Digestive system
Intestinal microbiota
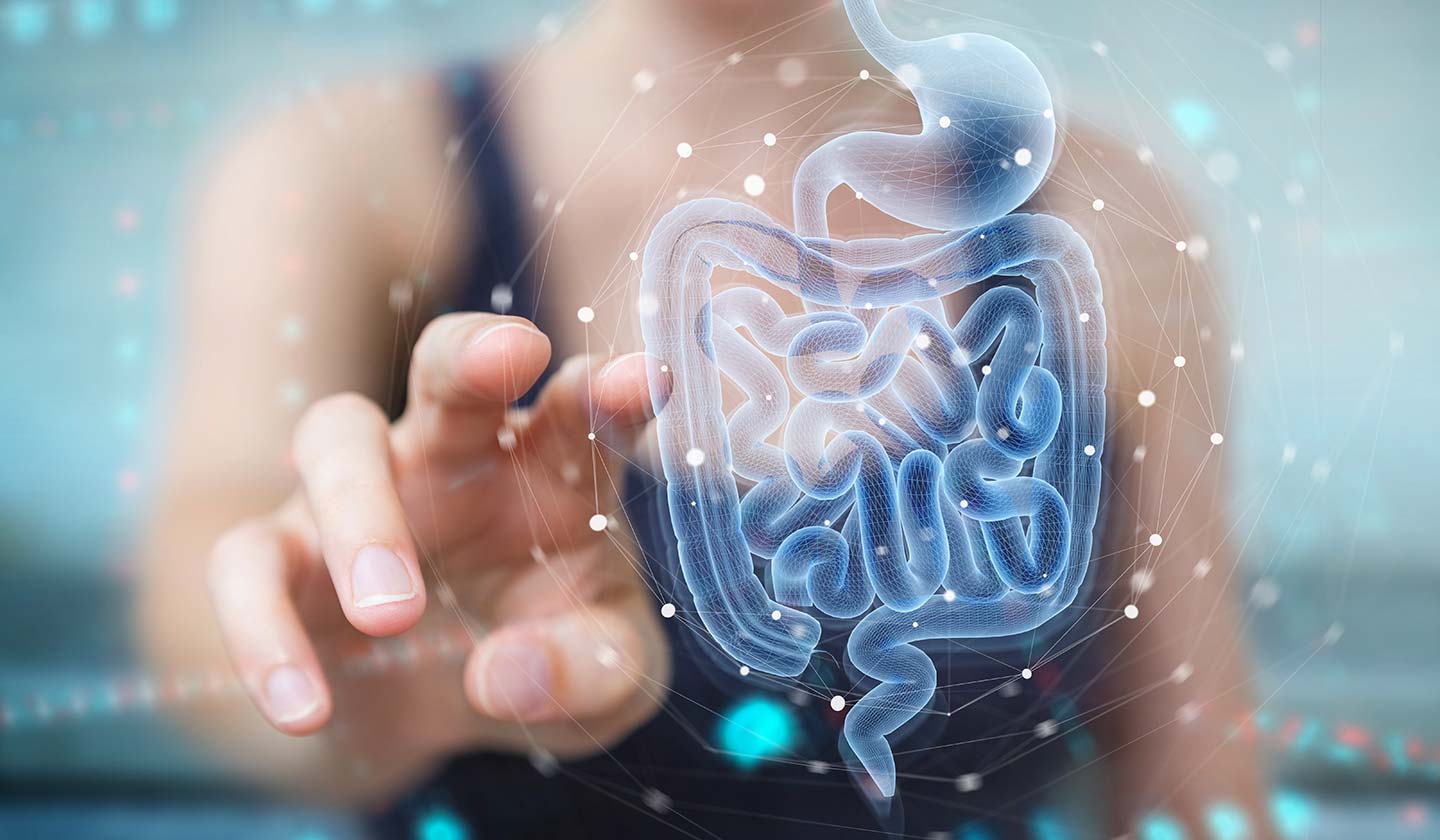
The intestinal microbiota, also known as the gut microbiome, is a complex ecosystem of microorganisms that inhabit the gastrointestinal tract of humans and other animals. This microbial community is composed of trillions of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microorganisms that play a critical role in human health and disease.
Functions of the gut microbiota
The intestinal microbiota is essential for the proper functioning of the digestive system and the regulation of immune responses. The microbiota helps to break down food into nutrients that the body can absorb, synthesizes vitamins and other essential compounds, and produces short-chain fatty acids that help to maintain the integrity of the intestinal barrier.
Factors that influence the gut microbiota
The composition of the intestinal microbiota is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, diet, age, environment, and the use of antibiotics and other medications. Studies have shown that a healthy and diverse microbiota is associated with better health outcomes, while an imbalanced microbiota, known as dysbiosis, can contribute to a range of health problems, including inflammatory bowel disease, irritable bowel syndrome, and metabolic disorders.

1. Diet
Diet is one of the most important factors influencing the composition of the intestinal microbiota. A diet rich in fiber and plant-based foods is associated with a more diverse and healthy microbiota, while a diet high in sugar, fat, and processed foods can lead to dysbiosis and inflammation.
