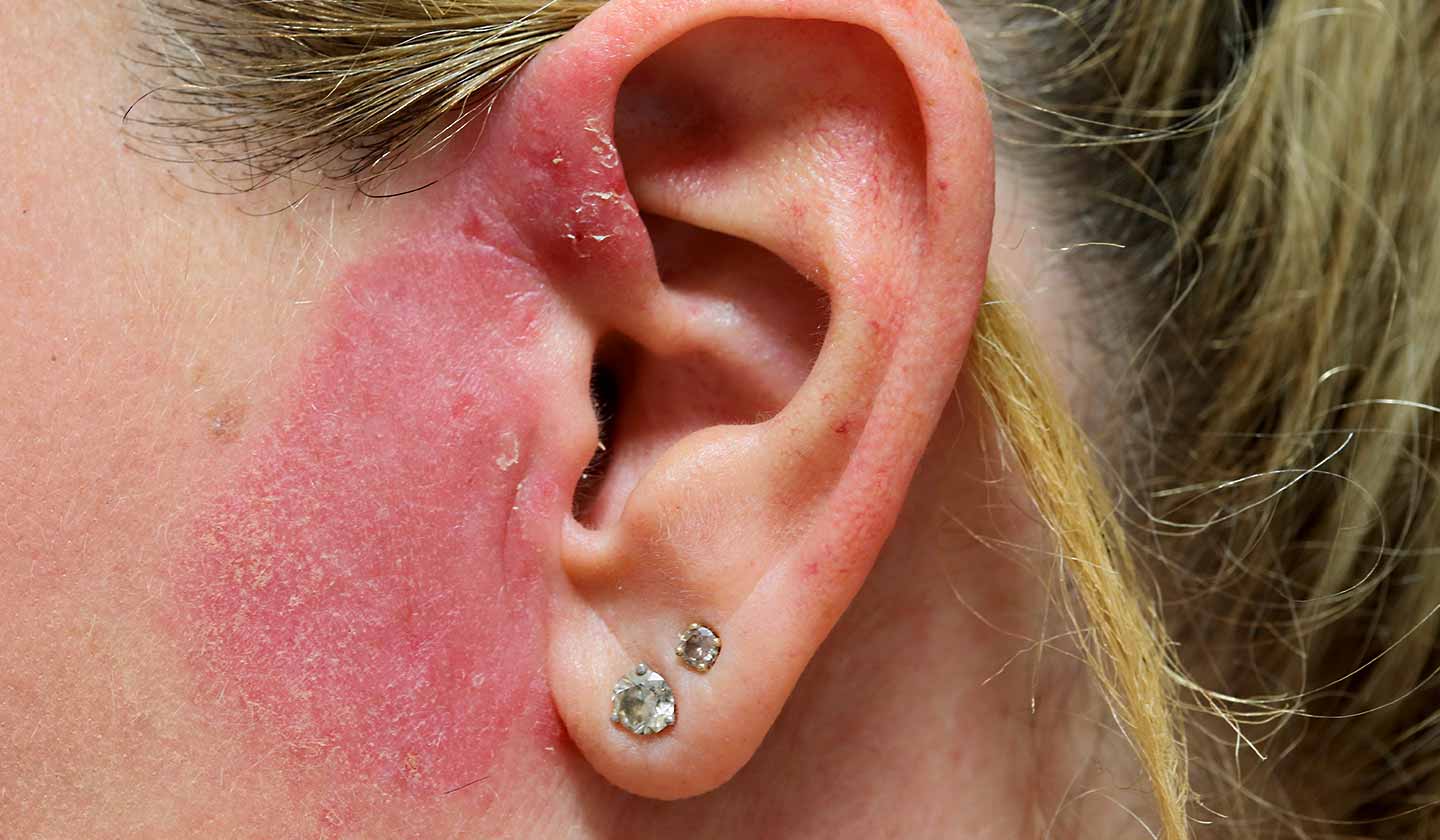
Signs and Symptoms
- Itching
- Redness
- Pimples that may form crusts
- Edema (swelling)
- Pain and tenderness to touch
- Burning sensation
- Dry, rough, chapped and flaking skin
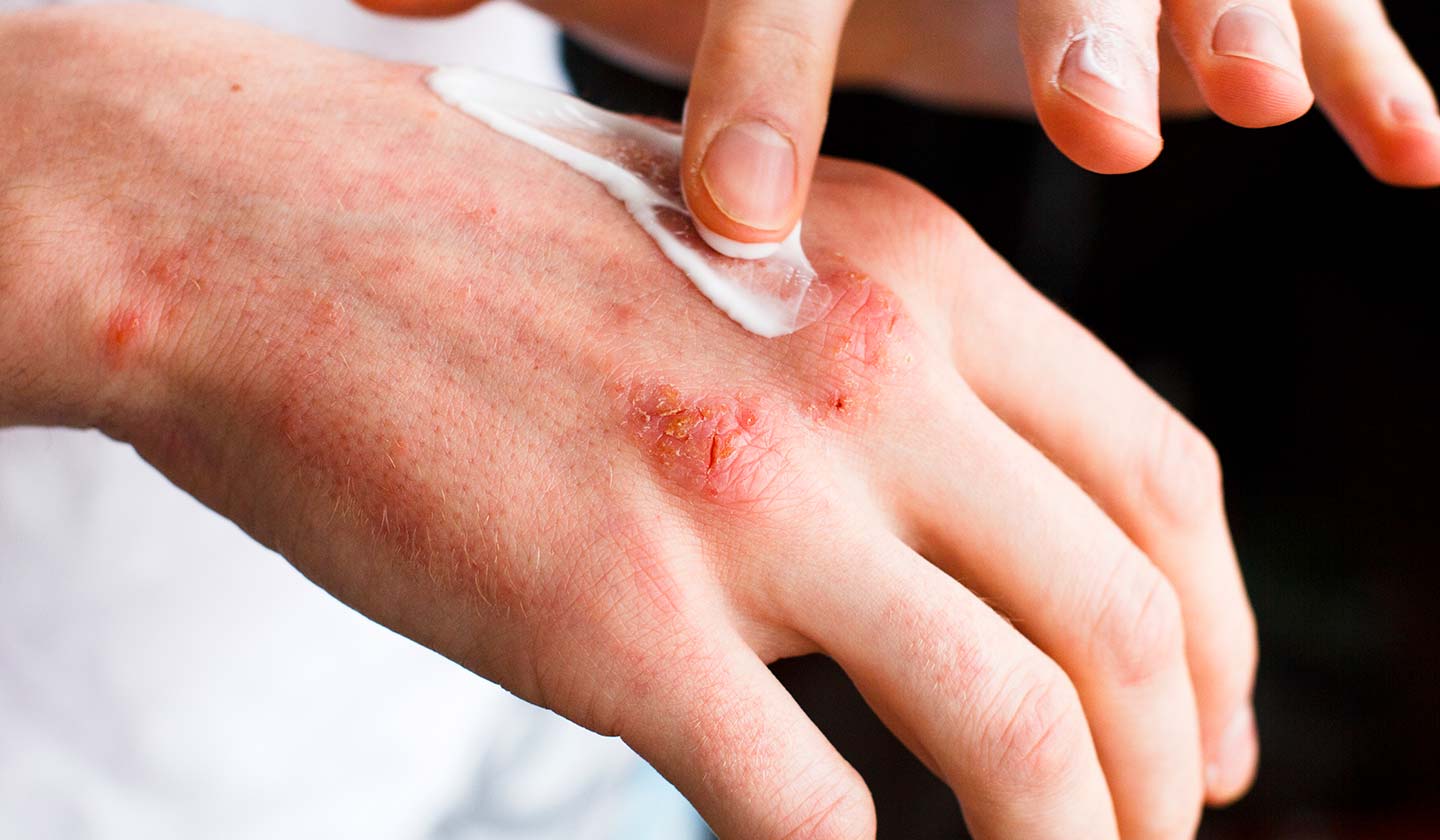
Treatment
- Stop using the substance that causes the irritation
- Creams, lotions, ointments, sprays to reduce inflammation