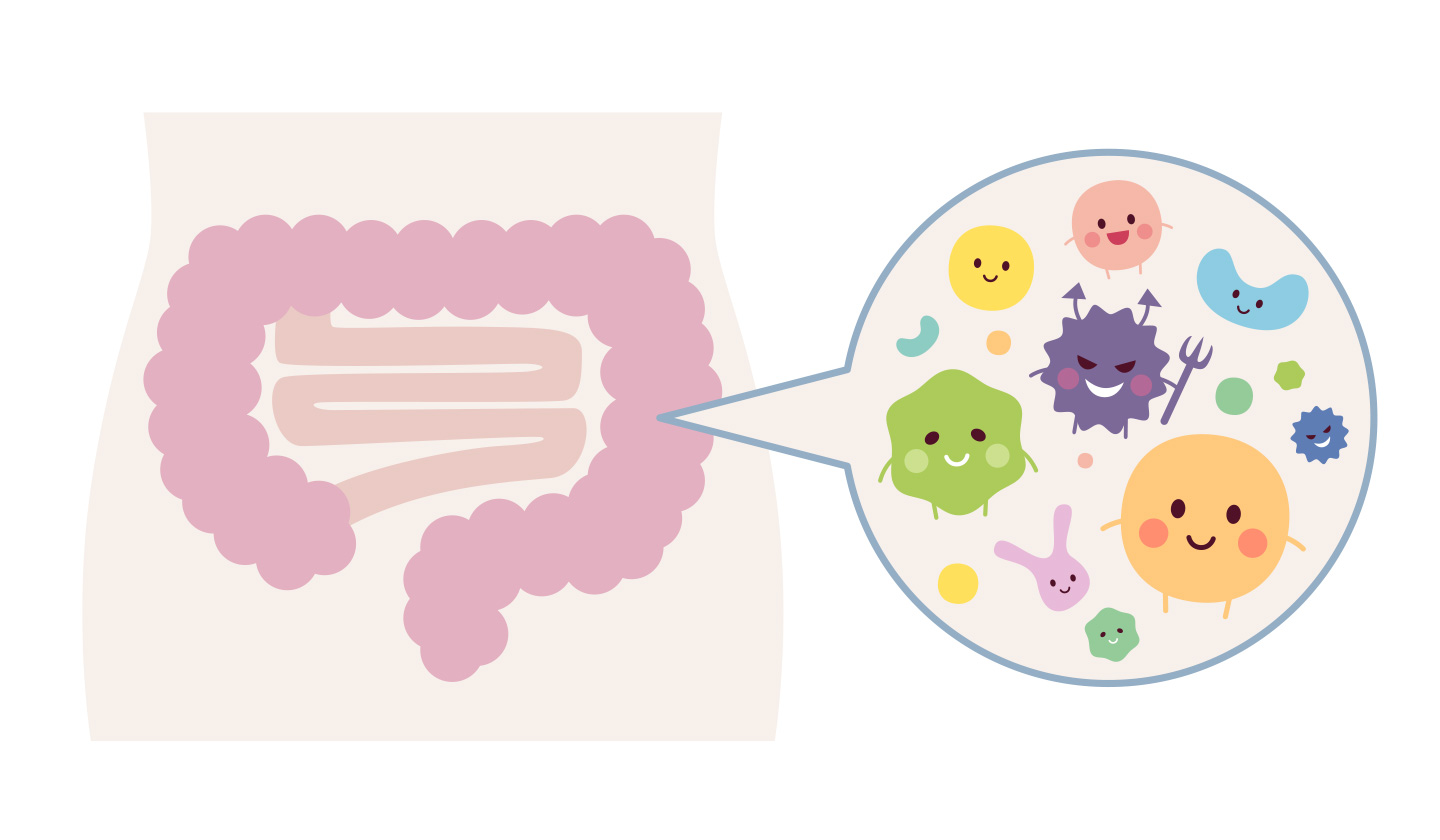
2. Environmental microorganisms
Another important factor in the development of a healthy microbiota is exposure to a diverse range of microorganisms from the environment. Children who grow up in environments that are less hygienic, such as farms, are less likely to develop allergies and autoimmune diseases, likely due to exposure to a wider range of microorganisms.

3. Medicines
The use of antibiotics and other medications can also have a profound effect on the intestinal microbiota. Antibiotics can kill off both pathogenic and beneficial bacteria, leading to dysbiosis and an increased risk of infection. Other medications, such as proton-pump inhibitors, can alter the pH of the gut, which can affect the growth of different types of bacteria.
Microbiota and health
There is increasing evidence that the intestinal microbiota plays a role in the development of a range of health conditions, including obesity, diabetes, and mental health disorders. Researchers are currently exploring ways to manipulate the microbiota through diet, probiotics, and other interventions in order to promote better health outcomes.
In conclusion, the intestinal microbiota is a complex ecosystem of microorganisms that plays a critical role in human health and disease. Diet, environmental exposures, and medications can all have a profound effect on the composition of the microbiota, highlighting the importance of maintaining a healthy and diverse microbiota through lifestyle interventions and targeted therapies.
Ana Neto
(Pharmaceutical)
Também lhe poderá interessar
Digestive system
Diarrhoea - When nothing is better than a nearby toilet
Digestive system