- Corticosteroids and antihistamines prescribed by the doctor
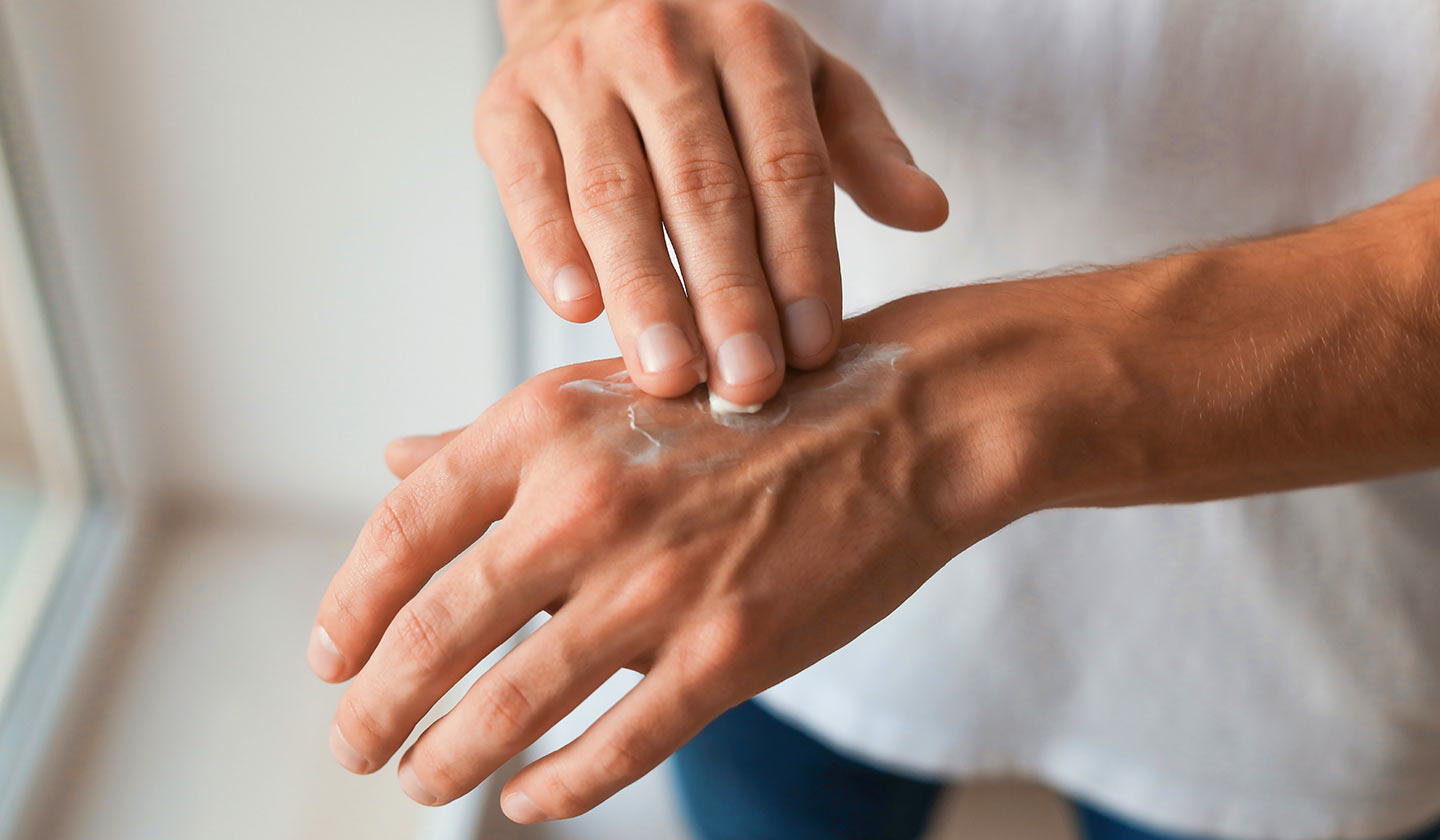

Prevention
- Identify the irritant or allergen that triggered the dermatitis and avoid using it
- Use hypoallergenic products
- Wash hands after exposure to substances that may cause irritation
- Wear gloves, shoes or gowns when the use of these substances is mandatory
- Apply a moisturising cream regularly - ask your pharmacist for advice
Contact dermatitis is an annoying and often limiting condition. To avoid complications, in the presence of one or more symptoms contact your pharmacist.
Sources
Ordem dos Farmacêuticos
Também lhe poderá interessar
Dermatology
Atopic dermatitis - Skin hydration is the key factor
Dermatology






